| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E17118-04 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E17118-04 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
Use the CREATE SPFILE statement to create a server parameter file either from a traditional plain-text initialization parameter file or from the current system-wide settings. Server parameter files are binary files that exist only on the server and are called from client locations to start up the database.
Server parameter files let you make persistent changes to individual parameters. When you use a server parameter file, you can specify in an ALTER SYSTEM SET parameter statement that the new parameter value should be persistent. This means that the new value applies not only in the current instance, but also to any instances that are started up subsequently. Traditional plain-text parameter files do not let you make persistent changes to parameter values.
Server parameter files are located on the server, so they allow for automatic database tuning by Oracle Database and for backup by Recovery Manager (RMAN).
To use a server parameter file when starting up the database, you must create it using the CREATE SPFILE statement.
All instances in an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment must use the same server parameter file. However, when otherwise permitted, individual instances can have different settings of the same parameter within this one file. Instance-specific parameter definitions are specified as SID.parameter = value, where SID is the instance identifier.
The method of starting up the database with a server parameter file depends on whether you create a default or nondefault server parameter file. Refer to "Creating a Server Parameter File: Examples" for examples of how to use server parameter files.
See Also:
CREATE PFILE for information on creating a regular text parameter file from a binary server parameter file
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for information on traditional plain-text initialization parameter files and server parameter files
Oracle Real Application Clusters Administration and Deployment Guide for information on using server parameter files in an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment
You must have the SYSDBA or the SYSOPER system privilege to execute this statement. You can execute this statement before or after instance startup. However, if you have already started an instance using spfile_name, you cannot specify the same spfile_name in this statement.
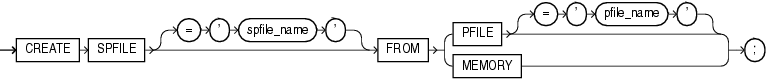
This clause lets you specify a name for the server parameter file you are creating.
If you do not specify spfile_name, then Oracle Database uses the platform-specific default server parameter filename. If spfile_name already exists on the server, then this statement will overwrite it. When using a default server parameter file, you start up the database without referring to the file by name.
If you do specify spfile_name, then you are creating a nondefault server parameter file. In this case, to start up the database, you must first create a single-line traditional parameter file that points to the server parameter file, and then name the single-line file in your STARTUP command.
The spfile_name can be either a traditional filename or an Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) filename. By using the Oracle ASM filename syntax, you can create the spfile in an Oracle ASM disk group. For an Oracle ASM instance, creation of the single-line traditional parameter file to start up the database is not required.
spfile_name can include a path prefix. If you do not specify such a path prefix, then the database adds the path prefix for the default storage location, which is platform dependent.
See Also:
"Creating a Server Parameter File: Examples" for information on starting up the database with default and nondefault server parameter files
file_specification for the syntax of traditional and Oracle ASM filenames and ALTER DISKGROUP for information on modifying the characteristics of an Oracle ASM file
The appropriate operating-system-specific documentation for default parameter file names
Specify the traditional plain-text initialization parameter file from which you want to create a server parameter file. The traditional parameter file must reside on the server.
If you specify pfile_name and the traditional parameter file does not reside in the default directory for parameter files on your operating system, then you must specify the full path.
If you do not specify pfile_name, then Oracle Database looks in the default directory for parameter files on your operating system for the default parameter filename and uses that file. If that file does not exist in the expected directory, then the database returns an error.
Note:
In an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment, you must first combine all instance parameter files into one file before specifying that filename in this statement to create a server parameter file. For information on accomplishing this step, see Oracle Real Application Clusters Administration and Deployment Guide.Specify MEMORY to create an spfile using the current system-wide parameter settings. In an Oracle RAC environment, the created file will contain the parameter settings from each instance.
Creating a Server Parameter File: Examples The following example creates a default server parameter file from a traditional plain-text parameter file named t_init1.ora:
CREATE SPFILE FROM PFILE = '$ORACLE_HOME/work/t_init1.ora';
Note:
Typically you will need to specify the full path and filename for parameter files on your operating system.When you create a default server parameter file, you subsequently start up the database using that server parameter file by using the SQL*Plus command STARTUP without the PFILE parameter, as follows:
STARTUP
The following example creates a nondefault server parameter file s_params.ora from a traditional plain-text parameter file named t_init1.ora:
CREATE SPFILE = 's_params.ora' FROM PFILE = '$ORACLE_HOME/work/t_init1.ora';
When you create a nondefault server parameter file, you subsequently start up the database by first creating a traditional parameter file containing the following single line:
spfile = 's_params.ora'
The name of this parameter file must comply with the naming conventions of your operating system. You then use the single-line parameter file in the STARTUP command. The following example shows how to start up the database, assuming that the single-line parameter file is named new_param.ora:
STARTUP PFILE=new_param.ora