| Oracle® Database Utilities 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E16536-05 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database Utilities 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E16536-05 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
This chapter describes the Oracle Data Pump Export utility (expdp). The following topics are discussed:
Data Pump Export (hereinafter referred to as Export for ease of reading) is a utility for unloading data and metadata into a set of operating system files called a dump file set. The dump file set can be imported only by the Data Pump Import utility. The dump file set can be imported on the same system or it can be moved to another system and loaded there.
The dump file set is made up of one or more disk files that contain table data, database object metadata, and control information. The files are written in a proprietary, binary format. During an import operation, the Data Pump Import utility uses these files to locate each database object in the dump file set.
Because the dump files are written by the server, rather than by the client, the database administrator (DBA) must create directory objects. See "Default Locations for Dump, Log, and SQL Files" for more information about directory objects.
Data Pump Export enables you to specify that a job should move a subset of the data and metadata, as determined by the export mode. This is done using data filters and metadata filters, which are specified through Export parameters. See "Filtering During Export Operations".
To see some examples of the various ways in which you can use Data Pump Export, refer to "Examples of Using Data Pump Export".
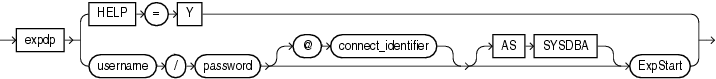
The Data Pump Export utility is invoked using the expdp command. The characteristics of the export operation are determined by the Export parameters you specify. These parameters can be specified either on the command line or in a parameter file.
Note:
Do not invoke Export asSYSDBA, except at the request of Oracle technical support. SYSDBA is used internally and has specialized functions; its behavior is not the same as for general users.The following sections contain more information about invoking Export:
You can interact with Data Pump Export by using a command line, a parameter file, or an interactive-command mode.
Command-Line Interface: Enables you to specify most of the Export parameters directly on the command line. For a complete description of the parameters available in the command-line interface, see "Parameters Available in Export's Command-Line Mode".
Parameter File Interface: Enables you to specify command-line parameters in a parameter file. The only exception is the PARFILE parameter, because parameter files cannot be nested. The use of parameter files is recommended if you are using parameters whose values require quotation marks. See "Use of Quotation Marks On the Data Pump Command Line".
Interactive-Command Interface: Stops logging to the terminal and displays the Export prompt, from which you can enter various commands, some of which are specific to interactive-command mode. This mode is enabled by pressing Ctrl+C during an export operation started with the command-line interface or the parameter file interface. Interactive-command mode is also enabled when you attach to an executing or stopped job.
For a complete description of the commands available in interactive-command mode, see "Commands Available in Export's Interactive-Command Mode".
Export provides different modes for unloading different portions of the database. The mode is specified on the command line, using the appropriate parameter. The available modes are described in the following sections:
Note:
Several system schemas cannot be exported because they are not user schemas; they contain Oracle-managed data and metadata. Examples of system schemas that are not exported includeSYS, ORDSYS, and MDSYS.See Also:
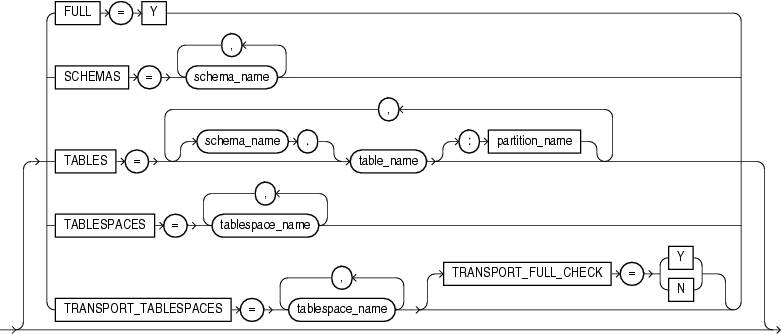
"Examples of Using Data Pump Export"A full export is specified using the FULL parameter. In a full database export, the entire database is unloaded. This mode requires that you have the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE role.
A schema export is specified using the SCHEMAS parameter. This is the default export mode. If you have the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE role, then you can specify a list of schemas, optionally including the schema definitions themselves and also system privilege grants to those schemas. If you do not have the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE role, then you can export only your own schema.
The SYS schema cannot be used as a source schema for export jobs.
Cross-schema references are not exported unless the referenced schema is also specified in the list of schemas to be exported. For example, a trigger defined on a table within one of the specified schemas, but that resides in a schema not explicitly specified, is not exported. This is also true for external type definitions upon which tables in the specified schemas depend. In such a case, it is expected that the type definitions already exist in the target instance at import time.
A table mode export is specified using the TABLES parameter. In table mode, only a specified set of tables, partitions, and their dependent objects are unloaded.
If you specify the TRANSPORTABLE=ALWAYS parameter with the TABLES parameter, then only object metadata is unloaded. To move the actual data, you copy the data files to the target database. This results in quicker export times. If you are moving data files between releases or platforms, then the data files may need to be processed by Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN).
See Also:
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for more information on transporting data across platformsYou must have the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE role to specify tables that are not in your own schema. Note that type definitions for columns are not exported in table mode. It is expected that the type definitions already exist in the target instance at import time. Also, as in schema exports, cross-schema references are not exported.
See Also:
"TABLES" for a description of the Export TABLES parameter
"TRANSPORTABLE" for a description of the Export TRANSPORTABLE parameter
A tablespace export is specified using the TABLESPACES parameter. In tablespace mode, only the tables contained in a specified set of tablespaces are unloaded. If a table is unloaded, then its dependent objects are also unloaded. Both object metadata and data are unloaded. In tablespace mode, if any part of a table resides in the specified set, then that table and all of its dependent objects are exported. Privileged users get all tables. Nonprivileged users get only the tables in their own schemas.
See Also:
"TABLESPACES" for a description of the Export TABLESPACES parameter
A transportable tablespace export is specified using the TRANSPORT_TABLESPACES parameter. In transportable tablespace mode, only the metadata for the tables (and their dependent objects) within a specified set of tablespaces is exported. The tablespace data files are copied in a separate operation. Then, a transportable tablespace import is performed to import the dump file containing the metadata and to specify the data files to use.
Transportable tablespace mode requires that the specified tables be completely self-contained. That is, all storage segments of all tables (and their indexes) defined within the tablespace set must also be contained within the set. If there are self-containment violations, then Export identifies all of the problems without actually performing the export.
Transportable tablespace exports cannot be restarted once stopped. Also, they cannot have a degree of parallelism greater than 1.
Encrypted columns are not supported in transportable tablespace mode.
Note:
You cannot export transportable tablespaces and then import them into a database at a lower release level. The target database must be at the same or higher release level as the source database.Considerations for Time Zone File Versions in Transportable Tablespace Mode
Jobs performed in transportable tablespace mode have the following requirements concerning time zone file versions:
If the source database is release 11.2.0.2 or later and there are tables in the transportable set that use TIMESTAMP WITH TIMEZONE (TSTZ) columns, then the time zone file version on the target database must exactly match the time zone file version on the source database.
If the source database is earlier than release 11.2.0.2, then the time zone file version must be the same on the source and target database for all transportable jobs regardless of whether the transportable set uses TSTZ columns.
If these requirements are not met, then the import job aborts before anything is imported. This is because if the import job were allowed to import the objects, there might be inconsistent results when tables with TSTZ columns were read.
To identify the time zone file version of a database, you can execute the following SQL statement:
SQL> SELECT VERSION FROM V$TIMEZONE_FILE;
See Also:
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for more information about transportable tablespaces
Oracle Database Globalization Support Guide for more information about time zone file versions
You can specify a connect identifier in the connect string when you invoke the Data Pump Export utility. This identifier can specify a database instance that is different from the current instance identified by the current Oracle System ID (SID). The connect identifier can be an Oracle*Net connect descriptor or a net service name (usually defined in the tnsnames.ora file) that maps to a connect descriptor. Use of a connect identifier requires that you have Oracle Net Listener running (to start the default listener, enter lsnrctl start). The following example invokes Export for user hr, using the connect identifier inst1:
expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=hr.dmp TABLES=employees
Export: Release 11.2.0.2.0 - Production on Fri May 14 10:15:45 2010
Copyright (c) 1982, 2009, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Password: password@inst1
Connected to: Oracle Database 11g Enterprise Edition Release 11.2.0.2.0 - Production
With the Partitioning, Data Mining and Real Application Testing options
The local Export client connects to the database instance defined by the connect identifier inst1 (a net service name), retrieves data from inst1, and writes it to the dump file hr.dmp on inst1.
Specifying a connect identifier when you invoke the Export utility is different from performing an export operation using the NETWORK_LINK parameter. When you start an export operation and specify a connect identifier, the local Export client connects to the database instance identified by the connect identifier, retrieves data from that database instance, and writes it to a dump file set on that database instance. Whereas, when you perform an export using the NETWORK_LINK parameter, the export is performed using a database link. (A database link is a connection between two physical database servers that allows a client to access them as one logical database.)
See Also:
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for more information about database links
Oracle Database Net Services Administrator's Guide for more information about connect identifiers and Oracle Net Listener
Data Pump Export provides data and metadata filtering capability to help you limit the type of information that is exported.
Data specific filtering is implemented through the QUERY and SAMPLE parameters, which specify restrictions on the table rows that are to be exported.
Data filtering can also occur indirectly because of metadata filtering, which can include or exclude table objects along with any associated row data.
Each data filter can be specified once per table within a job. If different filters using the same name are applied to both a particular table and to the whole job, then the filter parameter supplied for the specific table takes precedence.
Metadata filtering is implemented through the EXCLUDE and INCLUDE parameters. The EXCLUDE and INCLUDE parameters are mutually exclusive.
Metadata filters identify a set of objects to be included or excluded from an Export or Import operation. For example, you could request a full export, but without Package Specifications or Package Bodies.
To use filters correctly and to get the results you expect, remember that dependent objects of an identified object are processed along with the identified object. For example, if a filter specifies that an index is to be included in an operation, then statistics from that index will also be included. Likewise, if a table is excluded by a filter, then indexes, constraints, grants, and triggers upon the table will also be excluded by the filter.
If multiple filters are specified for an object type, then an implicit AND operation is applied to them. That is, objects pertaining to the job must pass all of the filters applied to their object types.
The same metadata filter name can be specified multiple times within a job.
To see a list of valid object types, query the following views: DATABASE_EXPORT_OBJECTS for full mode, SCHEMA_EXPORT_OBJECTS for schema mode, and TABLE_EXPORT_OBJECTS for table and tablespace mode. The values listed in the OBJECT_PATH column are the valid object types. For example, you could perform the following query:
SQL> SELECT OBJECT_PATH, COMMENTS FROM SCHEMA_EXPORT_OBJECTS 2 WHERE OBJECT_PATH LIKE '%GRANT' AND OBJECT_PATH NOT LIKE '%/%';
The output of this query looks similar to the following:
OBJECT_PATH -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- COMMENTS -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- GRANT Object grants on the selected tables OBJECT_GRANT Object grants on the selected tables PROCDEPOBJ_GRANT Grants on instance procedural objects PROCOBJ_GRANT Schema procedural object grants in the selected schemas ROLE_GRANT Role grants to users associated with the selected schemas SYSTEM_GRANT System privileges granted to users associated with the selected schemas
This section describes the parameters available in the command-line mode of Data Pump Export. Be sure to read the following sections before using the Export parameters:
Many of the parameter descriptions include an example of how to use the parameter. For background information on setting up the necessary environment to run the examples, see:
For parameters that can have multiple values specified, the values can be separated by commas or by spaces. For example, you could specify TABLES=employees,jobs or TABLES=employees jobs.
For every parameter you enter, you must enter an equal sign (=) and a value. Data Pump has no other way of knowing that the previous parameter specification is complete and a new parameter specification is beginning. For example, in the following command line, even though NOLOGFILE is a valid parameter, it would be interpreted as another dumpfile name for the DUMPFILE parameter:
expdp DIRECTORY=dpumpdir DUMPFILE=test.dmp NOLOGFILE TABLES=employees
This would result in two dump files being created, test.dmp and nologfile.dmp.
To avoid this, specify either NOLOGFILE=y or NOLOGFILE=n.
Use of Quotation Marks On the Data Pump Command Line
Some operating systems treat quotation marks as special characters and will therefore not pass them to an application unless they are preceded by an escape character, such as the backslash (\). This is true both on the command line and within parameter files. Some operating systems may require an additional set of single or double quotation marks on the command line around the entire parameter value containing the special characters.
The following examples are provided to illustrate these concepts. Be aware that they may not apply to your particular operating system and that this documentation cannot anticipate the operating environments unique to each user.
Suppose you specify the TABLES parameter in a parameter file, as follows:
TABLES = \"MixedCaseTableName\"
If you were to specify that on the command line, some operating systems would require that it be surrounded by single quotation marks, as follows:
TABLES - '\"MixedCaseTableName\"'
To avoid having to supply additional quotation marks on the command line, Oracle recommends the use of parameter files. Also, note that if you use a parameter file and the parameter value being specified does not have quotation marks as the first character in the string (for example, TABLES=scott."EmP"), then the use of escape characters may not be necessary on some systems.
See Also:
The Export "PARFILE" parameter
"Default Locations for Dump, Log, and SQL Files" for information about creating default directory objects
Your Oracle operating system-specific documentation for information about how special and reserved characters are handled on your system
Using the Export Parameter Examples
If you try running the examples that are provided for each parameter, be aware of the following:
After you enter the username and parameters as shown in the example, Export is started and you are prompted for a password before a database connection is made:
Export: Release 11.2.0.2.0 - Production on Fri May 14 10:22:45 2010
Copyright (c) 1982, 2009, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Password: password
Connected to: Oracle Database 11g Enterprise Edition Release 11.2.0.2.0 - Production
With the Partitioning, Data Mining and Real Application Testing options
Most of the examples use the sample schemas of the seed database, which is installed by default when you install Oracle Database. In particular, the human resources (hr) schema is often used.
The examples assume that the directory objects, dpump_dir1 and dpump_dir2, already exist and that READ and WRITE privileges have been granted to the hr schema for these directory objects. See "Default Locations for Dump, Log, and SQL Files" for information about creating directory objects and assigning privileges to them.
Some of the examples require the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE and DATAPUMP_IMP_FULL_DATABASE roles. The examples assume that the hr schema has been granted these roles.
If necessary, ask your DBA for help in creating these directory objects and assigning the necessary privileges and roles.
Syntax diagrams of these parameters are provided in "Syntax Diagrams for Data Pump Export".
Unless specifically noted, these parameters can also be specified in a parameter file.
Default: job currently in the user's schema, if there is only one
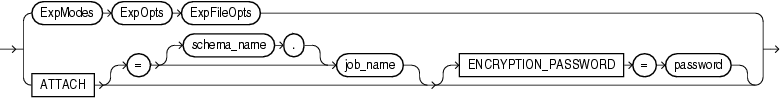
Attaches the client session to an existing export job and automatically places you in the interactive-command interface. Export displays a description of the job to which you are attached and also displays the Export prompt.
ATTACH [=[schema_name.]job_name]
The schema_name is optional. To specify a schema other than your own, you must have the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE role.
The job_name is optional if only one export job is associated with your schema and the job is active. To attach to a stopped job, you must supply the job name. To see a list of Data Pump job names, you can query the DBA_DATAPUMP_JOBS view or the USER_DATAPUMP_JOBS view.
When you are attached to the job, Export displays a description of the job and then displays the Export prompt.
When you specify the ATTACH parameter, the only other Data Pump parameter you can specify on the command line is ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD.
If the job you are attaching to was initially started using an encryption password, then when you attach to the job you must again enter the ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter on the command line to re-specify that password. The only exception to this is if the job was initially started with the ENCRYPTION=ENCRYPTED_COLUMNS_ONLY parameter. In that case, the encryption password is not needed when attaching to the job.
You cannot attach to a job in another schema unless it is already running.
If the dump file set or master table for the job have been deleted, then the attach operation will fail.
Altering the master table in any way will lead to unpredictable results.
The following is an example of using the ATTACH parameter. It assumes that the job, hr.export_job, already exists.
> expdp hr ATTACH=hr.export_job
Default: Y
Determines whether Data Pump can use Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) resources and start workers on other Oracle RAC instances.
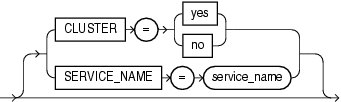
CLUSTER=[Y | N]
To force Data Pump Export to use only the instance where the job is started and to replicate pre-Oracle Database 11g release 2 (11.2) behavior, specify CLUSTER=N.
To specify a specific, existing service and constrain worker processes to run only on instances defined for that service, use the SERVICE_NAME parameter with the CLUSTER=Y parameter.
Use of the CLUSTER parameter may affect performance because there is some additional overhead in distributing the export job across Oracle RAC instances. For small jobs, it may be better to specify CLUSTER=N to constrain the job to run on the instance where it is started. Jobs whose performance benefits the most from using the CLUSTER parameter are those involving large amounts of data.
See Also:
The following is an example of using the CLUSTER parameter:
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=hr_clus%U.dmp CLUSTER=N PARALLEL=3
This example starts a schema-mode export (the default) of the hr schema. Because CLUSTER=N is specified, the job uses only the instance on which it started. (If the CLUSTER parameter had not been specified at all, then the default value of Y would have been used and workers would have been started on other instances in the Oracle RAC, if necessary.) The dump files will be written to the location specified for the dpump_dir1 directory object. The job can have up to 3 parallel processes.
Default: METADATA_ONLY
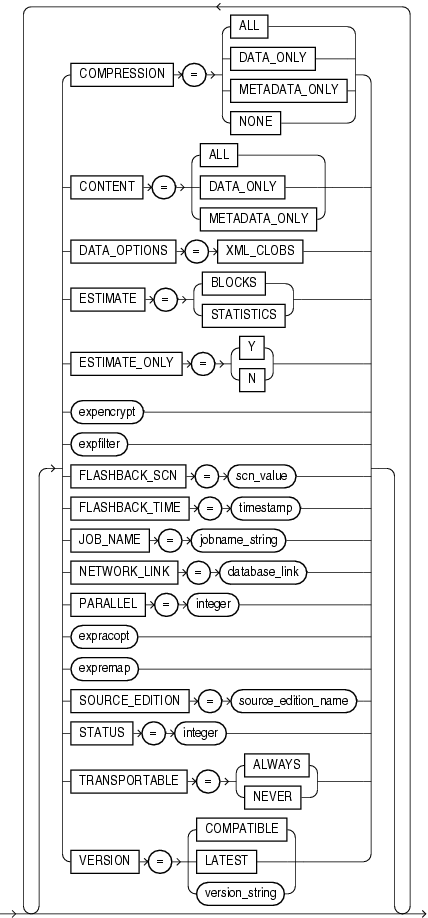
Specifies which data to compress before writing to the dump file set.
COMPRESSION={ALL | DATA_ONLY | METADATA_ONLY | NONE}
ALL enables compression for the entire export operation. The ALL option requires that the Oracle Advanced Compression option be enabled.
DATA_ONLY results in all data being written to the dump file in compressed format. The DATA_ONLY option requires that the Oracle Advanced Compression option be enabled.
METADATA_ONLY results in all metadata being written to the dump file in compressed format. This is the default.
NONE disables compression for the entire export operation.
See Also:
Oracle Database Licensing Information for information about licensing requirements for the Oracle Advanced Compression optionTo make full use of all these compression options, the COMPATIBLE initialization parameter must be set to at least 11.0.0.
The METADATA_ONLY option can be used even if the COMPATIBLE initialization parameter is set to 10.2.
Compression of data (using values ALL or DATA_ONLY) is valid only in the Enterprise Edition of Oracle Database 11g.
The following is an example of using the COMPRESSION parameter:
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=hr_comp.dmp COMPRESSION=METADATA_ONLY
This command will execute a schema-mode export that will compress all metadata before writing it out to the dump file, hr_comp.dmp. It defaults to a schema-mode export because no export mode is specified.
Default: ALL
Enables you to filter what Export unloads: data only, metadata only, or both.
CONTENT={ALL | DATA_ONLY | METADATA_ONLY}
ALL unloads both data and metadata. This is the default.
DATA_ONLY unloads only table row data; no database object definitions are unloaded.
METADATA_ONLY unloads only database object definitions; no table row data is unloaded. Be aware that if you specify CONTENT=METADATA_ONLY, then when the dump file is subsequently imported, any index or table statistics imported from the dump file will be locked after the import.
The CONTENT=METADATA_ONLY parameter cannot be used with the TRANSPORT_TABLESPACES (transportable-tablespace-mode) parameter or with the QUERY parameter.
The following is an example of using the CONTENT parameter:
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=hr.dmp CONTENT=METADATA_ONLY
This command will execute a schema-mode export that will unload only the metadata associated with the hr schema. It defaults to a schema-mode export of the hr schema because no export mode is specified.
Default: There is no default. If this parameter is not used, then the special data handling options it provides simply do not take effect.
The DATA_OPTIONS parameter provides options for how to handle certain types of data during exports and imports. For export operations, the only valid option for the DATA_OPTIONS parameter is XML_CLOBS.
DATA_OPTIONS=XML_CLOBS
The XML_CLOBS option specifies that XMLType columns are to be exported in uncompressed CLOB format regardless of the XMLType storage format that was defined for them.
If a table has XMLType columns stored only as CLOBs, then it is not necessary to specify the XML_CLOBS option because Data Pump automatically exports them in CLOB format.If a table has XMLType columns stored as any combination of object-relational (schema-based), binary, or CLOB formats, then Data Pump exports them in compressed format, by default. This is the preferred method. However, if you need to export the data in uncompressed CLOB format, you can use the XML_CLOBS option to override the default.
See Also:
Oracle XML DB Developer's Guide for information specific to exporting and importing XMLType tablesUsing the XML_CLOBS option requires that the same XML schema be used at both export and import time.
The Export DATA_OPTIONS parameter requires the job version to be set at 11.0.0 or higher. See "VERSION".
This example shows an export operation in which any XMLType columns in the hr.xdb_tab1 table are exported in uncompressed CLOB format regardless of the XMLType storage format that was defined for them.
> expdp hr TABLES=hr.xdb_tab1 DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=hr_xml.dmp VERSION=11.2 DATA_OPTIONS=xml_clobs
Default: DATA_PUMP_DIR
Specifies the default location to which Export can write the dump file set and the log file.
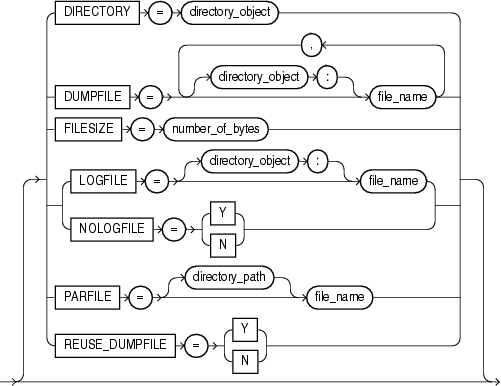
DIRECTORY=directory_object
The directory_object is the name of a database directory object (not the file path of an actual directory). Upon installation, privileged users have access to a default directory object named DATA_PUMP_DIR. Users with access to DATA_PUMP_DIR need not use the DIRECTORY parameter at all.
A directory object specified on the DUMPFILE or LOGFILE parameter overrides any directory object that you specify for the DIRECTORY parameter.
The following is an example of using the DIRECTORY parameter:
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=employees.dmp CONTENT=METADATA_ONLY
The dump file, employees.dmp, will be written to the path that is associated with the directory object dpump_dir1.
See Also:
"Default Locations for Dump, Log, and SQL Files" for more information about default directory objects
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for information about the CREATE DIRECTORY command
Default: expdat.dmp
Specifies the names, and optionally, the directory objects of dump files for an export job.
DUMPFILE=[directory_object:]file_name [, ...]
The directory_object is optional if one has already been established by the DIRECTORY parameter. If you supply a value here, then it must be a directory object that already exists and that you have access to. A database directory object that is specified as part of the DUMPFILE parameter overrides a value specified by the DIRECTORY parameter or by the default directory object.
You can supply multiple file_name specifications as a comma-delimited list or in separate DUMPFILE parameter specifications. If no extension is given for the file name, then Export uses the default file extension of .dmp. The file names can contain a substitution variable (%U), which implies that multiple files may be generated. The substitution variable is expanded in the resulting file names into a 2-digit, fixed-width, incrementing integer starting at 01 and ending at 99. If a file specification contains two substitution variables, both are incremented at the same time. For example, exp%Uaa%U.dmp would resolve to exp01aa01.dmp, exp02aa02.dmp, and so forth.
If the FILESIZE parameter is specified, then each dump file will have a maximum of that size and be nonextensible. If more space is required for the dump file set and a template with a substitution variable (%U) was supplied, then a new dump file is automatically created of the size specified by the FILESIZE parameter, if there is room on the device.
As each file specification or file template containing a substitution variable is defined, it is instantiated into one fully qualified file name and Export attempts to create it. The file specifications are processed in the order in which they are specified. If the job needs extra files because the maximum file size is reached, or to keep parallel workers active, then additional files are created if file templates with substitution variables were specified.
Although it is possible to specify multiple files using the DUMPFILE parameter, the export job may only require a subset of those files to hold the exported data. The dump file set displayed at the end of the export job shows exactly which files were used. It is this list of files that is required to perform an import operation using this dump file set. Any files that were not used can be discarded.
Any resulting dump file names that match preexisting dump file names will generate an error and the preexisting dump files will not be overwritten. You can override this behavior by specifying the Export parameter REUSE_DUMPFILES=Y.
The following is an example of using the DUMPFILE parameter:
> expdp hr SCHEMAS=hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=dpump_dir2:exp1.dmp, exp2%U.dmp PARALLEL=3
The dump file, exp1.dmp, will be written to the path associated with the directory object dpump_dir2 because dpump_dir2 was specified as part of the dump file name, and therefore overrides the directory object specified with the DIRECTORY parameter. Because all three parallel processes will be given work to perform during this job, dump files named exp201.dmp and exp202.dmp will be created based on the wildcard exp2%U.dmp specification. Because no directory is specified for them, they will be written to the path associated with the directory object, dpump_dir1, that was specified with the DIRECTORY parameter.
See Also:
"File Allocation" for information on how wildcards are handled when you specify them in dump file names
Default: The default value depends upon the combination of encryption-related parameters that are used. To enable encryption, either the ENCRYPTION or ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter, or both, must be specified. If only the ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter is specified, then the ENCRYPTION parameter defaults to ALL. If neither ENCRYPTION nor ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD is specified, then ENCRYPTION defaults to NONE.
Specifies whether to encrypt data before writing it to the dump file set.
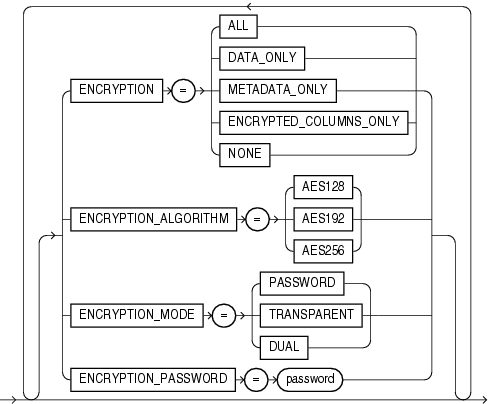
ENCRYPTION = {ALL | DATA_ONLY | ENCRYPTED_COLUMNS_ONLY | METADATA_ONLY | NONE}
ALL enables encryption for all data and metadata in the export operation.
DATA_ONLY specifies that only data is written to the dump file set in encrypted format.
ENCRYPTED_COLUMNS_ONLY specifies that only encrypted columns are written to the dump file set in encrypted format.
METADATA_ONLY specifies that only metadata is written to the dump file set in encrypted format.
NONE specifies that no data is written to the dump file set in encrypted format.
Note:
If the data being exported includes SecureFiles that you want to be encrypted, then you must specifyENCRYPTION=ALL to encrypt the entire dump file set. Encryption of the entire dump file set is the only way to achieve encryption security for SecureFiles during a Data Pump export operation. For more information about SecureFiles, see Oracle Database SecureFiles and Large Objects Developer's Guide.To specify the ALL, DATA_ONLY, or METADATA_ONLY options, the COMPATIBLE initialization parameter must be set to at least 11.0.0.
This parameter is valid only in the Enterprise Edition of Oracle Database 11g.
The following example performs an export operation in which only data is encrypted in the dump file:
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=hr_enc.dmp JOB_NAME=enc1 ENCRYPTION=data_only ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD=foobar
Default: AES128
Specifies which cryptographic algorithm should be used to perform the encryption.
ENCRYPTION_ALGORITHM = { AES128 | AES192 | AES256 }
See Oracle Database Advanced Security Administrator's Guide for information about encryption algorithms.
To use this encryption feature, the COMPATIBLE initialization parameter must be set to at least 11.0.0.
The ENCRYPTION_ALGORITHM parameter requires that you also specify either the ENCRYPTION or ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter; otherwise an error is returned.
This parameter is valid only in the Enterprise Edition of Oracle Database 11g.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=hr_enc3.dmp ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD=foobar ENCRYPTION_ALGORITHM=AES128
Default: The default mode depends on which other encryption-related parameters are used. If only the ENCRYPTION parameter is specified and the Oracle encryption wallet is open, then the default mode is TRANSPARENT. If only the ENCRYPTION parameter is specified and the wallet is closed, then an error is returned.
If the ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter is specified and the wallet is open, then the default is DUAL. If the ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter is specified and the wallet is closed, then the default is PASSWORD.
Specifies the type of security to use when encryption and decryption are performed.
ENCRYPTION_MODE = { DUAL | PASSWORD | TRANSPARENT }
DUAL mode creates a dump file set that can later be imported either transparently or by specifying a password that was used when the dual-mode encrypted dump file set was created. When you later import the dump file set created in DUAL mode, you can use either the wallet or the password that was specified with the ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter. DUAL mode is best suited for cases in which the dump file set will be imported on-site using the wallet, but which may also need to be imported offsite where the wallet is not available.
PASSWORD mode requires that you provide a password when creating encrypted dump file sets. You will need to provide the same password when you import the dump file set. PASSWORD mode requires that you also specify the ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter. The PASSWORD mode is best suited for cases in which the dump file set will be imported into a different or remote database, but which must remain secure in transit.
TRANSPARENT mode allows an encrypted dump file set to be created without any intervention from a database administrator (DBA), provided the required wallet is available. Therefore, the ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter is not required, and will in fact, cause an error if it is used in TRANSPARENT mode. This encryption mode is best suited for cases in which the dump file set will be imported into the same database from which it was exported.
To use DUAL or TRANSPARENT mode, the COMPATIBLE initialization parameter must be set to at least 11.0.0.
When you use the ENCRYPTION_MODE parameter, you must also use either the ENCRYPTION or ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter. Otherwise, an error is returned.
When you use the ENCRYPTION parameter with a value of ENCRYPTED_COLUMNS_ONLY, you cannot use the ENCRYPTION_MODE parameter. Otherwise, an error is returned.
This parameter is valid only in the Enterprise Edition of Oracle Database 11g.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=hr_enc4.dmp ENCRYPTION=all ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD=secretwords ENCRYPTION_ALGORITHM=AES256 ENCRYPTION_MODE=dual
Default: There is no default; the value is user-provided.
Specifies a password for encrypting encrypted column data, metadata, or table data in the export dumpfile. This prevents unauthorized access to an encrypted dump file set.
Note:
Data Pump encryption functionality changed as of Oracle Database 11g release 1 (11.1). Before release 11.1, theENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter applied only to encrypted columns. However, as of release 11.1, the new ENCRYPTION parameter provides options for encrypting other types of data. This means that if you now specify ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD without also specifying ENCRYPTION and a specific option, then all data written to the dump file will be encrypted (equivalent to specifying ENCRYPTION=ALL). If you want to re-encrypt only encrypted columns, then you must now specify ENCRYPTION=ENCRYPTED_COLUMNS_ONLY in addition to ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD.ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD = password
Thee password value that is supplied specifies a key for re-encrypting encrypted table columns, metadata, or table data so that they are not written as clear text in the dump file set. If the export operation involves encrypted table columns, but an encryption password is not supplied, then the encrypted columns will be written to the dump file set as clear text and a warning will be issued.
For export operations, this parameter is required if the ENCRYPTION_MODE parameter is set to either PASSWORD or DUAL.
Note:
There is no connection or dependency between the key specified with the Data PumpENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter and the key specified with the ENCRYPT keyword when the table with encrypted columns was initially created. For example, suppose a table is created as follows, with an encrypted column whose key is xyz:
CREATE TABLE emp (col1 VARCHAR2(256) ENCRYPT IDENTIFIED BY "xyz");
When you export the emp table, you can supply any arbitrary value for ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD. It does not have to be xyz.
This parameter is valid only in the Enterprise Edition of Oracle Database 11g.
If ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD is specified but ENCRYPTION_MODE is not specified, then it is not necessary to have the Transparent Data Encryption option set up since ENCRYPTION_MODE will default to PASSWORD.
The ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter is not valid if the requested encryption mode is TRANSPARENT.
To use the ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter if ENCRYPTION_MODE is set to DUAL, you must have the Transparent Data Encryption option set up. See Oracle Database Advanced Security Administrator's Guide for more information about the Transparent Data Encryption option.
For network exports, the ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter in conjunction with ENCRYPTED_COLUMNS_ONLY is not supported with user-defined external tables that have encrypted columns. The table will be skipped and an error message will be displayed, but the job will continue.
Encryption attributes for all columns must match between the exported table definition and the target table. For example, suppose you have a table, EMP, and one of its columns is named EMPNO. Both of the following situations would result in an error because the encryption attribute for the EMP column in the source table would not match the encryption attribute for the EMP column in the target table:
The EMP table is exported with the EMPNO column being encrypted, but before importing the table you remove the encryption attribute from the EMPNO column.
The EMP table is exported without the EMPNO column being encrypted, but before importing the table you enable encryption on the EMPNO column.
In the following example, an encryption password, 123456, is assigned to the dump file, dpcd2be1.dmp.
expdp hr TABLES=employee_s_encrypt DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=dpcd2be1.dmp ENCRYPTION=ENCRYPTED_COLUMNS_ONLY ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD=123456
Encrypted columns in the employee_s_encrypt table, will not be written as clear text in the dpcd2be1.dmp dump file. Note that to subsequently import the dpcd2be1.dmp file created by this example, you will need to supply the same encryption password. (See "ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD" for an example of an import operation using the ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD parameter.)
Default: BLOCKS
Specifies the method that Export will use to estimate how much disk space each table in the export job will consume (in bytes). The estimate is printed in the log file and displayed on the client's standard output device. The estimate is for table row data only; it does not include metadata.
ESTIMATE={BLOCKS | STATISTICS}
BLOCKS - The estimate is calculated by multiplying the number of database blocks used by the source objects, times the appropriate block sizes.
STATISTICS - The estimate is calculated using statistics for each table. For this method to be as accurate as possible, all tables should have been analyzed recently.
If the Data Pump export job involves compressed tables, then the default size estimation given for the compressed table is inaccurate when ESTIMATE=BLOCKS is used. This is because the size estimate does not reflect that the data was stored in a compressed form. To get a more accurate size estimate for compressed tables, use ESTIMATE=STATISTICS.
The estimate may also be inaccurate if the QUERY, SAMPLE, or REMAP_DATA parameter is used.
The following example shows a use of the ESTIMATE parameter in which the estimate is calculated using statistics for the employees table:
> expdp hr TABLES=employees ESTIMATE=STATISTICS DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=estimate_stat.dmp
Default: n
Instructs Export to estimate the space that a job would consume, without actually performing the export operation.
ESTIMATE_ONLY={y | n}
If ESTIMATE_ONLY=y, then Export estimates the space that would be consumed, but quits without actually performing the export operation.
The ESTIMATE_ONLY parameter cannot be used in conjunction with the QUERY parameter.
The following shows an example of using the ESTIMATE_ONLY parameter to determine how much space an export of the HR schema will take.
> expdp hr ESTIMATE_ONLY=y NOLOGFILE=y SCHEMAS=HR
Default: There is no default
Enables you to filter the metadata that is exported by specifying objects and object types to be excluded from the export operation.
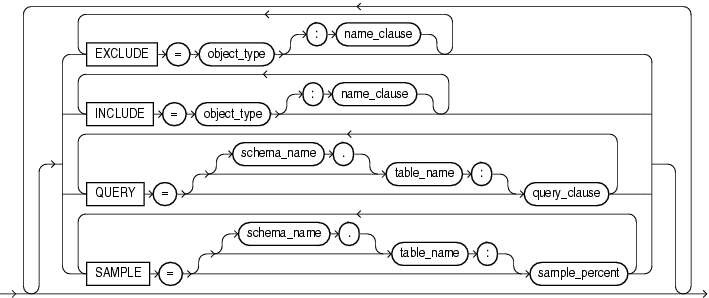
EXCLUDE=object_type[:name_clause] [, ...]
The object_type specifies the type of object to be excluded. To see a list of valid values for object_type, query the following views: DATABASE_EXPORT_OBJECTS for full mode, SCHEMA_EXPORT_OBJECTS for schema mode, and TABLE_EXPORT_OBJECTS for table and tablespace mode. The values listed in the OBJECT_PATH column are the valid object types.
All object types for the given mode of export will be included in the export except those specified in an EXCLUDE statement. If an object is excluded, then all of its dependent objects are also excluded. For example, excluding a table will also exclude all indexes and triggers on the table.
The name_clause is optional. It allows selection of specific objects within an object type. It is a SQL expression used as a filter on the type's object names. It consists of a SQL operator and the values against which the object names of the specified type are to be compared. The name clause applies only to object types whose instances have names (for example, it is applicable to TABLE, but not to GRANT). The name clause must be separated from the object type with a colon and enclosed in double quotation marks, because single quotation marks are required to delimit the name strings. For example, you could set EXCLUDE=INDEX:"LIKE 'EMP%'" to exclude all indexes whose names start with EMP.
The name that you supply for the name_clause must exactly match, including upper and lower casing, an existing object in the database. For example, if the name_clause you supply is for a table named EMPLOYEES, then there must be an existing table named EMPLOYEES using all upper case. If the name_clause were supplied as Employees or employees or any other variation, then the table would not be found.
If no name_clause is provided, then all objects of the specified type are excluded.
More than one EXCLUDE statement can be specified.
Depending on your operating system, the use of quotation marks when you specify a value for this parameter may also require that you use escape characters. Oracle recommends that you place this parameter in a parameter file, which can reduce the number of escape characters that might otherwise be needed on the command line.
See Also:
"INCLUDE" for an example of using a parameter file
If the object_type you specify is CONSTRAINT, GRANT, or USER, then you should be aware of the effects this will have, as described in the following paragraphs.
The following constraints cannot be explicitly excluded:
NOT NULL constraints
Constraints needed for the table to be created and loaded successfully; for example, primary key constraints for index-organized tables, or REF SCOPE and WITH ROWID constraints for tables with REF columns
This means that the following EXCLUDE statements will be interpreted as follows:
EXCLUDE=CONSTRAINT will exclude all (nonreferential) constraints, except for NOT NULL constraints and any constraints needed for successful table creation and loading.
EXCLUDE=REF_CONSTRAINT will exclude referential integrity (foreign key) constraints.
Specifying EXCLUDE=GRANT excludes object grants on all object types and system privilege grants.
Specifying EXCLUDE=USER excludes only the definitions of users, not the objects contained within users' schemas.
To exclude a specific user and all objects of that user, specify a command such as the following, where hr is the schema name of the user you want to exclude.
expdp FULL=Y DUMPFILE=expfull.dmp EXCLUDE=SCHEMA:"='HR'"
Note that in this situation, an export mode of FULL is specified. If no mode were specified, then the default mode, SCHEMAS, would be used. This would cause an error because the command would indicate that the schema should be both exported and excluded at the same time.
If you try to exclude a user by using a statement such as EXCLUDE=USER:"='HR'", then only the information used in CREATE USER hr DDL statements will be excluded, and you may not get the results you expect.
The EXCLUDE and INCLUDE parameters are mutually exclusive.
The following is an example of using the EXCLUDE statement.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=hr_exclude.dmp EXCLUDE=VIEW, PACKAGE, FUNCTION
This will result in a schema-mode export (the default export mode) in which all of the hr schema will be exported except its views, packages, and functions.
See Also:
"Filtering During Export Operations" for more information about the effects of using the EXCLUDE parameter
Default: 0 (equivalent to the maximum size of 16 terabytes)
Specifies the maximum size of each dump file. If the size is reached for any member of the dump file set, then that file is closed and an attempt is made to create a new file, if the file specification contains a substitution variable or if additional dump files have been added to the job.
FILESIZE=integer[B | KB | MB | GB | TB]
The integer can be immediately followed (do not insert a space) by B, KB, MB, GB, or TB (indicating bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, and terabytes respectively). Bytes is the default. The actual size of the resulting file may be rounded down slightly to match the size of the internal blocks used in dump files.
The minimum size for a file is ten times the default Data Pump block size, which is 4 kilobytes.
The maximum size for a file is 16 terabytes.
The following shows an example in which the size of the dump file is set to 3 megabytes:
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=hr_3m.dmp FILESIZE=3MB
If 3 megabytes had not been sufficient to hold all the exported data, then the following error would have been displayed and the job would have stopped:
ORA-39095: Dump file space has been exhausted: Unable to allocate 217088 bytes
The actual number of bytes that could not be allocated may vary. Also, this number does not represent the amount of space needed to complete the entire export operation. It indicates only the size of the current object that was being exported when the job ran out of dump file space.This situation can be corrected by first attaching to the stopped job, adding one or more files using the ADD_FILE command, and then restarting the operation.
Default: There is no default
Specifies the system change number (SCN) that Export will use to enable the Flashback Query utility.
FLASHBACK_SCN=scn_value
The export operation is performed with data that is consistent as of the specified SCN. If the NETWORK_LINK parameter is specified, then the SCN refers to the SCN of the source database.
FLASHBACK_SCN and FLASHBACK_TIME are mutually exclusive.
The FLASHBACK_SCN parameter pertains only to the Flashback Query capability of Oracle Database. It is not applicable to Flashback Database, Flashback Drop, or Flashback Data Archive.
The following example assumes that an existing SCN value of 384632 exists. It exports the hr schema up to SCN 384632.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=hr_scn.dmp FLASHBACK_SCN=384632
Note:
If you are on a logical standby system and using a network link to access the logical standby primary, then theFLASHBACK_SCN parameter is ignored because SCNs are selected by logical standby. See Oracle Data Guard Concepts and Administration for information about logical standby databases.Default: There is no default
The SCN that most closely matches the specified time is found, and this SCN is used to enable the Flashback utility. The export operation is performed with data that is consistent as of this SCN.
FLASHBACK_TIME="TO_TIMESTAMP(time-value)"
Because the TO_TIMESTAMP value is enclosed in quotation marks, it would be best to put this parameter in a parameter file. See "Use of Quotation Marks On the Data Pump Command Line".
FLASHBACK_TIME and FLASHBACK_SCN are mutually exclusive.
The FLASHBACK_TIME parameter pertains only to the flashback query capability of Oracle Database. It is not applicable to Flashback Database, Flashback Drop, or Flashback Data Archive.
You can specify the time in any format that the DBMS_FLASHBACK.ENABLE_AT_TIME procedure accepts. For example, suppose you have a parameter file, flashback.par, with the following contents:
DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1
DUMPFILE=hr_time.dmp
FLASHBACK_TIME="TO_TIMESTAMP('25-08-2008 14:35:00', 'DD-MM-YYYY HH24:MI:SS')"
You could then issue the following command:
> expdp hr PARFILE=flashback.par
The export operation will be performed with data that is consistent with the SCN that most closely matches the specified time.
Note:
If you are on a logical standby system and using a network link to access the logical standby primary, then theFLASHBACK_SCN parameter is ignored because SCNs are selected by logical standby. See Oracle Data Guard Concepts and Administration for information about logical standby databases.See Also:
Oracle Database Advanced Application Developer's Guide for information about using Flashback QueryDefault: n
Specifies that you want to perform a full database mode export.
FULL={y | n}
FULL=y indicates that all data and metadata are to be exported. Filtering can restrict what is exported using this export mode. See "Filtering During Export Operations".
To perform a full export, you must have the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE role.
Note:
Be aware that when you later import a dump file that was created by a full-mode export, the import operation attempts to copy the password for theSYS account from the source database. This sometimes fails (for example, if the password is in a shared password file). If it does fail, then after the import completes, you must set the password for the SYS account at the target database to a password of your choice.A full export does not export system schemas that contain Oracle-managed data and metadata. Examples of system schemas that are not exported include SYS, ORDSYS, and MDSYS.
Grants on objects owned by the SYS schema are never exported.
If you are exporting data that is protected by a realm, then you must have authorization for that realm.
See Also:
Oracle Database Vault Administrator's Guide for information about configuring realmsThe following is an example of using the FULL parameter. The dump file, expfull.dmp is written to the dpump_dir2 directory.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir2 DUMPFILE=expfull.dmp FULL=y NOLOGFILE=y
Default: n
Displays online help for the Export utility.
HELP = {y | n}
If HELP=y is specified, then Export displays a summary of all Export command-line parameters and interactive commands.
> expdp HELP = y
This example will display a brief description of all Export parameters and commands.
Default: There is no default
Enables you to filter the metadata that is exported by specifying objects and object types for the current export mode. The specified objects and all their dependent objects are exported. Grants on these objects are also exported.
INCLUDE = object_type[:name_clause] [, ...]
The object_type specifies the type of object to be included. To see a list of valid values for object_type, query the following views: DATABASE_EXPORT_OBJECTS for full mode, SCHEMA_EXPORT_OBJECTS for schema mode, and TABLE_EXPORT_OBJECTS for table and tablespace mode. The values listed in the OBJECT_PATH column are the valid object types.
Only object types explicitly specified in INCLUDE statements, and their dependent objects, are exported. No other object types, including the schema definition information that is normally part of a schema-mode export when you have the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE role, are exported.
The name_clause is optional. It allows fine-grained selection of specific objects within an object type. It is a SQL expression used as a filter on the object names of the type. It consists of a SQL operator and the values against which the object names of the specified type are to be compared. The name clause applies only to object types whose instances have names (for example, it is applicable to TABLE, but not to GRANT). The optional name clause must be separated from the object type with a colon and enclosed in double quotation marks, because single quotation marks are required to delimit the name strings.
The name that you supply for the name_clause must exactly match, including upper and lower casing, an existing object in the database. For example, if the name_clause you supply is for a table named EMPLOYEES, then there must be an existing table named EMPLOYEES using all upper case. If the name_clause were supplied as Employees or employees or any other variation, then the table would not be found.
Depending on your operating system, the use of quotation marks when you specify a value for this parameter may also require that you use escape characters. Oracle recommends that you place this parameter in a parameter file, which can reduce the number of escape characters that might otherwise be needed on the command line. See "Use of Quotation Marks On the Data Pump Command Line".
For example, suppose you have a parameter file named hr.par with the following content:
SCHEMAS=HR
DUMPFILE=expinclude.dmp
DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1
LOGFILE=expinclude.log
INCLUDE=TABLE:"IN ('EMPLOYEES', 'DEPARTMENTS')"
INCLUDE=PROCEDURE
INCLUDE=INDEX:"LIKE 'EMP%'"
You could then use the hr.par file to start an export operation, without having to enter any other parameters on the command line:
> expdp hr parfile=hr.par
If the object_type you specify is a CONSTRAINT, then you should be aware of the effects this will have.
The following constraints cannot be explicitly included:
NOT NULL constraints
Constraints needed for the table to be created and loaded successfully; for example, primary key constraints for index-organized tables, or REF SCOPE and WITH ROWID constraints for tables with REF columns
This means that the following INCLUDE statements will be interpreted as follows:
INCLUDE=CONSTRAINT will include all (nonreferential) constraints, except for NOT NULL constraints and any constraints needed for successful table creation and loading
INCLUDE=REF_CONSTRAINT will include referential integrity (foreign key) constraints
The INCLUDE and EXCLUDE parameters are mutually exclusive.
Grants on objects owned by the SYS schema are never exported.
The following example performs an export of all tables (and their dependent objects) in the hr schema:
> expdp hr INCLUDE=TABLE DUMPFILE=dpump_dir1:exp_inc.dmp NOLOGFILE=y
Default: system-generated name of the form SYS_EXPORT_<mode>_NN
Used to identify the export job in subsequent actions, such as when the ATTACH parameter is used to attach to a job, or to identify the job using the DBA_DATAPUMP_JOBS or USER_DATAPUMP_JOBS views. The job name becomes the name of the master table in the current user's schema. The master table is used to control the export job.
JOB_NAME=jobname_string
The jobname_string specifies a name of up to 30 bytes for this export job. The bytes must represent printable characters and spaces. If spaces are included, then the name must be enclosed in single quotation marks (for example, 'Thursday Export'). The job name is implicitly qualified by the schema of the user performing the export operation.
The default job name is system-generated in the form SYS_EXPORT_<mode>_NN, where NN expands to a 2-digit incrementing integer starting at 01. An example of a default name is 'SYS_EXPORT_TABLESPACE_02'.
The following example shows an export operation that is assigned a job name of exp_job:
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=exp_job.dmp JOB_NAME=exp_job NOLOGFILE=y
Default: export.log
Specifies the name, and optionally, a directory, for the log file of the export job.
LOGFILE=[directory_object:]file_name
You can specify a database directory_object previously established by the DBA, assuming that you have access to it. This overrides the directory object specified with the DIRECTORY parameter.
The file_name specifies a name for the log file. The default behavior is to create a file named export.log in the directory referenced by the directory object specified in the DIRECTORY parameter.
All messages regarding work in progress, work completed, and errors encountered are written to the log file. (For a real-time status of the job, use the STATUS command in interactive mode.)
A log file is always created for an export job unless the NOLOGFILE parameter is specified. As with the dump file set, the log file is relative to the server and not the client.
An existing file matching the file name will be overwritten.
To perform a Data Pump Export using Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM), you must specify a LOGFILE parameter that includes a directory object that does not include the Oracle ASM + notation. That is, the log file must be written to a disk file, and not written into the Oracle ASM storage. Alternatively, you can specify NOLOGFILE=Y. However, this prevents the writing of the log file.
The following example shows how to specify a log file name if you do not want to use the default:
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=hr.dmp LOGFILE=hr_export.log
Note:
Data Pump Export writes the log file using the database character set. If your clientNLS_LANG environment setting sets up a different client character set from the database character set, then it is possible that table names may be different in the log file than they are when displayed on the client output screen.See Also:
"Using Directory Objects When Oracle Automatic Storage Management Is Enabled" for information about Oracle Automatic Storage Management and directory objects
Default: There is no default
Enables an export from a (source) database identified by a valid database link. The data from the source database instance is written to a dump file set on the connected database instance.
NETWORK_LINK=source_database_link
The NETWORK_LINK parameter initiates an export using a database link. This means that the system to which the expdp client is connected contacts the source database referenced by the source_database_link, retrieves data from it, and writes the data to a dump file set back on the connected system.
The source_database_link provided must be the name of a database link to an available database. If the database on that instance does not already have a database link, then you or your DBA must create one using the SQL CREATE DATABASE LINK statement.
If the source database is read-only, then the user on the source database must have a locally managed temporary tablespace assigned as the default temporary tablespace. Otherwise, the job will fail.
Caution:
If an export operation is performed over an unencrypted network link, then all data is exported as clear text even if it is encrypted in the database. See Oracle Database Advanced Security Administrator's Guide for information about network security.See Also:
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for more information about database links
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for more information about the CREATE DATABASE LINK statement
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for more information about locally managed tablespaces
The only types of database links supported by Data Pump Export are: public, fixed user, and connected user. Current-user database links are not supported.
Network exports do not support LONG columns.
When operating across a network link, Data Pump requires that the source and target databases differ by no more than one version. For example, if one database is Oracle Database 11g, then the other database must be either 11g or 10g. Note that Data Pump checks only the major version number (for example, 10g and 11g), not specific release numbers (for example, 10.1, 10.2, 11.1, or 11.2).
The following is an example of using the NETWORK_LINK parameter. The source_database_link would be replaced with the name of a valid database link that must already exist.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 NETWORK_LINK=source_database_link
DUMPFILE=network_export.dmp LOGFILE=network_export.log
Default: n
Specifies whether to suppress creation of a log file.
NOLOGFILE={y | n}
Specify NOLOGFILE=y to suppress the default behavior of creating a log file. Progress and error information is still written to the standard output device of any attached clients, including the client that started the original export operation. If there are no clients attached to a running job and you specify NOLOGFILE=y, then you run the risk of losing important progress and error information.
The following is an example of using the NOLOGFILE parameter:
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=hr.dmp NOLOGFILE=y
This command results in a schema-mode export (the default) in which no log file is written.
Default: 1
Specifies the maximum number of threads of active execution operating on behalf of the export job. This execution set consists of a combination of worker processes and parallel I/O server processes. The master control process and worker processes acting as query coordinators in parallel query operations do not count toward this total.
This parameter enables you to make trade-offs between resource consumption and elapsed time.
PARALLEL=integer
The value you specify for integer should be less than, or equal to, the number of files in the dump file set (or you should specify substitution variables in the dump file specifications). Because each active worker process or I/O server process writes exclusively to one file at a time, an insufficient number of files can have adverse effects. Some of the worker processes will be idle while waiting for files, thereby degrading the overall performance of the job. More importantly, if any member of a cooperating group of parallel I/O server processes cannot obtain a file for output, then the export operation will be stopped with an ORA-39095 error. Both situations can be corrected by attaching to the job using the Data Pump Export utility, adding more files using the ADD_FILE command while in interactive mode, and in the case of a stopped job, restarting the job.
To increase or decrease the value of PARALLEL during job execution, use interactive-command mode. Decreasing parallelism does not result in fewer worker processes associated with the job; it decreases the number of worker processes that will be executing at any given time. Also, any ongoing work must reach an orderly completion point before the decrease takes effect. Therefore, it may take a while to see any effect from decreasing the value. Idle workers are not deleted until the job exits.
Increasing the parallelism takes effect immediately if there is work that can be performed in parallel.
See Also:
"Controlling Resource Consumption"Using PARALLEL During An Export In An Oracle RAC Environment
In an Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) environment, if an export operation has PARALLEL=1, then all Data Pump processes reside on the instance where the job is started. Therefore, the directory object can point to local storage for that instance.
If the export operation has PARALLEL set to a value greater than 1, then Data Pump processes can reside on instances other than the one where the job was started. Therefore, the directory object must point to shared storage that is accessible by all instances of the Oracle RAC.
This parameter is valid only in the Enterprise Edition of Oracle Database 11g.
The following is an example of using the PARALLEL parameter:
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 LOGFILE=parallel_export.log JOB_NAME=par4_job DUMPFILE=par_exp%u.dmp PARALLEL=4
This results in a schema-mode export (the default) of the hr schema in which up to four files could be created in the path pointed to by the directory object, dpump_dir1.
Default: There is no default
Specifies the name of an export parameter file.
PARFILE=[directory_path]file_name
Unlike dump files, log files, and SQL files which are created and written by the server, the parameter file is opened and read by the expdp client. Therefore, a directory object name is neither required nor appropriate. The default is the user's current directory. The use of parameter files is highly recommended if you are using parameters whose values require the use of quotation marks.
The PARFILE parameter cannot be specified within a parameter file.
The content of an example parameter file, hr.par, might be as follows:
SCHEMAS=HR DUMPFILE=exp.dmp DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 LOGFILE=exp.log
You could then issue the following Export command to specify the parameter file:
> expdp hr parfile=hr.par
Default: There is no default
Allows you to specify a query clause that is used to filter the data that gets exported.
QUERY = [schema.][table_name:] query_clause
The query_clause is typically a SQL WHERE clause for fine-grained row selection, but could be any SQL clause. For example, an ORDER BY clause could be used to speed up a migration from a heap-organized table to an index-organized table. If a schema and table name are not supplied, then the query is applied to (and must be valid for) all tables in the export job. A table-specific query overrides a query applied to all tables.
When the query is to be applied to a specific table, a colon must separate the table name from the query clause. More than one table-specific query can be specified, but only one query can be specified per table.
If the NETWORK_LINK parameter is specified along with the QUERY parameter, then any objects specified in the query_clause that are on the remote (source) node must be explicitly qualified with the NETWORK_LINK value. Otherwise, Data Pump assumes that the object is on the local (target) node; if it is not, then an error is returned and the import of the table from the remote (source) system fails.
For example, if you specify NETWORK_LINK=dblink1, then the query_clause of the QUERY parameter must specify that link, as shown in the following example:
QUERY=(hr.employees:"WHERE last_name IN(SELECT last_name FROM hr.employees@dblink1)")
Depending on your operating system, the use of quotation marks when you specify a value for this parameter may also require that you use escape characters. Oracle recommends that you place this parameter in a parameter file, which can reduce the number of escape characters that might otherwise be needed on the command line. See "Use of Quotation Marks On the Data Pump Command Line".
To specify a schema other than your own in a table-specific query, you must be granted access to that specific table.
The QUERY parameter cannot be used with the following parameters:
CONTENT=METADATA_ONLY
ESTIMATE_ONLY
TRANSPORT_TABLESPACES
When the QUERY parameter is specified for a table, Data Pump uses external tables to unload the target table. External tables uses a SQL CREATE TABLE AS SELECT statement. The value of the QUERY parameter is the WHERE clause in the SELECT portion of the CREATE TABLE statement. If the QUERY parameter includes references to another table with columns whose names match the table being unloaded, and if those columns are used in the query, then you will need to use a table alias to distinguish between columns in the table being unloaded and columns in the SELECT statement with the same name. The table alias used by Data Pump for the table being unloaded is KU$.
For example, suppose you want to export a subset of the sh.sales table based on the credit limit for a customer in the sh.customers table. In the following example, KU$ is used to qualify the cust_id field in the QUERY parameter for unloading sh.sales. As a result, Data Pump exports only rows for customers whose credit limit is greater than $10,000.
QUERY='sales:"WHERE EXISTS (SELECT cust_id FROM customers c WHERE cust_credit_limit > 10000 AND ku$.cust_id = c.cust_id)"'
If, as in the following query, KU$ is not used for a table alias, then the result will be that all rows are unloaded:
QUERY='sales:"WHERE EXISTS (SELECT cust_id FROM customers c WHERE cust_credit_limit > 10000 AND cust_id = c.cust_id)"'
The maximum length allowed for a QUERY string is 4000 bytes including quotation marks, which means that the actual maximum length allowed is 3998 bytes.
The following is an example of using the QUERY parameter:
> expdp hr parfile=emp_query.par
The contents of the emp_query.par file are as follows:
QUERY=employees:"WHERE department_id > 10 AND salary > 10000" NOLOGFILE=y DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=exp1.dmp
This example unloads all tables in the hr schema, but only the rows that fit the query expression. In this case, all rows in all tables (except employees) in the hr schema will be unloaded. For the employees table, only rows that meet the query criteria are unloaded.
Default: There is no default
The REMAP_DATA parameter allows you to specify a remap function that takes as a source the original value of the designated column and returns a remapped value that will replace the original value in the dump file. A common use for this option is to mask data when moving from a production system to a test system. For example, a column of sensitive customer data such as credit card numbers could be replaced with numbers generated by a REMAP_DATA function. This would allow the data to retain its essential formatting and processing characteristics without exposing private data to unauthorized personnel.
The same function can be applied to multiple columns being dumped. This is useful when you want to guarantee consistency in remapping both the child and parent column in a referential constraint.
REMAP_DATA=[schema.]tablename.column_name:[schema.]pkg.function
The description of each syntax element, in the order in which they appear in the syntax, is as follows:
schema -- the schema containing the table to be remapped. By default, this is the schema of the user doing the export.
tablename -- the table whose column will be remapped.
column_name -- the column whose data is to be remapped. The maximum number of columns that can be remapped for a single table is 10.
schema -- the schema containing the PL/SQL package you have created that contains the remapping function. As a default, this is the schema of the user doing the export.
pkg -- the name of the PL/SQL package you have created that contains the remapping function.
function -- the name of the function within the PL/SQL that will be called to remap the column table in each row of the specified table.
The datatypes of the source argument and the returned value should both match the data type of the designated column in the table.
Remapping functions should not perform commits or rollbacks except in autonomous transactions.
The maximum number of columns you can remap on a single table is 10. You can remap 9 columns on table a and 8 columns on table b, and so on, but the maximum for each table is 10.
The following example assumes a package named remap has been created that contains functions named minus10 and plusx which change the values for employee_id and first_name in the employees table.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=remap1.dmp TABLES=employees REMAP_DATA=hr.employees.employee_id:hr.remap.minus10 REMAP_DATA=hr.employees.first_name:hr.remap.plusx
Default: N
Specifies whether to overwrite a preexisting dump file.
REUSE_DUMPFILES={Y | N}
Normally, Data Pump Export will return an error if you specify a dump file name that already exists. The REUSE_DUMPFILES parameter allows you to override that behavior and reuse a dump file name. For example, if you performed an export and specified DUMPFILE=hr.dmp and REUSE_DUMPFILES=Y, then hr.dmp would be overwritten if it already existed. Its previous contents would be lost and it would contain data for the current export instead.
The following export operation creates a dump file named enc1.dmp, even if a dump file with that name already exists.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=enc1.dmp TABLES=employees REUSE_DUMPFILES=y
Default: There is no default
Allows you to specify a percentage of the data rows to be sampled and unloaded from the source database.
SAMPLE=[[schema_name.]table_name:]sample_percent
This parameter allows you to export subsets of data by specifying the percentage of data to be sampled and exported. The sample_percent indicates the probability that a row will be selected as part of the sample. It does not mean that the database will retrieve exactly that amount of rows from the table. The value you supply for sample_percent can be anywhere from .000001 up to, but not including, 100.
The sample_percent can be applied to specific tables. In the following example, 50% of the HR.EMPLOYEES table will be exported:
SAMPLE="HR"."EMPLOYEES":50
If you specify a schema, then you must also specify a table. However, you can specify a table without specifying a schema; the current user will be assumed. If no table is specified, then the sample_percent value applies to the entire export job.
Note that you can use this parameter with the Data Pump Import PCTSPACE transform, so that the size of storage allocations matches the sampled data subset. (See "TRANSFORM".)
The SAMPLE parameter is not valid for network exports.
In the following example, the value 70 for SAMPLE is applied to the entire export job because no table name is specified.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=sample.dmp SAMPLE=70
Default: current user's schema
Specifies that you want to perform a schema-mode export. This is the default mode for Export.
SCHEMAS=schema_name [, ...]
If you have the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE role, then you can specify a single schema other than your own or a list of schema names. The DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE role also allows you to export additional nonschema object information for each specified schema so that the schemas can be re-created at import time. This additional information includes the user definitions themselves and all associated system and role grants, user password history, and so on. Filtering can further restrict what is exported using schema mode (see "Filtering During Export Operations").
If you do not have the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE role, then you can specify only your own schema.
The SYS schema cannot be used as a source schema for export jobs.
The following is an example of using the SCHEMAS parameter. Note that user hr is allowed to specify more than one schema because the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE role was previously assigned to it for the purpose of these examples.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=expdat.dmp SCHEMAS=hr,sh,oe
This results in a schema-mode export in which the schemas, hr, sh, and oe will be written to the expdat.dmp dump file located in the dpump_dir1 directory.
Default: There is no default
Used to specify a service name to be used in conjunction with the CLUSTER parameter.
SERVICE_NAME=name
The SERVICE_NAME parameter can be used with the CLUSTER=Y parameter to specify an existing service associated with a resource group that defines a set of Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) instances belonging to that resource group, typically a subset of all the Oracle RAC instances.
The service name is only used to determine the resource group and instances defined for that resource group. The instance where the job is started is always used, regardless of whether it is part of the resource group.
The SERVICE_NAME parameter is ignored if CLUSTER=N is also specified.
Suppose you have an Oracle RAC configuration containing instances A, B, C, and D. Also suppose that a service named my_service exists with a resource group consisting of instances A, B, and C only. In such a scenario, the following would be true:
If you start a Data Pump job on instance A and specify CLUSTER=Y (or accept the default, which is Y) and you do not specify the SERVICE_NAME parameter, then Data Pump creates workers on all instances: A, B, C, and D, depending on the degree of parallelism specified.
If you start a Data Pump job on instance A and specify CLUSTER=Y and SERVICE_NAME=my_service, then workers can be started on instances A, B, and C only.
If you start a Data Pump job on instance A and specify CLUSTER=N, then any SERVICE_NAME parameter you specify is ignored and all processes will start on instance A.
See Also:
"CLUSTER"The following is an example of using the SERVICE_NAME parameter:
expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=hr_svname2.dmp SERVICE_NAME=SALES
This example starts a schema-mode export (the default mode) of the hr schema. Even though CLUSTER=Y is not specified on the command line, it is the default behavior, so the job will use all instances in the resource group associated with the service name SALES. A dump file named hr_svname2.dmp will be written to the location specified by the dpump_dir1 directory object.
Default: the default database edition on the system
Specifies the database edition from which objects will be exported.
SOURCE_EDITION=edition_name
If SOURCE_EDITION=name is specified, then the objects from that edition are exported. Data Pump selects all inherited objects that have not changed and all actual objects that have changed.
If this parameter is not specified, then the default edition is used. If the specified edition does not exist or is not usable, then an error message is returned.
See Also:
Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for information about how editions are created
Oracle Database Advanced Application Developer's Guide for more information about the editions feature, including inherited and actual objects
This parameter is only useful if there are two or more versions of the same versionable objects in the database.
The job version must be 11.2 or higher. See "VERSION".
The following is an example of using the SOURCE_EDITION parameter:
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=exp_dat.dmp SOURCE_EDITION=exp_edition EXCLUDE=user
This example assumes the existence of an edition named exp_edition on the system from which objects are being exported. Because no export mode is specified, the default of schema mode will be used. The EXCLUDE=user parameter excludes only the definitions of users, not the objects contained within users' schemas.
Default: 0
Specifies the frequency at which the job status display is updated.
STATUS=[integer]
If you supply a value for integer, it specifies how frequently, in seconds, job status should be displayed in logging mode. If no value is entered or if the default value of 0 is used, then no additional information is displayed beyond information about the completion of each object type, table, or partition.
This status information is written only to your standard output device, not to the log file (if one is in effect).
The following is an example of using the STATUS parameter.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 SCHEMAS=hr,sh STATUS=300
This example will export the hr and sh schemas and display the status of the export every 5 minutes (60 seconds x 5 = 300 seconds).
Default: There is no default
Specifies that you want to perform a table-mode export.
TABLES=[schema_name.]table_name[:partition_name] [, ...]
Filtering can restrict what is exported using this mode (see "Filtering During Export Operations"). You can filter the data and metadata that is exported, by specifying a comma-delimited list of tables and partitions or subpartitions. If a partition name is specified, then it must be the name of a partition or subpartition in the associated table. Only the specified set of tables, partitions, and their dependent objects are unloaded.
If an entire partitioned table is exported, then it will be imported in its entirety, as a partitioned table. The only case in which this is not true is if PARTITION_OPTIONS=DEPARTITION is specified during import.
The table name that you specify can be preceded by a qualifying schema name. The schema defaults to that of the current user. To specify a schema other than your own, you must have the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE role.
The use of wildcards to specify table names and partition names is supported.
The following restrictions apply to table names:
By default, table names in a database are stored as uppercase. If you have a table name in mixed-case or lowercase, and you want to preserve case-sensitivity for the table name, then you must enclose the name in quotation marks. The name must exactly match the table name stored in the database.
Some operating systems require that quotation marks on the command line be preceded by an escape character. The following are examples of how case-sensitivity can be preserved in the different Export modes.
In command-line mode:
TABLES='\"Emp\"'
In interactive mode:
Table(T) to be exported: "Exp"
In parameter file mode:
TABLES='"Emp"'
Table names specified on the command line cannot include a pound sign (#), unless the table name is enclosed in quotation marks. Similarly, in the parameter file, if a table name includes a pound sign (#), then the Export utility interprets the rest of the line as a comment, unless the table name is enclosed in quotation marks.
For example, if the parameter file contains the following line, then Export interprets everything on the line after emp# as a comment and does not export the tables dept and mydata:
TABLES=(emp#, dept, mydata)
However, if the parameter file contains the following line, then the Export utility exports all three tables because emp# is enclosed in quotation marks:
TABLES=('"emp#"', dept, mydata)
Note:
Some operating systems require single quotation marks rather than double quotation marks, or the reverse. See your Oracle operating system-specific documentation. Different operating systems also have other restrictions on table naming.For example, the UNIX C shell attaches a special meaning to a dollar sign ($) or pound sign (#) (or certain other special characters). You must use escape characters to get such characters in the name past the shell and into Export.
Using the Transportable Option During Table-Mode Export
To use the transportable option during a table-mode export, specify the TRANSPORTABLE=ALWAYS parameter with the TABLES parameter. Metadata for the specified tables, partitions, or subpartitions is exported to the dump file. To move the actual data, you copy the data files to the target database.
If only a subset of a table's partitions are exported and the TRANSPORTABLE=ALWAYS parameter is used, then on import each partition becomes a non-partitioned table.
See Also:
The Import "REMAP_TABLE" command
Cross-schema references are not exported. For example, a trigger defined on a table within one of the specified schemas, but that resides in a schema not explicitly specified, is not exported.
Types used by the table are not exported in table mode. This means that if you subsequently import the dump file and the type does not already exist in the destination database, then the table creation will fail.
The use of synonyms as values for the TABLES parameter is not supported. For example, if the regions table in the hr schema had a synonym of regn, then it would not be valid to use TABLES=regn. An error would be returned.
The export of tables that include wildcards in the table name is not supported if the table has partitions.
The length of the table name list specified for the TABLES parameter is limited to a maximum of 4 MB, unless you are using the NETWORK_LINK parameter to an Oracle Database release 10.2.0.3 or earlier or to a read-only database. In such cases, the limit is 4 KB.
You can only specify partitions from one table if TRANSPORTABLE=ALWAYS is also set on the export.
The following example shows a simple use of the TABLES parameter to export three tables found in the hr schema: employees, jobs, and departments. Because user hr is exporting tables found in the hr schema, the schema name is not needed before the table names.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=tables.dmp TABLES=employees,jobs,departments
The following example assumes that user hr has the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE role. It shows the use of the TABLES parameter to export partitions.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=tables_part.dmp TABLES=sh.sales:sales_Q1_2008,sh.sales:sales_Q2_2008
This example exports the partitions, sales_Q1_2008 and sales_Q2_2008, from the table sales in the schema sh.
Default: There is no default
Specifies a list of tablespace names to be exported in tablespace mode.
TABLESPACES=tablespace_name [, ...]
In tablespace mode, only the tables contained in a specified set of tablespaces are unloaded. If a table is unloaded, then its dependent objects are also unloaded. Both object metadata and data are unloaded. If any part of a table resides in the specified set, then that table and all of its dependent objects are exported. Privileged users get all tables. Nonprivileged users get only the tables in their own schemas
Filtering can restrict what is exported using this mode (see "Filtering During Export Operations").
The length of the tablespace name list specified for the TABLESPACES parameter is limited to a maximum of 4 MB, unless you are using the NETWORK_LINK to an Oracle Database release 10.2.0.3 or earlier or to a read-only database. In such cases, the limit is 4 KB.
The following is an example of using the TABLESPACES parameter. The example assumes that tablespaces tbs_4, tbs_5, and tbs_6 already exist.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=tbs.dmp TABLESPACES=tbs_4, tbs_5, tbs_6
This results in a tablespace export in which tables (and their dependent objects) from the specified tablespaces (tbs_4, tbs_5, and tbs_6) will be unloaded.
Default: n
Specifies whether to check for dependencies between those objects inside the transportable set and those outside the transportable set. This parameter is applicable only to a transportable-tablespace mode export.
TRANSPORT_FULL_CHECK={y | n}
If TRANSPORT_FULL_CHECK=y, then Export verifies that there are no dependencies between those objects inside the transportable set and those outside the transportable set. The check addresses two-way dependencies. For example, if a table is inside the transportable set but its index is not, then a failure is returned and the export operation is terminated. Similarly, a failure is also returned if an index is in the transportable set but the table is not.
If TRANSPORT_FULL_CHECK=n, then Export verifies only that there are no objects within the transportable set that are dependent on objects outside the transportable set. This check addresses a one-way dependency. For example, a table is not dependent on an index, but an index is dependent on a table, because an index without a table has no meaning. Therefore, if the transportable set contains a table, but not its index, then this check succeeds. However, if the transportable set contains an index, but not the table, then the export operation is terminated.
There are other checks performed as well. For instance, export always verifies that all storage segments of all tables (and their indexes) defined within the tablespace set specified by TRANSPORT_TABLESPACES are actually contained within the tablespace set.
The following is an example of using the TRANSPORT_FULL_CHECK parameter. It assumes that tablespace tbs_1 exists.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=tts.dmp TRANSPORT_TABLESPACES=tbs_1 TRANSPORT_FULL_CHECK=y LOGFILE=tts.log
Default: There is no default
Specifies that you want to perform a transportable-tablespace-mode export.
TRANSPORT_TABLESPACES=tablespace_name [, ...]
Use the TRANSPORT_TABLESPACES parameter to specify a list of tablespace names for which object metadata will be exported from the source database into the target database.
The log file for the export lists the data files that are used in the transportable set, the dump files, and any containment violations.
The TRANSPORT_TABLESPACES parameter exports metadata for all objects within the specified tablespace. If you want to perform a transportable export of only certain tables, partitions, or subpartitions, then you must use the TABLES parameter with the TRANSPORTABLE=ALWAYS parameter.
Note:
You cannot export transportable tablespaces and then import them into a database at a lower release level. The target database must be at the same or higher release level as the source database.Transportable jobs are not restartable.
Transportable jobs are restricted to a degree of parallelism of 1.
Transportable tablespace mode requires that you have the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE role.
Transportable mode does not support encrypted columns.
The default tablespace of the user performing the export must not be set to one of the tablespaces being transported.
The SYS and SYSAUX tablespaces are not transportable.
All tablespaces in the transportable set must be set to read-only.
If the Data Pump Export VERSION parameter is specified along with the TRANSPORT_TABLESPACES parameter, then the version must be equal to or greater than the Oracle Database COMPATIBLE initialization parameter.
The TRANSPORT_TABLESPACES parameter cannot be used in conjunction with the QUERY parameter.
The following is an example of using the TRANSPORT_TABLESPACES parameter in a file-based job (rather than network-based). The tablespace tbs_1 is the tablespace being moved. This example assumes that tablespace tbs_1 exists and that it has been set to read-only. This example also assumes that the default tablespace was changed before this export command was issued.
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=tts.dmp TRANSPORT_TABLESPACES=tbs_1 TRANSPORT_FULL_CHECK=y LOGFILE=tts.log
See Also:
"Considerations for Time Zone File Versions in Transportable Tablespace Mode"
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for detailed information about transporting tablespaces between databases
Default: NEVER
Specifies whether the transportable option should be used during a table mode export (specified with the TABLES parameter) to export metadata for specific tables, partitions, and subpartitions.
TRANSPORTABLE = {ALWAYS | NEVER}
The definitions of the allowed values are as follows:
ALWAYS - Instructs the export job to use the transportable option. If transportable is not possible, then the job will fail. The transportable option exports only metadata for the specified tables, partitions, or subpartitions specified by the TABLES parameter. You must copy the actual data files to the target database. See "Using Data File Copying to Move Data".
NEVER - Instructs the export job to use either the direct path or external table method to unload data rather than the transportable option. This is the default.
Note:
If you want to export an entire tablespace in transportable mode, then use theTRANSPORT_TABLESPACES parameter.If only a subset of a table's partitions are exported and the TRANSPORTABLE=ALWAYS parameter is used, then on import each partition becomes a non-partitioned table.
If only a subset of a table's partitions are exported and the TRANSPORTABLE parameter is not used at all or is set to NEVER (the default), then on import:
If PARTITION_OPTIONS=DEPARTITION is used, theb each partition included in the dump file set is created as a non-partitioned table.
If PARTITION_OPTIONS is not used, then the complete table is created. That is, all the metadata for the complete table is present so that the table definition looks the same on the target system as it did on the source. But only the data that was exported for the specified partitions is inserted into the table.
The TRANSPORTABLE parameter is only valid in table mode exports.
The schema performing a transportable export requires the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE privilege.
Tablespaces associated with tables, partitions, and subpartitions must be read-only.
Transportable mode does not export any data. Data is copied when the tablespace data files are copied from the source system to the target system. The tablespaces that must be copied are listed at the end of the log file for the export operation.
To make use of the TRANSPORTABLE parameter, the COMPATIBLE initialization parameter must be set to at least 11.0.0.
The default tablespace of the user performing the export must not be set to one of the tablespaces being transported.
The following example assumes that the sh schema has the DATAPUMP_EXP_FULL_DATABASE privilege and that table sales2 is partitioned and contained within tablespace tbs2. (The tbs2 tablespace must be set to read-only in the source database.)
> expdp sh DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=tto1.dmp TABLES=sh.sales2 TRANSPORTABLE=always
After the export completes successfully, you must copy the data files to the target database area. You could then perform an import operation using the PARTITION_OPTIONS and REMAP_SCHEMA parameters to make each of the partitions in sales2 its own table.
> impdp system PARTITION_OPTIONS=departition TRANSPORT_DATAFILES=oracle/dbs/tbs2 DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=tto1.dmp REMAP_SCHEMA=sh:dp
Default: COMPATIBLE
Specifies the version of database objects to be exported (that is, only database objects and attributes that are compatible with the specified release will be exported). This can be used to create a dump file set that is compatible with a previous release of Oracle Database. Note that this does not mean that Data Pump Export can be used with releases of Oracle Database prior to Oracle Database 10g release 1 (10.1). Data Pump Export only works with Oracle Database 10g release 1 (10.1) or later. The VERSION parameter simply allows you to identify the version of the objects being exported.
VERSION={COMPATIBLE | LATEST | version_string}
The legal values for the VERSION parameter are as follows:
COMPATIBLE - This is the default value. The version of the metadata corresponds to the database compatibility level. Database compatibility must be set to 9.2 or higher.
LATEST - The version of the metadata corresponds to the database release.
version_string - A specific database release (for example, 11.2.0). In Oracle Database 11g, this value cannot be lower than 9.2.
Database objects or attributes that are incompatible with the specified release will not be exported. For example, tables containing new datatypes that are not supported in the specified release will not be exported.
Exporting a table with archived LOBs to a database release earlier than 11.2 is not allowed.
If the Data Pump Export VERSION parameter is specified along with the TRANSPORT_TABLESPACES parameter, then the value must be equal to or greater than the Oracle Database COMPATIBLE initialization parameter.
The following example shows an export for which the version of the metadata will correspond to the database release:
> expdp hr TABLES=hr.employees VERSION=LATEST DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 DUMPFILE=emp.dmp NOLOGFILE=y
In interactive-command mode, the current job continues running, but logging to the terminal is suspended and the Export prompt (Export>) is displayed.
To start interactive-command mode, do one of the following:
From an attached client, press Ctrl+C.
From a terminal other than the one on which the job is running, specify the ATTACH parameter in an expdp command to attach to the job. This is a useful feature in situations in which you start a job at one location and need to check on it at a later time from a different location.
Table 2-1 lists the activities you can perform for the current job from the Data Pump Export prompt in interactive-command mode.
Table 2-1 Supported Activities in Data Pump Export's Interactive-Command Mode
| Activity | Command Used |
|---|---|
|
Add additional dump files. |
|
|
Exit interactive mode and enter logging mode. |
|
|
Stop the export client session, but leave the job running. |
|
|
Redefine the default size to be used for any subsequent dump files. |
|
|
Display a summary of available commands. |
|
|
Detach all currently attached client sessions and terminate the current job. |
|
|
Increase or decrease the number of active worker processes for the current job. This command is valid only in the Enterprise Edition of Oracle Database 11g. |
|
|
Restart a stopped job to which you are attached. |
|
|
Display detailed status for the current job and/or set status interval. |
|
|
Stop the current job for later restart. |
The following are descriptions of the commands available in the interactive-command mode of Data Pump Export.
Adds additional files or substitution variables to the export dump file set.
ADD_FILE=[directory_object:]file_name [,...]
The file_name must not contain any directory path information. However, it can include a substitution variable, %U, which indicates that multiple files may be generated using the specified file name as a template. It can also specify another directory_object.
The size of the file being added is determined by the setting of the FILESIZE parameter.
See Also:
"File Allocation" for information about the effects of using substitution variablesThe following example adds two dump files to the dump file set. A directory object is not specified for the dump file named hr2.dmp, so the default directory object for the job is assumed. A different directory object, dpump_dir2, is specified for the dump file named hr3.dmp.
Export> ADD_FILE=hr2.dmp, dpump_dir2:hr3.dmp
Changes the Export mode from interactive-command mode to logging mode.
CONTINUE_CLIENT
In logging mode, status is continually output to the terminal. If the job is currently stopped, then CONTINUE_CLIENT will also cause the client to attempt to start the job.
Export> CONTINUE_CLIENT
Stops the export client session, exits Export, and discontinues logging to the terminal, but leaves the current job running.
EXIT_CLIENT
Because EXIT_CLIENT leaves the job running, you can attach to the job at a later time. To see the status of the job, you can monitor the log file for the job or you can query the USER_DATAPUMP_JOBS view or the V$SESSION_LONGOPS view.
Export> EXIT_CLIENT
Redefines the maximum size of subsequent dump files. If the size is reached for any member of the dump file set, then that file is closed and an attempt is made to create a new file, if the file specification contains a substitution variable or if additional dump files have been added to the job.
FILESIZE=integer[B | KB | MB | GB | TB]
The integer can be immediately followed (do not insert a space) by B, KB, MB, GB, or TB (indicating bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, and terabytes respectively). Bytes is the default. The actual size of the resulting file may be rounded down slightly to match the size of the internal blocks used in dump files.
A file size of 0 is equivalent to the maximum file size of 16 TB.
The minimum size for a file is ten times the default Data Pump block size, which is 4 kilobytes.
The maximum size for a file is 16 terabytes.
Export> FILESIZE=100MB
Provides information about Data Pump Export commands available in interactive-command mode.
HELP
Displays information about the commands available in interactive-command mode.
Export> HELP
Detaches all currently attached client sessions and then terminates the current job. It exits Export and returns to the terminal prompt.
KILL_JOB
A job that is terminated using KILL_JOB cannot be restarted. All attached clients, including the one issuing the KILL_JOB command, receive a warning that the job is being terminated by the current user and are then detached. After all clients are detached, the job's process structure is immediately run down and the master table and dump files are deleted. Log files are not deleted.
Export> KILL_JOB
Enables you to increase or decrease the number of active processes (worker and parallel slaves) for the current job.
PARALLEL=integer
PARALLEL is available as both a command-line parameter and as an interactive-command mode parameter. (It is only available in Enterprise Edition.) You set it to the desired number of parallel processes (worker and parallel slaves). An increase takes effect immediately if there are sufficient files and resources. A decrease does not take effect until an existing process finishes its current task. If the value is decreased, then workers are idled but not deleted until the job exits.
See Also:
"PARALLEL" for more information about parallelismExport> PARALLEL=10
Starts the current job to which you are attached.
START_JOB
The START_JOB command restarts the current job to which you are attached (the job cannot be currently executing). The job is restarted with no data loss or corruption after an unexpected failure or after you issued a STOP_JOB command, provided the dump file set and master table have not been altered in any way.
Transportable-tablespace-mode exports are not restartable.
Export> START_JOB
Displays cumulative status of the job, along with a description of the current operation. An estimated completion percentage for the job is also returned. Also allows resetting the display interval for logging mode status.
STATUS[=integer]
You have the option of specifying how frequently, in seconds, this status should be displayed in logging mode. If no value is entered or if the default value of 0 is used, then the periodic status display is turned off and status is displayed only once.
This status information is written only to your standard output device, not to the log file (even if one is in effect).
The following example will display the current job status and change the logging mode display interval to five minutes (300 seconds):
Export> STATUS=300
Stops the current job either immediately or after an orderly shutdown, and exits Export.
STOP_JOB[=IMMEDIATE]
If the master table and dump file set are not disturbed when or after the STOP_JOB command is issued, then the job can be attached to and restarted at a later time with the START_JOB command.
To perform an orderly shutdown, use STOP_JOB (without any associated value). A warning requiring confirmation will be issued. An orderly shutdown stops the job after worker processes have finished their current tasks.
To perform an immediate shutdown, specify STOP_JOB=IMMEDIATE. A warning requiring confirmation will be issued. All attached clients, including the one issuing the STOP_JOB command, receive a warning that the job is being stopped by the current user and they will be detached. After all clients are detached, the process structure of the job is immediately run down. That is, the master process will not wait for the worker processes to finish their current tasks. There is no risk of corruption or data loss when you specify STOP_JOB=IMMEDIATE. However, some tasks that were incomplete at the time of shutdown may have to be redone at restart time.
Export> STOP_JOB=IMMEDIATE
This section provides the following examples of using Data Pump Export:
For information that will help you to successfully use these examples, see "Using the Export Parameter Examples".
Example 2-1 shows a table-mode export, specified using the TABLES parameter. Issue the following Data Pump export command to perform a table export of the tables employees and jobs from the human resources (hr) schema:
Example 2-1 Performing a Table-Mode Export
expdp hr TABLES=employees,jobs DUMPFILE=dpump_dir1:table.dmp NOLOGFILE=y
Because user hr is exporting tables in his own schema, it is not necessary to specify the schema name for the tables. The NOLOGFILE=y parameter indicates that an Export log file of the operation will not be generated.
Example 2-2 shows the contents of a parameter file (exp.par) that you could use to perform a data-only unload of all tables in the human resources (hr) schema except for the tables countries and regions. Rows in the employees table are unloaded that have a department_id other than 50. The rows are ordered by employee_id.
Example 2-2 Data-Only Unload of Selected Tables and Rows
DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1
DUMPFILE=dataonly.dmp
CONTENT=DATA_ONLY
EXCLUDE=TABLE:"IN ('COUNTRIES', 'REGIONS')"
QUERY=employees:"WHERE department_id !=50 ORDER BY employee_id"
You can issue the following command to execute the exp.par parameter file:
> expdp hr PARFILE=exp.par
A schema-mode export (the default mode) is performed, but the CONTENT parameter effectively limits the export to an unload of just the table's data. The DBA previously created the directory object dpump_dir1 which points to the directory on the server where user hr is authorized to read and write export dump files. The dump file dataonly.dmp is created in dpump_dir1.
Example 2-3 shows the use of the ESTIMATE_ONLY parameter to estimate the space that would be consumed in a table-mode export, without actually performing the export operation. Issue the following command to use the BLOCKS method to estimate the number of bytes required to export the data in the following three tables located in the human resource (hr) schema: employees, departments, and locations.
Example 2-3 Estimating Disk Space Needed in a Table-Mode Export
> expdp hr DIRECTORY=dpump_dir1 ESTIMATE_ONLY=y TABLES=employees, departments, locations LOGFILE=estimate.log
The estimate is printed in the log file and displayed on the client's standard output device. The estimate is for table row data only; it does not include metadata.
Example 2-4 shows a schema-mode export of the hr schema. In a schema-mode export, only objects belonging to the corresponding schemas are unloaded. Because schema mode is the default mode, it is not necessary to specify the SCHEMAS parameter on the command line, unless you are specifying more than one schema or a schema other than your own.
Example 2-5 shows a full database Export that will have up to 3 parallel processes (worker or PQ slaves).
Example 2-5 Parallel Full Export
> expdp hr FULL=y DUMPFILE=dpump_dir1:full1%U.dmp, dpump_dir2:full2%U.dmp FILESIZE=2G PARALLEL=3 LOGFILE=dpump_dir1:expfull.log JOB_NAME=expfull
Because this is a full database export, all data and metadata in the database will be exported. Dump files full101.dmp, full201.dmp, full102.dmp, and so on will be created in a round-robin fashion in the directories pointed to by the dpump_dir1 and dpump_dir2 directory objects. For best performance, these should be on separate I/O channels. Each file will be up to 2 gigabytes in size, as necessary. Initially, up to three files will be created. More files will be created, if needed. The job and master table will have a name of expfull. The log file will be written to expfull.log in the dpump_dir1 directory.
To start this example, reexecute the parallel full export in Example 2-5. While the export is running, press Ctrl+C. This will start the interactive-command interface of Data Pump Export. In the interactive interface, logging to the terminal stops and the Export prompt is displayed.
Example 2-6 Stopping and Reattaching to a Job
At the Export prompt, issue the following command to stop the job:
Export> STOP_JOB=IMMEDIATE Are you sure you wish to stop this job ([y]/n): y
The job is placed in a stopped state and exits the client.
Enter the following command to reattach to the job you just stopped:
> expdp hr ATTACH=EXPFULL
After the job status is displayed, you can issue the CONTINUE_CLIENT command to resume logging mode and restart the expfull job.
Export> CONTINUE_CLIENT
A message is displayed that the job has been reopened, and processing status is output to the client.
This section provides syntax diagrams for Data Pump Export. These diagrams use standard SQL syntax notation. For more information about SQL syntax notation, see Oracle Database SQL Language Reference.