39 Creating and Removing PDBs with Cloud Control
This chapter explains how you can create, clone, unplug, and remove pluggable databases (PDBs) in a multitenant container database (CDB) using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control (Cloud Control).
In particular, this chapter covers the following topics:
Getting Started
This section helps you get started with this chapter by providing an overview of the steps involved in creating a new PDB, cloning a PDB, migrating a non-CDB as a PDB, unplugging a PDB, and deleting PDBs. Consider this section to be a documentation map to understand the sequence of actions you must perform to successfully perform these tasks using Cloud Control. Click the reference links provided against the steps to reach the relevant sections that provide more information.
Table 39-1 Getting Started with PDBs
| Step | Description | Reference Links |
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
Obtaining an Overview Obtain a conceptual overview of PDBs. |
To obtain a conceptual overview of PDBs, see "Overview". For detailed conceptual information, see "Overview of Managing a Multitenant Environment" and Oracle Database Concepts |
|
Step 2 |
Selecting the Use Case Among the following use cases, select the one that best matches your requirement:
|
|
|
Step 3 |
Meeting the Prerequisites Meet the prerequisites for the selected use case. |
|
|
Step 4 |
Following the Procedure Follow the procedure for the selected use case. |
|
Overview
An Oracle Database can contain a portable collection of schemas, schema objects, and nonschema objects, that appear to an Oracle Net client as a separate database. This self-contained collection is called a PDB. A CDB can include one or more PDBs. Oracle Database 12c allows you to create many PDBs within a single CDB. Applications that connect to databases view PDBs and earlier versions of Oracle Database in the same manner.
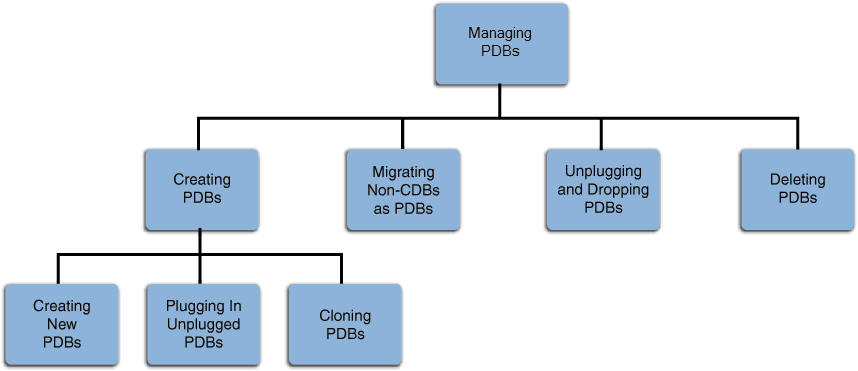
Cloud Control enables administrators to manage the entire PDB lifecycle, including provisioning CDBs, provisioning PDBs (from the seed or from an unplugged PDB), cloning existing PDBs, migrating non-CDBs as PDBs, unplugging PDBs, and deleting PDBs.
Important:
To manage the PDB lifecycle using Cloud Control, you must have the 12.1.0.3 Enterprise Manager for Oracle Database plug-in, or a later version, deployed. To delete PDBs using Cloud Control, you must have the 12.1.0.5 Enterprise Manager for Oracle Database plug-in deployed.For information on how to deploy a plug-in and upgrade an existing plug-in, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Administrator's Guide.
Figure 39-1 provides a graphical overview of how you can manage the PDB lifecycle in Cloud Control.
Provisioning a PDB
You can provision PDBs by creating a new PDB within a CDB, by cloning an existing PDB, or by migrating existing non-CDBs to a CDB as PDBs. You can also use unplugged PDBs for provisioning, by plugging them into a CDB.
This section provides information about provisioning a PDB. In particular, it contains the following topics:
Note:
As an alternative to using the methods described in this section, you can use Enterprise Manager Command Line Interface (EM CLI) to provision PDBs. For more information, see Oracle® Enterprise Manager Lifecycle Management Administrator's Guide.Creating a New PDB
This section provides information about creating a new PDB. In particular, it contains the following topics:
Prerequisites
-
Oracle Software Library (Software Library) must be set up in Cloud Control.
For information on how to set up Software Library in Cloud Control, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Lifecycle Management Administrator's Guide.
-
The CDB within which you want to create a PDB must exist, and must be a Cloud Control target.
-
The CDB (within which you want to create a PDB) must be in read/write mode.
-
The target host user must be the owner of the Oracle Home that the CDB (within which you want to create the PDB) belongs to.
Procedure
To create a new PDB in a CDB, follow these steps:
-
From the Enterprise menu, select Provisioning and Patching, then select Database Provisioning. In the Database Provisioning page, in the Related Links section of the left menu pane, click Provision Pluggable Databases.
Note:
You can also access the Provision Pluggable Database Console from the Home page of the CDB. To do so, in the CDB's Home page, from the Oracle Database menu, select Provisioning, then select Provision Pluggable Database. -
In the Provision Pluggable Database Console, in the Container Database section, select the CDB within which you want to create new PDBs.
Note:
Skip this step if you have accessed the Provision Pluggable Database Console from the CDB's Home page. -
In the PDB Operations section, select Create New Pluggable Databases.
-
Click Launch.
Note:
You will be prompted to log in to the database if you have not already logged in to it through Enterprise Manager. Make sure you log in usingSYSDBAuser account credentials. -
In the Creation Options page of the Create Pluggable Database Wizard, in the Pluggable Database Creation Options section, select Create a New PDB.
-
In the Container Database Host Credentials section, select or specify the target CDB Oracle Home owner host credentials. If you have already registered the credentials with Enterprise Manager, then you can select Preferred or Named. Otherwise, you can select New and enter the credentials.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Identification page, enter a unique name for the PDB you are creating.
If you prefer to create more than one PDB in this procedure, then select Create Multiple Copies, and set the number of PDBs you want to create. Note that you can create a maximum of 252 PDBs.
Note:
If you choose to create multiple PDBs, then the unique name you enter here is used as a prefix for all PDBs, and the suffix is a numeric value that indicates the count of PDBs.For example, if you create five PDBs with the name
accountsPDB,then the PDBs are created with the namesaccountsPDB1, accountsPDB2, accountsPDB3, accountsPDB4,andaccountsPDB5. -
In the PDB Administrator section, enter the credentials of the admin user account you need to create for administering the PDB.
Note:
If you choose to create multiple PDBs, then an admin user account is created for each PDB that you create, with the same set of the specified credentials. -
Click Next.
-
In the Storage page, in the PDB Datafile Locations section, select the type of location where you want to store the datafiles.
-
If the target CDB (CDB in which you are creating the PDB) is enabled with Oracle Managed Files and if you want to use the same, then select Use Oracle Managed Files (OMF).
-
If you want to enter a custom location, then select Use Common Location for PDB Datafiles. Select the storage type and the location where the datafiles can be stored.
-
-
In the Temporary Working Directory section, enter a location where the temporary files generated during the PDB creation process can be stored.
-
In the Post-Creation Scripts section, select a custom SQL script you want to run as part of this procedure, once the PDB is created.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Schedule page, enter a unique deployment procedure instance name and a schedule for the deployment. The instance name you enter here helps you identify and track the progress of this procedure on the Procedure Activity page.
If you want to run the procedure immediately, then retain the default selection, that is, Immediately. Otherwise, select Later and provide time zone, start date, and start time details.
You can optionally set a grace period for this schedule. A grace period is a period of time that defines the maximum permissible delay when attempting to run a scheduled procedure. If the procedure does not start within the grace period you have set, then the procedure skips running. To set a grace period, select Grace Period, and set the permissible delay time.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Review page, review the details you have provided for the deployment procedure. If you are satisfied with the details, click Submit.
If you want to modify the details, then click Back repeatedly to reach the page where you want to make the changes.
-
In the Procedure Activity page, view the status of the procedure. From the Procedure Actions menu, you can select Debug to set the logging level to Debug, and select Stop to stop the procedure execution.
When you create a new PDB, the Enterprise Manager job system creates a Create Pluggable Database job. For information about viewing the details of this job, refer "Viewing Create PDB Job Details".
Plugging In an Unplugged PDB
This section provides information about plugging an unplugged PDB into a CDB. In particular, it contains the following topics:
Prerequisites
Before plugging an unplugged PDB, ensure that you meet the following prerequisites:
-
Oracle Software Library (Software Library) must be set up in Cloud Control.
For information on how to set up Software Library in Cloud Control, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Lifecycle Management Administrator's Guide.
-
The target CDB (the CDB within which you want to plug in the unplugged PDB) must exist, and must be a Cloud Control target.
-
The target CDB must be in read/write mode.
-
The XML file that describes the unplugged PDB, and the other files associated with the unplugged PDB, such as the data files, must exist and must be readable.
-
The target host user must be the owner of the Oracle Home that the CDB (into which you want to plug the unplugged PDB) belongs to.
-
The platforms of the source CDB host (the host on which the CDB that previously contained the unplugged PDB is installed) and the target CDB host (the host on which the target CDB is installed) must have the same endianness, and must have the same set of database options installed.
-
The CDB that contained the unplugged PDB and the target CDB must have compatible character sets and national character sets. To be compatible, the character sets and national character sets must meet all of the requirements specified in Oracle Database Globalization Support Guide.
Procedure
To plug an unplugged PDB into a CDB, follow these steps:
-
From the Enterprise menu, select Provisioning and Patching, then select Database Provisioning. In the Database Provisioning page, in the Related Links section of the left menu pane, click Provision Pluggable Databases.
Note:
You can also access the Provision Pluggable Database Console from the Home page of the CDB. To do so, in the CDB's Home page, from the Oracle Database menu, select Provisioning, then select Provision Pluggable Database. -
In the Provision Pluggable Database Console, in the Container Database section, select the CDB to which you want to add the unplugged PDBs.
Note:
Skip this step if you have accessed the Provision Pluggable Database Console from the CDB's Home page. -
In the PDB Operations section, select Create New Pluggable Databases.
-
Click Launch.
Note:
You will be prompted to log in to the database if you have not already logged in to it through Enterprise Manager. Make sure you log in usingSYSDBAuser account credentials. -
In the Creation Options page of the Create Pluggable Database Wizard, in the Pluggable Database Creation Options section, select Plug an Unplugged PDB.
-
In the Container Database Host Credentials section, select or specify the target CDB Oracle Home owner host credentials. If you have already registered the credentials with Enterprise Manager, then you can select Preferred or Named. Otherwise, you can select New and enter the credentials.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Identification page, enter a unique name for the PDB you are plugging in.
Select Create As Clone if you are plugging a PDB into a CDB that contains one or more PDBs that were created by plugging in the same PDB. Selecting this option ensures that Oracle Database generates unique PDB DBID, GUID, and other identifiers expected for the new PDB.
If you prefer to create more than one PDB in this procedure, then select Create Multiple Copies, and set the number of PDBs you want to create. Note that you can create a maximum of 252 PDBs.
Note:
If you choose to create multiple PDBs, then the unique name you enter here is used as a prefix for all PDBs, and the suffix is a numeric value that indicates the count of PDBs.For example, if you create five PDBs with the name
accountsPDB,then the PDBs are created with the namesaccountsPDB1, accountsPDB2, accountsPDB3, accountsPDB4,andaccountsPDB5. -
In the PDB Administrator section, do one of the following to administer the PDB:
-
If you prefer to use the admin user account that was created as part of the source PDB that you are plugging in, then deselect Create PDB Administrator.
-
If you want to create a brand new admin user account for the PDB you are plugging in, then select Create PDB Administrator, and enter the desired credentials.
Note:
If you choose to create multiple PDBs, then an admin user account is created for each PDB that you create, with the same set of the specified credentials.To lock and expire all the users in the newly created PDB, (except the newly created Admin), select Lock All Existing PDB Users.
-
-
In the PDB Template Location section, select the location where the source PDB's template is available, and then select the type of PDB template.
-
If the PDB template is available on your CDB host (CDB to which you are plugging in the unplugged PDB), then select Target Host File System.
-
If the PDB template is a single archive file—a TAR file with data files and metadata XML file included in it, then select Create Pluggable Database from Pluggable Database Archive, then select the PDB template.
-
If the PDB template is a PDB file set—a separate DFB file with all the data files and a separate metadata XML file, then select Create the PDB using PDB File Set, then select the DBF and XML files.
-
If you want to plug in a PDB using the PDB metadata XML file and the existing data files, then select Create PDB using Metadata file.
-
-
If the PDB template is available in Oracle Software Library (Software Library), then select Software Library, then select the component in the Software Library that contains the PDB template.
-
-
Click Next.
-
In the Storage page, do one of the following:
-
In the previous page, if you chose to create the PDB from a PDB archive (single TAR file) or using a PDB file set (DFB file and an XML file), then select the type of location where you want to store the target data files for the PDB you are plugging in.
-
If the target CDB (CDB to which you are plugging in the unplugged PDB) is enabled with Oracle Managed Files and if you want to use the same, then select Use Oracle Managed Files (OMF).
-
If you want to enter a common custom location, then select Use Common Location for PDB datafiles. Select the storage type and the location where the data files can be stored.
-
-
In the previous page, if you chose to create the PDB using a PDB template (XML file only), then do the following:
In the PDB Datafile Locations section, validate the locations mapped for the data files. If they are incorrect, correct the paths. Alternatively, if you have a single location where the data files are all available, then enter the absolute path in the Set Common Source File Mapping Location field, and click Set.
You can choose to store the target data files for the PDB you are plugging in, in the same location as the source data files. However, if you want the target data files to be stored in a different location, then select Copy Datafiles, and select the type of location:
-
If the target CDB (CDB to which you are plugging in the unplugged PDB) is enabled with Oracle Managed Files and if you want to use the same, then select Use Oracle Managed Files (OMF).
-
If you want to enter a common custom location, then select Use Common Location for Pluggable Database Files. Select the storage type and the location where the data files can be stored.
-
If you prefer to use different custom locations for different data files, then select Customized Location, and enter the custom location paths.
-
-
-
In the Temporary Working Directory section, enter a location where the temporary files generated during the PDB creation process can be stored.
-
In the Post-Creation Scripts section, select a custom SQL script you want to run as part of this procedure, once the PDB is plugged in.
If the script is available in the Software Library, select Select from Software Library, then select the component that contains the custom script.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Schedule page, enter a unique deployment procedure instance name and a schedule for the deployment. The instance name you enter here helps you identify and track the progress of this procedure on the Procedure Activity page.
If you want to run the procedure immediately, then retain the default selection, that is, Immediately. Otherwise, select Later and provide time zone, start date, and start time details.
You can optionally set a grace period for this schedule. A grace period is a period of time that defines the maximum permissible delay when attempting to run a scheduled procedure. If the procedure does not start within the grace period you have set, then the procedure skips running. To set a grace period, select Grace Period, then set the permissible delay time.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Review page, review the details you have provided for the deployment procedure. If you are satisfied with the details, click Submit.
If you want to modify the details, then click Back repeatedly to reach the page where you want to make the changes.
-
In the Procedure Activity page, view the status of the procedure. From the Procedure Actions menu, you can select Debug to set the logging level to Debug, and select Stop to stop the procedure execution.
When you plug in an unplugged PDB, the Enterprise Manager job system creates a Create Pluggable Database job. For information about viewing the details of this job, refer "Viewing Create PDB Job Details".
Cloning a PDB
You can clone a PDB using either the Full Clone method, or the Snap Clone method. This section provides information about cloning a PDB using these methods. In particular, it contains the following topics:
Prerequisites
To clone a PDB, you must meet the following prerequisites:
-
Oracle Software Library (Software Library) must be set up in Cloud Control.
For information on how to set up Software Library in Cloud Control, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Lifecycle Management Administrator's Guide.
-
The source PDB (the PDB that you want to clone) must exist, and must be a Cloud Control target.
Note:
For information on how to create a new PDB, refer to "Creating a New PDB". -
The source PDB must be open.
-
The target CDB (the CDB into which you want to plug in the cloned PDB) must exist, and must be a Cloud Control target.
-
The target CDB must be in read/write mode.
-
The target host user must be the owner of the Oracle Home that the source CDB belongs to.
To clone a PDB using the Snap Clone method, you must meet the following additional prerequisites:
-
The 12.1.0.5 Enterprise Manager for Oracle Database plug-in must be downloaded and deployed. Also, the 12.1.0.3 SMF plug-in or higher must be downloaded and deployed.
-
The PDB that you want to clone must reside on a registered storage server. This storage server must be synchronized.
For information on how to register a storage server and synchronize storage servers, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Administration Guide.
-
All the datafiles of the PDB that you want to clone must reside on the storage volumes of the storage server, and not on the local disk.
-
Metric collections must be run on the source CDB (the CDB containing the PDB that you want to clone), the source CDB host, and the PDB that you want to clone.
-
The Snap Clone feature must be enabled for the PDB that you want to clone.
For information on how to enable the Snap Clone feature, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Administration Guide.
Procedure
To clone an existing PDB, follow these steps:
Important:
If you use the Full Clone method to clone a PDB, you can clone the PDB only to the source CDB (the CDB containing the PDB that you are cloning).-
From the Enterprise menu, select Provisioning and Patching, then select Database Provisioning. In the Database Provisioning page, in the Related Links section of the left menu pane, click Provision Pluggable Databases.
Note:
You can also access the Provision Pluggable Database Console from the Home page of the CDB. To do so, in the CDB's Home page, from the Oracle Database menu, select Provisioning, then select Provision Pluggable Database. -
In the Provision Pluggable Database Console, in the CDB section, select the source CDB, that is, the CDB containing the PDB that you want to clone.
Note:
Skip this step if you have accessed the Provision Pluggable Database Console from the CDB's Home page. -
In the PDB Operations section, select Create New Pluggable Databases.
-
Click Launch.
Note:
You will be prompted to log in to the database if you have not already logged in to it through Enterprise Manager. Make sure you log in usingSYSDBAuser account credentials. -
In the Creation Options page of the Create Pluggable Database Wizard, in the PDB Creation Options section, select Clone an Existing PDB.
To clone a PDB using the traditional method of cloning the PDB datafiles, select Full Clone. Use this method if you want to clone a PDB for long term usage. This method is ideal for load testing, when you plan to make significant data updates to the PDB clone. However, this method takes a longer period of time, and a clone that is created using this method occupies a fairly large amount of space, as compared to the Snap Clone method.
To clone a PDB using the Storage Management Framework (SMF) Snap Clone feature, select Snap Clone. Use this method if you want to clone a PDB for short term purposes. This method is ideal for functional testing, as the cloning process is quick, and a PDB clone that is created using this method occupies very little space. However, this method is not suitable if you plan to make significant data updates to the PDB clone.
For Source PDB, select the PDB that you want to clone.
-
In the CDB Host Credentials section, select or specify the source CDB Oracle Home owner host credentials. If you have already registered the credentials with Enterprise Manager, you can select Preferred or Named. Otherwise, you can select New and enter the credentials.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Identification page, enter a unique name for the PDB you are cloning.
If you prefer to create more than one PDB in this procedure, then select Create Multiple Copies, and set the number of PDBs you want to create. Note that you can create a maximum of 252 PDBs.
Note:
If you choose to create multiple PDBs, then the unique name you enter here is used as a prefix for all the cloned PDBs, and the suffix is a numeric value that indicates the count of PDBs.For example, if you create five PDBs with the name
accountsPDB,then the PDBs are created with the namesaccountsPDB1, accountsPDB2, accountsPDB3, accountsPDB4,andaccountsPDB5. -
In the PDB Administrator section, do one of the following to administer the PDB:
-
If you prefer to use the admin user account that was created as part of the source PDB that you are cloning, then deselect Create PDB Administrator.
-
If you want to create a brand new admin user account for the PDB you are cloning, then select Create PDB Administrator, and enter the desired credentials.
Note:
If you choose to create multiple PDBs, then an admin user account is created for each PDB that you create, with the same set of the specified credentials. -
-
In the Source CDB Login Credentials section, select or specify the login credentials of the source CDB. If you have already registered the credentials with Enterprise Manager, you can select Preferred or Named. Otherwise, you can select New and enter the credentials.
The credentials are used to bring the source PDB to read-only mode before the cloning operation begins, and to restore it to the original state after the cloning operation ends.
If you chose the Snap Clone method (on the Source page of the Create Pluggable Database Wizard) to clone the PDB, specify the host credentials for the source CDB.
Note:
If you are cloning the source PDB to the source CDB itself, then the Source CDB Login Credentials section is not displayed, that is, you do not need to provide the source CDB login credentials or the source CDB host credentials.If you are cloning the source PDB to a CDB different from the source CDB, and this CDB resides on the source CDB host, then you must provide the source CDB login credentials. You do not need to provide the source CDB host credentials.
If you are cloning the source PDB to a CDB different from the source CDB, and this CDB resides on a host different from the source CDB host, then you must provide the source CDB login credentials and the source CDB host credentials.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Storage page, specify the storage information.
If you chose the Full Clone method to clone the PDB, select the type of location where you want to store the PDB datafiles in the following manner:
-
If the source CDB is enabled with Oracle Managed Files and if you want to use the same, then select Use Oracle Managed Files (OMF).
-
If you want to enter a custom location, then select Use Common Location for PDB datafiles. Select the storage type and the location where the datafiles can be stored.
If you chose the Snap Clone method to clone the PDB, do the following:
-
In the PDB Datafile Locations section, specify a value for Mount Point Prefix, that is, the mount location for the storage volumes. You can choose to specify the same prefix for all the volumes, or a different prefix for each volume. Also, specify a value for Writable Space, that is, the space that you want to allocate for writing the changes made to the PDB clone. You can choose to specify the same writable space value for all the volumes, or a different value for each volume.
-
In the Privileged Host Credentials section, select or specify the credentials of the root user. These credentials are used for mounting the cloned volumes on the destination host.
If you have already registered the credentials with Enterprise Manager, you can select Preferred or Named. Otherwise, you can select New and enter the credentials.
-
-
In the Temporary Working Directory section, enter a location where the temporary files generated during the PDB creation process can be stored.
-
In the Post-Creation Scripts section, select a custom SQL script you want to run as part of this procedure, once the PDB is cloned.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Schedule page, enter a unique deployment procedure instance name and a schedule for the deployment. The instance name you enter here helps you identify and track the progress of this procedure on the Procedure Activity page.
If you want to run the procedure immediately, then retain the default selection, that is, Immediately. Otherwise, select Later and provide time zone, start date, and start time details.
You can optionally set a grace period for this schedule. A grace period is a period of time that defines the maximum permissible delay when attempting to run a scheduled procedure. If the procedure does not start within the grace period you have set, then the procedure skips running. To set a grace period, select Grace Period, and set the permissible delay time.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Review page, review the details you have provided for the deployment procedure. If you are satisfied with the details, click Submit.
If you want to modify the details, then click Back repeatedly to reach the page where you want to make the changes.
-
In the Procedure Activity page, view the status of the procedure. From the Procedure Actions menu, you can select Debug to set the logging level to Debug, and select Stop to stop the procedure execution.
When you clone a PDB, the Enterprise Manager job system creates a Create Pluggable Database job. For information about viewing the details of this job, refer "Viewing Create PDB Job Details".
Migrating a Non-CDB to a PDB
This section provides information about migrating a non-CDB to a PDB. In particular, it contains the following topics:
Prerequisites
Before migrating a non-CDB to a PDB, ensure that you meet the following prerequisites:
-
Oracle Software Library (Software Library) must be set up in Cloud Control.
For information on how to set up Software Library in Cloud Control, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Lifecycle Management Administrator's Guide.
-
The target CDB (the CDB to which you want to migrate a non-CDB to a PDB) must exist, and must be a Cloud Control target.
-
The target CDB must be in read/write mode.
-
The non-CDB that you want to migrate and the target CDB must be running in
ARCHIVELOGmode. -
The database administrators of the database you want to migrate and the target CDB must have
SYSDBAprivileges. -
The target host user must be the owner of the Oracle Home that the target CDB belongs to.
Procedure
To migrate a non-CDB to a PDB, follow these steps:
-
From the Enterprise menu, select Provisioning and Patching, then select Database Provisioning. In the Database Provisioning page, in the Related Links section of the left menu pane, click Provision Pluggable Databases.
Note:
You can also access the Provision Pluggable Database Console from the Home page of the CDB. To do so, in the CDB's Home page, from the Oracle Database menu, select Provisioning, then select Provision Pluggable Database. -
In the Provision Pluggable Database Console, in the Container Database section, select the CDB to which you want to migrate a non-CDB to a PDB.
Note:
Skip this step if you have accessed the Provision Pluggable Database Console from the CDB's Home page. -
In the PDB Operations section of the Provision Pluggable Database page, select the Migrate Existing Databases option and click Launch.
-
On the Database Login page, select the Credential Name from the drop-down list. Click Login.
-
On the Migrate Non-CDBs launch page, select a data migration method, that is, Export/Import or Plug as a PDB. If you select Plug as a PDB, ensure that the non-CDB that you want to migrate is open, and is in read-only mode.
Enter the appropriate credentials for the Oracle Home Credential section.
Click Next.
-
On the Database page, select a Non-CDB to be migrated. You can select more than one. Click Add. In the database pane, provide the appropriate credential, properties, export, import, and datafile location information. Click Next.
-
On the Schedule page, enter the appropriate job and scheduling details. Click Next.
-
On the Review page, review all details entered. If there are no changes required, click Submit.
Removing PDBs
This section provides information about unplugging PDBs and deleting PDBs. In particular, it contains the following topics:
Unplugging and Dropping a PDB
This section provides information about unplugging and dropping a PDB. In particular, it contains the following topics:
Note:
As an alternative to using the method described in this section, you can use Enterprise Manager Command Line Interface (EM CLI) to unplug and drop PDBs. For more information, see Oracle® Enterprise Manager Lifecycle Management Administrator's Guide.Prerequisites
Before unplugging and dropping a PDB, ensure that you meet the following prerequisites:
-
Oracle Software Library (Software Library) must be set up in Cloud Control.
For information on how to set up Software Library in Cloud Control, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Lifecycle Management Administrator's Guide.
-
The PDB that you want to unplug and drop must have been opened at least once.
-
The target host user must be the owner of the Oracle Home that the CDB (containing the PDB that you want to unplug and drop) belongs to.
Procedure
To unplug a PDB from its CDB, follow these steps:
-
From the Enterprise menu, select Provisioning and Patching, then select Database Provisioning. In the Database Provisioning page, in the Related Links section of the left menu pane, click Provision Pluggable Databases.
Note:
You can also access the Provision Pluggable Database Console from the Home page of the CDB. To do so, in the CDB's Home page, from the Oracle Database menu, select Provisioning, then select Provision Pluggable Database. -
In the Provision Pluggable Database Console, in the Container Database section, select the CDB from which you want to unplug the PDBs.
Note:
Skip this step if you have accessed the Provision Pluggable Database Console from the CDB's Home page. -
In the PDB Operations section, select Unplug Pluggable Database.
-
Click Launch.
Note:
You will be prompted to log in to the database if you have not already logged in to it through Enterprise Manager. Make sure you log in usingSYSDBAuser account credentials. -
In the Select PDB page of the Unplug Pluggable Database Wizard, in the Select Pluggable Database section, select the PDB you want to unplug. Note that the PDB once unplugged will be stopped and dropped.
-
In the Container Database Host Credentials section, select or specify the target CDB Oracle Home owner host credentials. If you have already registered the credentials with Enterprise Manager, you can select Preferred or Named. Otherwise, you can select New and enter the credentials.
-
In the Destination page, select the type of PDB template you want to generate for unplugging the PDB, and the location where you want to store it. The PDB template consists of all data files as well as the metadata XML file.
-
If you want to store the PDB template on your CDB host (CDB from which you are unplugging the PDB), then select Target Host File System.
-
If you want to generate a single archive file—a TAR file with the data files and the metadata XML file included in it, then select Generate PDB Archive. Select a location where the archive file can be created.
Note:
Oracle recommends that you select this option if the source and target CDBs are using file system for storage. This option is not supported for PDBs using ASM as storage. -
If you want to generate an archive file set—a separate DFB file with all the data files and a separate metadata XML file, then select Generate PDB File Set. Select the locations where the DBF and XML files can be created.
Note:
Oracle recommends that you select this option if the source and target CDBs are using ASM for storage. -
If you want to generate only a metadata XML file, leaving the data files in their current location, then select Generate PDB Metadata File. Select a location where the metadata XML file can be created.
-
-
If you want to store the PDB template in Oracle Software Library (Software Library), then select Software Library.
-
If you want to generate a single archive file—a TAR file with the data files and the metadata XML file included in it, then select Generate PDB Archive. If you want to generate an archive file set—a separate DFB file with all the data files and a separate metadata XML file, then select Generate PDB File Set. If you want to generate only a metadata XML file, leaving the data files in their current location, then select Generate PDB Metadata File.
-
Enter a unique PDB template name.
The template is created in the default location that has the following format:
Database Configuration/db_release/platform/Database TemplatesFor example,
Database Configuration/12.1.0.0.2/unix/Database Templates -
Enter a temporary location where the archive can be created by Enterprise Manager before it is uploaded to the Software Library.
-
-
-
In the Schedule page, enter a unique deployment procedure instance name and a schedule for the deployment. The instance name you enter here helps you identify and track the progress of this procedure on the Procedure Activity page.
If you want to run the procedure immediately, then retain the default selection, that is, Immediately. Otherwise, select Later and provide time zone, start date, and start time details.
You can optionally set a grace period for this schedule. A grace period is a period of time that defines the maximum permissible delay when attempting to run a scheduled procedure. If the procedure does not start within the grace period you have set, then the procedure skips running. To set a grace period, select Grace Period, and set the permissible delay time.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Review page, review the details you have provided for the deployment procedure. If you are satisfied with the details, click Submit.
If you want to modify the details, then click Back repeatedly to reach the page where you want to make the changes.
-
In the Procedure Activity page, view the status of the procedure. From the Procedure Actions menu, you can select Debug to set the logging level to Debug, and select Stop to stop the procedure execution.
When you unplug and drop a PDB, the Enterprise Manager job system creates an Unplug Pluggable Database job. For information about viewing the details of this job, refer "Viewing Unplug PDB Job Details".
Deleting PDBs
This section provides information about permanently deleting PDBs from a CDB. In particular, it contains the following topics:
Prerequisites
Before permanently deleting a set of PDBs from a CDB, ensure that you meet the following prerequisites:
-
The 12.1.0.5 Enterprise Manager for Oracle Database plug-in must be downloaded and deployed.
For information on how to download and deploy a plug-in, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Administrator's Guide.
-
Oracle Software Library (Software Library) must be set up in Cloud Control.
For information on how to set up Software Library in Cloud Control, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Lifecycle Management Administrator's Guide.
-
The PDBs that you want to delete must have been opened at least once.
-
The target host user must be the owner of the Oracle home that the CDB (containing the PDBs that you want to delete) belongs to.
Procedure
To permanently delete a set of PDBs from a CDB, follow these steps:
-
From the Enterprise menu, select Provisioning and Patching, then select Database Provisioning. In the Database Provisioning page, in the Related Links section of the left menu pane, click Provision Pluggable Databases.
Note:
You can also access the Provision Pluggable Database Console from the Home page of the CDB. To do so, in the CDB's Home page, from the Oracle Database menu, select Provisioning, then select Provision Pluggable Database. -
In the Provision Pluggable Database Console, in the CDB section, select the CDB from which you want to delete the PDBs.
Note:
Skip this step if you have accessed the Provision Pluggable Database Console from the CDB's home page. -
In the PDB Operations section, select Delete Pluggable Databases.
-
Click Launch.
Note:
You will be prompted to log in to the database if you have not already logged in to it through Enterprise Manager. Make sure you log in usingSYSDBAuser account credentials. -
In the Select PDBs page of the Delete Pluggable Databases Wizard, click Add. Select the PDBs that you want to delete, then click Select.
Note:
If you choose to delete a PDB that was created using the Snap Clone method, the PDB mount points on the CDB host are cleaned up. The corresponding storage volumes on the storage server are also deleted. This action is irreversible. -
In the CDB Host Credentials section, select or specify the target CDB Oracle Home owner host credentials. If you have already registered the credentials with Enterprise Manager, you can select Preferred or Named. Otherwise, you can select New and enter the credentials.
If one (or more) of the PDBs that you selected for deletion is the Snap Clone of another PDB, you must also provide the privileged host credentials, that is, the credentials of the root user. If you have already registered the credentials with Enterprise Manager, you can select Preferred or Named. Otherwise, you can select New and enter the credentials.
-
In the Schedule page, enter a unique deployment procedure instance name and a schedule for the deployment. The instance name you enter here helps you identify and track the progress of this procedure on the Procedure Activity page.
If you want to run the procedure immediately, then retain the default selection, that is, Immediately. Otherwise, select Later and provide time zone, start date, and start time details.
You can optionally set a grace period for this schedule. A grace period is a period of time that defines the maximum permissible delay when attempting to run a scheduled procedure. If the procedure does not start within the grace period you have set, then the procedure skips running. To set a grace period, select Grace Period, and set the permissible delay time.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Review page, review the details you have provided for the deployment procedure. If you are satisfied with the details, click Submit.
If you want to modify the details, then click Back repeatedly to reach the page where you want to make the changes.
-
In the Procedure Activity page, view the status of the procedure. From the Procedure Actions menu, you can select Debug to set the logging level to Debug, and select Stop to stop the procedure execution.
When you delete a PDB, the Enterprise Manager job system creates a Delete Pluggable Database job. For information about viewing the details of this job, refer "Viewing Delete PDB Job Details".
Viewing PDB Job Details
This section provides information about viewing the details of the jobs that are created by the Enterprise Manager job system when you create a PDB, unplug a PDB, or delete a PDB. It contains the following topics:
Viewing Create PDB Job Details
To view the details of a create PDB job, follow these steps:
-
From the Enterprise menu, select Provisioning and Patching, then select Procedure Activity.
-
Click the deployment procedure that contains the required create PDB job.
-
Expand the deployment procedure steps. Select the PDB creation job.
-
Click Job Summary.
-
To view a summary of the job details, click Summary.
In the Prepare Configuration Data step, the system prepares for PDB creation.
In the Check Prerequisites step, the system checks the prerequisites for PDB creation.
In the Verify and Prepare step, the system runs tasks prior to PDB creation.
In the Perform Configuration step, the PDB creation is performed. For details of the performed tasks and their status, refer to the remote log files present on the host.
In the Post Configuration step, Enterprise Manager is updated with the newly created PDB details, and the custom scripts are run.
-
To view a visual representation of the create PDB job progress, click Results.
In the Configuration Progress section, you can view the completion percentage of the job, and a list of pending, currently running, and completed job steps. You can also view errors, warnings, and logs. The tail of the log for the currently running job step is displayed.
Viewing Unplug PDB Job Details
To view the details of an unplug PDB job, follow these steps:
-
From the Enterprise menu, select Provisioning and Patching, then select Procedure Activity.
-
Click the deployment procedure that contains the required unplug PDB job.
-
Expand the deployment procedure steps. Select the unplug PDB job.
-
Click Job Summary.
-
To view a summary of the job details, click Summary.
In the Prepare Configuration Data step, the system prepares for unplugging a PDB.
In the Check Prerequisites step, the system checks the prerequisites for unplugging a PDB.
In the Verify and Prepare step, the system runs tasks prior to unplugging the PDB.
In the Perform Configuration step, the PDB unplugging is performed. For details of the performed tasks and their status, refer to the remote log files present on the host.
In the Post Configuration step, Enterprise Manager is updated with the unplugged PDB details.
-
To view a visual representation of the unplug PDB job progress, click Results.
In the Configuration Progress section, you can view the completion percentage of the job, and a list of pending, currently running, and completed job steps. You can also view errors, warnings, and logs. The tail of the log for the currently running job step is displayed.
Viewing Delete PDB Job Details
To view the details of a delete PDB job, follow these steps:
-
From the Enterprise menu, select Provisioning and Patching, then select Procedure Activity.
-
Click the deployment procedure that contains the required delete PDB job.
-
Expand the deployment procedure steps. Select the delete PDB job.
-
Click Job Summary.
-
To view a summary of the job details, click Summary.
In the Prepare Configuration Data step, the system prepares for deleting the PDBs.
In the Verify and Prepare step, the system runs tasks prior to deleting the PDBs.
In the Perform Configuration step, the PDB deletion is performed. For details of the performed tasks and their status, refer to the remote log files present on the host.
In the Post Configuration step, Enterprise Manager is updated with the deleted PDB details.
-
To view a visual representation of the delete PDB job progress, click Results.
In the Configuration Progress section, you can view the completion percentage of the job, and a list of pending, currently running, and completed job steps. You can also view errors, warnings, and logs. The tail of the log for the currently running job step is displayed.