| Oracle® Database 2 Day + Java Developer's Guide 11g Release 2 Part Number E12137-01 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database 2 Day + Java Developer's Guide 11g Release 2 Part Number E12137-01 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
This chapter is the first in a series of five chapters, each of which describes how to create parts of a Java application that accesses Oracle Database and displays, modifies, deletes, and updates data on it. To be able to access the database from a Java application, you must connect to the database using a java.sql.Connection object.
This chapter includes the following sections:
You can set up and manage database connections in JDeveloper to enable your application to communicate with external data sources, including Oracle Database and offline database objects. This is done using the Database Navigator. The same navigator is also used to manage other connections your application needs, such as connections to application servers. The following subsections describe how you can use the Database Navigator to view the database and its objects and to create a connection to the database:
The Database Navigator displays all currently defined connections. To view the Database Navigator, select the Database Navigator tab in the navigator panel on the top left-hand side of the JDeveloper display, if it is displayed, or use the View menu. For an illustration of the default layout of the JDeveloper IDE, see Figure 1-1.
You can use the Database Navigator to browse through the connections it displays. In particular, for a database schema, you can also view database objects, tables, views, and their contents.
Database connections are shown under the IDE Connections node. To view the objects in the database, expand the connection. Expanding a schema displays nodes for the object types in that schema. Expanding the node for an object type displays its individual objects. When you expand a table node, you can view the structure of the table and the data within the table.
You can connect to any database for which you have connection details. When you create a database connection, you must specify a user name and a password. By default, the connection allows you to browse only the schema of the user that you specify in the connection.
To create a connection, follow these steps:
Start JDeveloper.
From the View menu select Database Navigator. The Database Navigator is displayed, showing you a list of available connections.
Right-click IDE Connection, and from the shortcut menu, select New Connection. The Create Database Connection screen is displayed.
On the Connection screen, do not change the default values for the connection name and type, Connection1 and Oracle (JDBC). Enter HR in both the Username and Password fields. Do not enter a value for Role, and select Deploy Password. You must provide information about the computer where your database is located. Your database administrator should provide you with this information.
Enter the following information:
Host Name: Host name of the computer where Oracle Database is installed
If database is on the same computer, then for the Host Name parameter, enter localhost.
Click Test Connection. If the connection is successful, the word Success! is displayed in the Status field.
Figure 3–1 shows the Connection screen where you enter these details.
Click Finish to create the connection and close the screen.
Disconnecting and Reconnecting from Oracle Database in JDeveloper
To disconnect from the database in JDeveloper, in the Database Navigator, right-click the connection name and select Disconnect. The display in the Database Navigator now shows only the name of the connection, without the plus (+) symbol for expanding the node. To reconnect to the database, right-click the connection name and select Connect.
After you have successfully established a connection to the database, you can browse its contents through the Database Navigator. The Database Navigator displays a navigable, hierarchical tree structure for the database, its objects, their instances, and the contents of each. To view the contents at each level of the hierarchy of the database connection that you created, do the following:
The IDE Connections node in the Database Navigator now shows a node with the name of your connection. Click the plus symbol (+) to the left of the connection name to expand the navigation tree. To display a list of the instances of an object type, for example Tables, expand the Table navigation tree.
The Structure window below the navigator shows the detailed structure of any object selected in the navigator. Select a table in the navigator (for example Employees) to see the columns of that table in the Structure window.
Figure 3-2 Accessing Database Objects in the Database Navigator
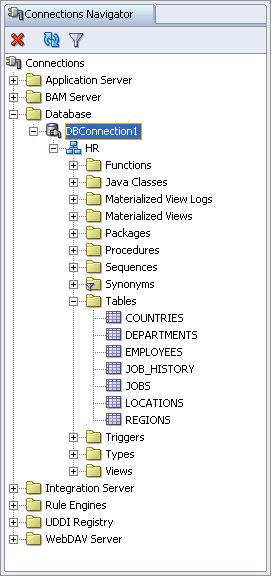
Figure 3-3 Viewing the Table Structure and Data

If you double-click a table in the navigator, the structure of that table is displayed in the main editing area of the window. It includes details about all the columns, such as Name, Type, and Size, so you can browse the table definition.
To view the data from a table, select the Data tab below the table structure. You can now view and browse through the table data.
You can also edit the objects in the Database Navigator. To edit a table, right-click the table and select Edit from the shortcut menu. A dialog box allows you to make changes to the selected table.
In JDeveloper, you create your work in an application, within which you can organize your work into a number of projects. JDeveloper provides a number of application templates, to help you to create the project structure for standard types of application relatively quickly and easily. At the time you create your application in JDeveloper, you can choose the application template that matches the type of application you will be building.
The application template you select determines the initial project structure (the named project folders within the application) and the application technologies that will be included. You can then add any extra libraries or technologies you need for your particular application, and create additional projects if you need them.
The Application Navigator displays all your applications and projects. When you first start JDeveloper, the Application Navigator is displayed by default on the left side of the JDeveloper IDE.
To view the Application Navigator when it is not displayed, you can click the Applications tab in the navigator panel on the top left-hand side of the JDeveloper display, or select Application Navigator from the View menu.
The Application Navigator shows a logical grouping of the items in your projects. To see the structure of an individual item, you can select it and the structure is displayed in the Structure window.
From the Application Navigator, you can display items in an appropriate default editor. For example, if you double-click a Java file, the file opens in the Java Source Editor, and if you double-click a JavaServer Pages (JSP) file, it opens in the JSP/HTML Visual Editor.
To get started with JDeveloper, you must create an application and at least one project in which to store your work, as follows:
In the Application Navigator, click on New Application.
The Create Generic Application wizard is displayed. Enter HRApp in the Application Name field, and from the Application Template list, select Generic Application. Click Next.
On the Name your Generic project screen, enter view as the name of the project. Click Finish.
The new HRApp application is displayed in the Application Navigator.
Save your application. To do this, from the File menu, select Save All.
You can view the Javadoc or the code for any of the classes available in the project technology scope within JDeveloper. In addition, you can view the details of all the methods available for those classes.
For example, to see the code or Javadoc for the Connection class, do the following:
With your project selected in the Application Navigator, from the Navigate menu select Go to Java Class. You can also do this for a specific file in your project.
In the Go to Java Class dialog box, select Source or Javadoc.
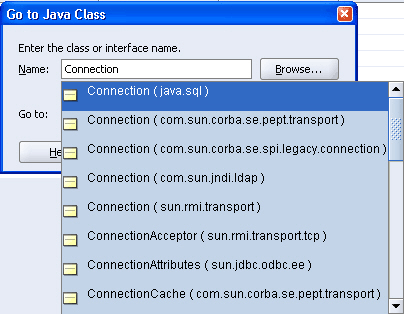
Enter the name of the class you want to view in the Name field, or click Browse to find the class. For the Connection class, start to enter Connection, and from the displayed list select Connection (java.sql).
Figure 3-4 Selecting the Class to View the Javadoc in JDeveloper
Click OK.
So far, you have seen how to connect to the database from JDeveloper. To initiate a connection from the Java application, you use the Connection object from the JDBC application programming interface (API).
This section describes connecting to the database from the Java application in the following subsections:
In Java, you use an instance of the DataSource object to get a connection to the database. The DataSource interface provides a complete replacement for the previous JDBC DriverManager class. Oracle implements the javax.sql.DataSource interface with the OracleDataSource class in the oracle.jdbc.pool package. The overloaded getConnection method returns a physical connection to the database.
You can either set properties using appropriate setxxx methods for the DataSource object or use the getConnection method that accepts these properties as input parameters.
Important DataSource Properties are listed in Table 3-1.
Table 3-1 Standard Data Source Properties
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Name of the particular database on the server. Also known as the service name (or SID) in Oracle terminology. For Oracle Database, this is |
|
|
|
Name of the underlying data source class. |
|
|
|
Description of the data source. |
|
|
|
Network protocol for communicating with the server. For Oracle, this applies only to the JDBC Oracle Call Interface (OCI) drivers and defaults to |
|
|
|
Password for the connecting user. |
|
|
|
Number of the port where the server listens for requests |
|
|
|
Name of the database server |
|
|
|
User name to be used for login |
|
|
|
Specifies the Oracle JDBC driver type. It can be either This is an Oracle-specific property. |
|
|
String |
Specifies the URL of the database connect string.You can use this property in place of the standard This is an Oracle-specific property. |
If you choose to set the url property of the DataSource object with all necessary parameters, then you can connect to the database without setting any other properties or specifying any additional parameters with the getDBConnection method. For more information on setting the database URL, refer to the Specifying Database URLs section.
Note:
The parameters specified through thegetConnection method override all property and url parameter settings previously specified in the application.This release of Oracle JVM supports Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) addresses in the URL and machine names of the Java code in the database, which resolve to IPv6 addresses.
Database URLs are strings that you specify for the value of the url property of the DataSource object. The complete URL syntax is the following:
jdbc:oracle:driver_type:[username/password]@database_specifier
The first part of the URL specifies which JDBC driver is to be used. The supported driver_type values for client-side applications are thin and oci. The brackets indicate that the user name and password pair is optional. The database_specifier value identifies the database to which the application is connected.
The following is the syntax for thin-style service names that are supported by the Thin driver:
jdbc:oracle:driver_type:[username/password]@//host_name:port_number:SID
For the sample application created in this guide, if you include the user name and password, and if the database is hosted locally, then the database connection URL is as shown in Example 3-1.
Example 3-1 Specifying the url Property for the DataSource Object
jdbc:oracle:thin:hr/hr@localhost:1521:UORCL
Oracle Database comes with a new connection feature. If you install the Oracle Database client, then you need not specify all the details in the database specifier part of the connection URL. Under certain conditions, the Oracle Database connection adapter requires only the host name of the computer where the database is installed.
Because of this feature introduced in Oracle Database, some parts of the JDBC connection URL syntax become optional:
jdbc:oracle:driver_type:[username/password]@[//]host_name[:port][:ORCL]
In this URL:
// is optional.
:port is optional.
Specify a port only if the default Oracle Net listener port (1521) is not used.
:ORCL (or the service name) is optional.
The connection adapter for the Oracle Database Client connects to the default service on the host. On the host, this is set to ORCL in the listener.ora file.
Example 3-2 shows a basic configuration of the listener.ora file, where the default service is defined.
Example 3-2 Default Service Configuration in listener.ora
MYLISTENER = (ADDRESS_LIST= (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=test555)(PORT=1521)) ) DEFAULT_SERVICE_MYLISTENER=dbjf.regress.rdbms.dev.testserver.com SID_LIST_MYLISTENER = (SID_LIST= (SID_DESC=(SID_NAME=dbjf)(GLOBAL_DBNAME=dbjf.regress.rdbms.dev.testserver.com)(ORACLE_HOME=/test/oracle)) )
After making changes to the listener.ora file, you must restart the listener with the following command:
> lsnrctl start mylistener
The following URLs should work with this configuration:
jdbc:oracle:thin:@//test555.testserver.com jdbc:oracle:thin:@//test555.testserver.com:1521 jdbc:oracle:thin:@test555.testserver.com jdbc:oracle:thin:@test555.testserver.com:1521 jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=test555.testserver.com)(PORT=1521))) jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=test555.testserver.com))) jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=test555.testserver.com)(PORT=1521))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=)))
Note:
Default service is a new feature in Oracle Database 11g Release 1. If you use any other version of the Oracle Database Client to connect to the database, then you must specify the SID and port number.The first step in building a Java application is to create a Java class. The following instructions describe how you create a class called DataHandler, which will contain the methods for querying the database and modifying the data in it.
In the Application Navigator, right-click the View project, and from the shortcut menu, select New.
In the New Gallery, select the General category. In the Items list, select Java Class, and click OK. The Create Java Class dialog box is displayed.
In the Create Java Class dialog box, enter DataHandler as the class Name, and hr as the Package. Do not change the default values of the Optional Attributes, and click OK. The Create Java Class dialog box with the appropriate values specified is shown in Figure 3-6.
The skeleton DataHandler class is created and is displayed in the Java Source Editor. The package declaration, the class declaration, and the default constructor are created by default. Figure 3-7 shows the class displayed in the Java Source Editor, ready for you to add your Java code:
Oracle JDeveloper comes with standard libraries to help Java application programming. These libraries include API support for Application Development Framework (ADF), Oracle libraries for JDBC, JSP, and so on.
To use JDBC in your project, you import the Oracle JDBC library into the project. Similarly, to use JSP technology, you import the JSP Runtime library.
Important packages of the Oracle JDBC library include the following:
oracle.jdbc: The interfaces of the oracle.jdbc package define the Oracle extensions to the interfaces in the java.sql package. These extensions provide access to Oracle SQL-format data and other Oracle-specific features, including Oracle performance enhancements.
oracle.sql: The oracle.sql package supports direct access to data in SQL format. This package consists primarily of classes that provide Java mappings to SQL data types and their support classes.
oracle.jdbc.pool: This package includes the OracleDataSource class that is used to get a connection to the database. The overloaded getConnection method returns a physical connection to the database.
To include libraries in your project, perform the following steps:
Double-click the View project in the Application Navigator to display the Project Properties dialog box.
Click Libraries and Classpath, and then click Add Library. The Add Library dialog box is displayed with a list of the available libraries for the Java2 Platform, Standard Edition (J2SE) version is displayed.
In the Add Library dialog box, scroll through the list of libraries in the Extension folder. Select the JSP Runtime library and click OK to add it to the list of selected libraries for your project. Similarly, add the Oracle JDBC library. Figure 3-8 shows the Oracle JDBC library added to the view project.
Click OK.
To use JDBC in the Java application, import the following JDBC packages:
If the DataHandler.java class is not already open in the Java Source Editor, in the Application Navigator, expand the View project, Application Sources, and your package (hr) and double-click DataHandler.java.
At the end of the generated package declaration, on a new line, enter the import statements shown in Example 3-3.
Connection information is passed to the connection method by using the following connection variables: the connection URL, a user name, and the corresponding password.
Use the Java Source Editor of JDeveloper to edit the DataHandler.java class as follows:
After the DataHandler constructor, on a new line, declare the three connection variables as follows:
String jdbcUrl = null; String userid = null; String password = null;
These variables will be used in the application to contain values supplied by the user at login to authenticate the user and to create a connection to the database. The jdbcUrl variable is used to hold the URL of the database that you will connect to. The userid and password variables are used to authenticate the user and identify the schema to be used for the session.
Note:
The login variables have been set to null to secure the application. At this point in the guide, application login functionality is yet to be built into the application. Therefore, to test the application until login functionality is built in, you can set values in the login variables as follows:Set the jdbcUrl variable to the connect string for your database.
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:ORCL";
Set the variables userid and password to hr as follows:
String userid = "hr"; String password = "hr";
Make sure you reset these to null as soon as you finish testing.
For more information on security features and practices, refer to Oracle Database Security Guide and the vendor-specific documentation for your development environment.
On a new line, declare a connection instance as follows:
Connection conn;
Your Java class should now contain the code in Example 3-4.
To connect to the database, you must create a method as follows:
Add the following method declaration after the connection declaration:
public void getDBConnection() throws SQLException
The Java Code Insight feature displays a message reminding you to import the SQLException error handling package. Press the Alt+Enter keys to import it. The import java.sql.SQLException statement is added to the list of import packages.
At the end of the same line, add an open brace ({) and then press the Enter key. JDeveloper automatically creates the closing brace, and positions the cursor in a new empty line between the braces.
On a new line, declare an OracleDataSource instance as follows:
OracleDataSource ds;
Enter the following to create a new OracleDataSource object:
ds = new OracleDataSource();
Start to enter the following to set the URL for the DataSource object:
ds.setURL(jdbcUrl);
Java Code Insight prompts you by providing you with a list of available OracleDataSource methods. Scroll through the list to select the setURL(String) method, and press the Enter key to select it into your code. In the parentheses for this function, enter jdbcUrl.
Figure 3-9 shows how the Java Code Insight feature in JDeveloper helps you with inserting code.
On the next line, enter the following:
conn = ds.getConnection(userid,password);
As usual, Java Code Insight will prompt you with a list of methods for ds. This time, select getConnection(String,String). In the parentheses, enter userid,password. End the line with a semicolon (;).
Your code should look similar to the code in Example 3-5.
Example 3-5 Adding a Method to Connect to the Database
package hr;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import oracle.jdbc.pool.OracleDataSource;
public class DataHandler {
public DataHandler() {
}
String jdbcUrl = null;
String userid = null;
String password = null;
Connection conn;
public void getDBConnection() throws SQLException{
OracleDataSource ds;
ds = new OracleDataSource();
ds.setURL(jdbcUrl);
conn=ds.getConnection(userid,password);
}
}
Compile your class to ensure that there are no syntax errors. To do this, right-click in the Java Source Editor, and select Make from the shortcut menu. A Successful compilation message is displayed in the Log window below the Java Source Editor window.