| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E17126-08 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E17126-08 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
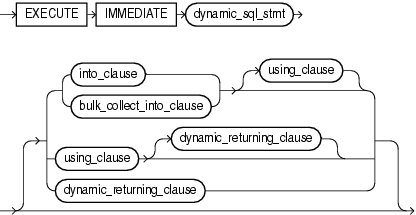
The EXECUTE IMMEDIATE statement builds and runs a dynamic SQL statement in a single operation. Native dynamic SQL uses the EXECUTE IMMEDIATE statement to process most dynamic SQL statements.
Caution:
When using dynamic SQL, beware of SQL injection, a security risk. For more information about SQL injection, see "SQL Injection".execute_immediate_statement ::=
See:
String literal, string variable, or string expression that represents a SQL statement. Its type must be either CHAR, VARCHAR2, or CLOB.
Specifies the variables or record in which to store the column values that the statement returns. For more information about this clause, see "RETURNING INTO Clause".
Restriction on into_clause Use if and only if dynamic_sql_stmt returns a single row.
Specifies one or more collections in which to store the rows that the statement returns. For more information about this clause, see "RETURNING INTO Clause".
Restriction on bulk_collect_into_clause Use if and only if dynamic_sql_stmt can return multiple rows.
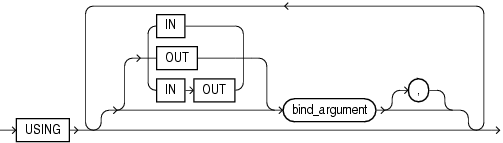
Specifies bind arguments.
Use if and only if dynamic_sql_stmt includes placeholders for bind arguments.
If dynamic_sql_stmt has a RETURNING INTO clause, using_clause can contain only IN bind arguments. The bind arguments in the RETURNING INTO clause are OUT bind arguments by definition.
Returns the column values of the rows affected by the dynamic SQL statement, in either individual variables or records. For more information about this clause, see "RETURNING INTO Clause".
Restriction on dynamic_returning_clause Use if and only if dynamic_sql_stmt has a RETURNING INTO clause.
Parameter modes of bind arguments. An IN bind argument passes its value to dynamic_sql_stmt. An OUT bind argument stores a value that dynamic_sql_stmt returns. An IN OUT bind argument passes its initial value to dynamic_sql_stmt and stores a value that dynamic_sql_stmt returns. Default: IN.
For DML a statement with a RETURNING clause, you can place OUT bind arguments in the RETURNING INTO clause without specifying the parameter mode, which is always OUT.
An expression whose value replaces its corresponding placeholder in dynamic_sql_stmt at run time.
Every placeholder in dynamic_sql_stmt must be associated with a bind_argument in the USING clause or RETURNING INTO clause (or both) or with a define variable in the INTO clause.
You can run dynamic_sql_stmt repeatedly using different values for the bind arguments. You incur some overhead, because EXECUTE IMMEDIATE prepares the dynamic string before every execution.
Restriction on bind_argument The value of bind_argument cannot be TRUE, FALSE, or NULL. To pass the value NULL to the dynamic SQL statement, use an uninitialized variable where you want to use NULL, as in "Uninitialized Variable Represents NULL in USING Clause".