| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E17118-04 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E17118-04 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
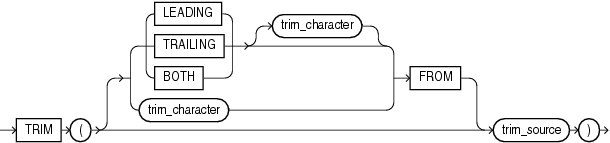
TRIM enables you to trim leading or trailing characters (or both) from a character string. If trim_character or trim_source is a character literal, then you must enclose it in single quotation marks.
If you specify LEADING, then Oracle Database removes any leading characters equal to trim_character.
If you specify TRAILING, then Oracle removes any trailing characters equal to trim_character.
If you specify BOTH or none of the three, then Oracle removes leading and trailing characters equal to trim_character.
If you do not specify trim_character, then the default value is a blank space.
If you specify only trim_source, then Oracle removes leading and trailing blank spaces.
The function returns a value with data type VARCHAR2. The maximum length of the value is the length of trim_source.
If either trim_source or trim_character is null, then the TRIM function returns null.
Both trim_character and trim_source can be VARCHAR2 or any data type that can be implicitly converted to VARCHAR2. The string returned is a VARCHAR2 (NVARCHAR2) data type if trim_source is a CHAR or VARCHAR2 (NCHAR or NVARCHAR2) data type, and a CLOB if trim_source is a CLOB data type. The return string is in the same character set as trim_source.
This example trims leading zeros from the hire date of the employees in the hr schema:
SELECT employee_id,
TO_CHAR(TRIM(LEADING 0 FROM hire_date))
FROM employees
WHERE department_id = 60
ORDER BY employee_id;
EMPLOYEE_ID TO_CHAR(T
----------- ---------
103 20-MAY-08
104 21-MAY-07
105 25-JUN-05
106 5-FEB-06
107 7-FEB-07