13 Using the XML SQL Utility
This chapter explains how to use the Extensible Markup Language (XML) SQL Utility (XSU).
Introduction to the XML SQL Utility (XSU)
XML SQL Utility (XSU) is an Oracle XML Developer's Kit (XDK) component that enables you to transfer XML data through Oracle SQL statements. You can use XSU to perform these tasks:
-
Transform data in object-relational database tables or views into XML. XSU can query the database and return the result set as an XML document.
-
Extract data from an XML document and use canonical mapping to insert the data into a table or a view or update or delete values of the appropriate columns or attributes.
Prerequisites
This chapter assumes that you are familiar with these technologies:
-
Oracle Database structured query language (SQL). XSU transfers XML to and from a database through
SELECTstatements and data manipulation language (DML). -
Procedural Language/Structured Query Language (PL/SQL). XDK supplies a PL/SQL application programming interface (API) for XSU that mirrors the Java API.
-
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC). Java applications that use XSU to transfer XML to and from a database require a JDBC connection.
XSU Features
XSU has these key features:
-
Dynamically generates document type definitions (DTDs) or XML schemas.
-
Generates XML documents in their string or Document Object Model (DOM) representations.
-
Performs simple transformations during generation such as modifying default tag names for each
<ROW>element. You can also register an XSL transformation that XSU applies to the generated XML documents as needed. -
Generates XML as a stream of Simple API for XML (SAX2) callbacks.
-
Supports XML attributes during generation, which enables you to specify that a particular column or group of columns maps to an XML attribute instead of an XML element.
-
Allows SQL to XML tag escaping. Sometimes column names are not valid XML tag names. To avoid this problem you can either alias all the column names or turn on tag escaping.
-
Supports
XMLTypecolumns in objects or tables. -
Inserts XML into relational database tables or views. When given an XML document, XSU can also update or delete records from a database object.
XSU Restrictions
Note these restrictions when using XSU:
-
XSU can store data only in a single table. You can store XML across tables, however, by using the Oracle Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformation (XSLT) processor to transform a document into multiple documents and inserting them separately. You can also define views over multiple tables and perform insertions into the views. If a view is nonupdatable (because of complex joins), then you can use
INSTEADOFtriggers over the views to perform the inserts. -
You cannot use XSU to load XML data stored in attributes into a database schema, but you can use an XSLT transformation to change the attributes into elements.
-
By default XSU is case-sensitive. You can either use the correct case, or specify that case is to be ignored.
-
XSU cannot generate a relational database schema from an input DTD.
-
Inserting into
XMLTypetables using XSU is not supported.XMLTypecolumns are supported.
Using the XML SQL Utility: Overview
Using XSU: Basic Process
XSU is accessible through these interfaces:
-
The
OracleXMLQueryandOracleXMLSaveJava classes in theoracle.xml.sql.querypackage. Use theOracleXMLQueryclass to generate XML from relational data andOracleXMLSaveclass to perform DML. -
The PL/SQL packages
DBMS_XMLQueryandDBMS_XMLSave, which mirror the Java classes.
You can write these types of XSU applications:
-
Java programs that run inside the database and access the internal XSU Java API
-
Java programs that run on the client and access the client-side XSU Java API
-
PL/SQL programs that access XSU through PL/SQL packages
Generating XML with the XSU Java API: Basic Process
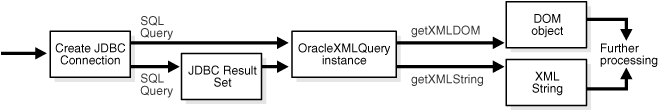
The OracleXMLQuery class makes up the XML generation part of the XSU Java API. Figure 13-1 shows the basic process for generating XML with XSU.
The basic steps in Figure 13-1 are:
-
Create a JDBC connection to the database. Normally, you establish a connection with the
DriverManagerclass, which manages a set of JDBC drivers. After the JDBC drivers are loaded, invokegetConnection(). When it finds the right driver, this method returns aConnectionobject that represents a database session. All SQL statements are executed within the context of this session.You have these options:
-
Create the connection with the JDBC Oracle Call Interface (OCI) driver. This code fragment shows this technique:
// import the Oracle driver class import oracle.jdbc.*; // load the Oracle JDBC driver DriverManager.registerDriver(new oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver()); // create the connection Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:oci:@","hr","password");The preceding example uses the default connection for the JDBC OCI driver.
-
Create the connection with the JDBC thin driver. The thin driver is written in pure Java and can be called from any Java program. This code fragment shows this technique:
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@dlsun489:1521:ORCL", "hr","password");The thin driver requires the host name (
dlsun489), port number (1521), and the Oracle system identifier (SID),ORCL. The database must have an active Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) listener. -
Use default connection used by the server-side internal JDBC driver. This driver runs within a default session and default transaction context. You are already connected to the database; your SQL operations are part of the default transaction. Thus, you do not have to register the driver. Create the
Connectionobject:Connection conn = new oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver().defaultConnection ();
Note:
OracleXMLDataSetExtJdbcis used only for Oracle JDBC, whereasOracleXMLDataSetGenJdbcis used for non-Oracle JDBC. These classes are in the oracle.xml.sql.dataset package. -
-
Create an XML query object and assign it a SQL query. You create an
OracleXMLQueryClass instance by passing a SQL query to the constructor, as shown in this example:OracleXMLQuery qry = new OracleXMLQuery (conn, "SELECT * from EMPLOYEES");
-
Configure the XML query object by invoking
OracleXMLQuerymethods. This example specifies that only 20 rows are to be included in the result set:xmlQry.setMaxRows(20);
-
Return a DOM object or string by invoking
OracleXMLQuerymethods. For example, get a DOM object:XMLDocument domDoc = (XMLDocument)qry.getXMLDOM();
Get a string object:
String xmlString = qry.getXMLString();
-
Perform additional processing on the string or DOM as needed.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Java Developer's Guide to learn about Oracle JDBC
-
Oracle Database XML Java API Reference to learn about
OracleXMLQuerymethods
-
Performing DML with the XSU Java API: Basic Process
Use the OracleXMLSave class to insert, update, and delete XML in the database. Figure 13-2 shows the basic process.
Figure 13-2 Storing XML in the Database Using XSU
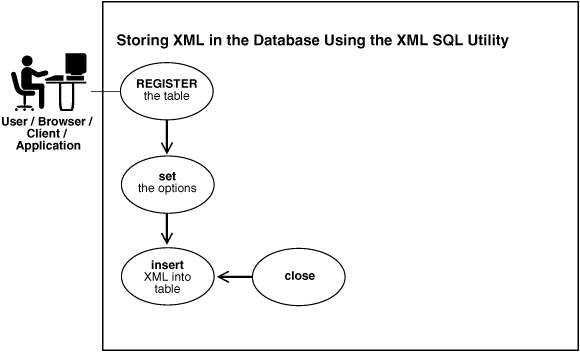
Description of "Figure 13-2 Storing XML in the Database Using XSU"
The basic steps in Figure 13-2 are:
-
Create a JDBC connection to the database. This step is identical to the first step described in "Generating XML with the XSU Java API: Basic Process."
-
Create an XML save object and assign it a table on which to perform DML. Pass a table or view name to the constructor, as shown in this example:
OracleXMLSave sav = new OracleXMLSave(conn, "employees");
-
Specify the primary key columns. For example, this code specifies that
employee_idis the key column:String [] keyColNames = new String[1]; keyColNames[0] = "EMPLOYEE_ID"; sav.setKeyColumnList(keyColNames);
-
Configure the XML save object by invoking
OracleXMLSavemethods. This example specifies an update of thesalaryandjob_idcolumns:String[] updateColNames = new String[2]; updateColNames[0] = "SALARY"; updateColNames[1] = "JOB_ID"; sav.setUpdateColumnList(updateColNames); // set the columns to update
-
Invoke the
insertXML(),updateXML(), ordeleteXML()methods on theOracleXMLSaveobject. This example shows an update:// Assume that the user passes in this XML document as the first argument sav.updateXML(sav.getURL(argv[0]));
When performing the DML, XSU performs these tasks:
-
Parses the input XML document.
-
Matches element names to column names in the target table or view.
-
Converts the elements to SQL types and binds them to the appropriate statement.
-
-
Close the
OracleXMLSaveobject and deallocate all contexts associated with it, as shown in this example:sav.close();
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Java Developer's Guide to learn about JDBC
-
Oracle Database XML Java API Reference to learn about
OracleXMLSave
-
Generating XML with the XSU PL/SQL API: Basic Process
The XSU PL/SQL API reflects the Java API in the generation and storage of XML documents from and to a database. DBMS_XMLQuery is the PL/SQL package that reflects the methods in the OracleXMLQuery Java class. This package has a context handle associated with it. Create a context by invoking a constructor-like function to get the handle, and then use the handle in all subsequent invocations.
Note:
For improved performance, consider using the C-basedDBMS_XMLGEN, which is written in C and built into the database, rather than DBMS_XMLQUERY.XSU supports the XMLType data type. Using XSU with XMLType is useful if, for example, you have XMLType columns in objects or tables.
Generating XML results in a character large object (CLOB) that contains the XML document. To use DBMS_XMLQuery and the XSU generation engine, follow these basic steps:
-
Declare a variable for the XML query context and a variable for the generated XML. For example:
v_queryCtx DBMS_XMLQuery.ctxType; v_result CLOB;
-
Get a context handle by invoking the
DBMS_XMLQuery.newContextfunction and supplying it the query, either as aCLOBor aVARCHAR2. This example registers a query to select the rows from theemployeestable with theWHEREclause containing the bind variables:EMPLOYEE_IDand:FIRST_NAME:v_queryCtx = DBMS_XMLQuery.newContext('SELECT * FROM employees WHERE employee_id=:EMPLOYEE_ID AND first_name=:FIRST_NAME'); -
Bind values to the query. The binds work by binding a name to the position.
clearBindValuesclears all the bind variables, whereassetBindValuesets a single bind variable with a string value. For example, bind theemployee_idandfirst_namevalues as shown:DBMS_XMLQuery.setBindValue(v_queryCtx,'EMPLOYEE_ID',20); DBMS_XMLQuery.setBindValue(v_queryCtx,'FIRST_NAME','John');
-
Configure the query context. Set optional arguments such as the
ROWtag name, theROWSETtag name, or the number of rows to fetch, and so on. This example specifies changes the defaultROWSETelement name toEMPSET:DBMS_XMLQuery.setRowSetTag(v_queryCtx,'EMPSET');
-
Fetch the results. You can get the XML as a CLOB with the
getXMLfunction, which generates XML with or without a DTD or XML schema. This example applies bind values to the statement and gets the result corresponding to the predicateemployee_id = 20andfirst_name = 'John':v_result := DBMS_XMLQuery.getXML(v_queryCtx);
-
Process the results of the XML generation. For example, suppose that your program declared these variables:
v_xmlstr VARCHAR2(32767); v_line VARCHAR2(2000);
You can print the
CLOBstored inv_result:v_xmlstr := DBMS_LOB.SUBSTR(v_result,32767); LOOP EXIT WHEN v_xmlstr IS NULL; v_line := substr(v_xmlstr,1,INSTR(v_xmlstr,CHR(10))-1); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('| ' || v_line); v_xmlstr := SUBSTR(v_xmlstr,INSTR(v_xmlstr,CHR(10))+1); END LOOP; -
Close the context. For example:
DBMS_XMLQuery.closeContext(v_queryCtx);
Performing DML with the PL/SQL API: Basic Process
DBMS_XMLSave is the PL/SQL package that reflects the methods in the OracleXMLSave Java class. This package has a context handle associated with it. Create a context by invoking a constructor-like function to get the handle, and then use the handle in all subsequent invocations.
To use DBMS_XMLSave, follow these basic steps:
-
Declare a variable for the XML save context and a variable for the number of rows touched by the DML. For example:
savCtx DBMS_XMLSave.ctxType; v_rows NUMBER;
-
Create a context handle by invoking the
DBMS_XMLSave.newContextfunction and supply it the table name to use for the DML operations.savCtx := DBMS_XMLSave.newContext('hr.employees'); -
Set options based on the type of DML to perform.
For inserts you can set the list of columns to insert into the
setUpdateColumnfunction. The default is to insert values into all columns. This example sets five columns in theemployeestable:DBMS_XMLSave.setUpdateColumn(savCtx,'EMPLOYEE_ID'); DBMS_XMLSave.setUpdateColumn(savCtx,'LAST_NAME'); DBMS_XMLSave.setUpdateColumn(savCtx,'EMAIL'); DBMS_XMLSave.setUpdatecolumn(savCtx,'JOB_ID'); DBMS_XMLSave.setUpdateColumn(savCtx,'HIRE_DATE');
For updates you must supply the list of key columns. Optionally, you can then supply the list of columns for update. In this case, the tags in the XML document matching the key column names are used in the
WHEREclause of theUPDATEstatement and the tags matching the update column list are used in theSETclause of theUPDATEstatement. For example:DBMS_XMLSave.setKeyColumn(savCtx,'employee_id'); -- set key column -- set list of columns to update. DBMS_XMLSave.setUpdateColumn(savCtx,'salary'); DBMS_XMLSave.setUpdateColumn(savCtx,'job_id');
For deletes the default is to create a
WHEREclause to match all the tag values present in each<ROW>element of the document supplied. To override this behavior, set the list of key columns. In this case only those tag values whose tag names match these columns are used to identify the rows to delete (in effect used in theWHEREclause of theDELETEstatement). For example:DBMS_XMLSave.setKeyColumn(savCtx,'EMPLOYEE_ID');
-
Supply a context and XML document to the
insertXML,updateXML, ordeleteXMLfunctions. For example:v_rows := DBMS_XMLSave.deleteXML(savCtx,xmlDoc);
-
Repeat the DML any number of times if needed.
-
Close the context. For example:
DBMS_XMLSave.closeContext(savCtx);
For a model use the Java examples described in "Programming with the XSU Java API."
Installing XSU
XSU is included as part of Oracle Database, along with the other XDK utilities. "XDK for Java Component Dependencies" describes the XSU components and dependencies.
By default, the Oracle Universal Installer installs XSU on disk and loads it into the database. No user intervention is required. If you did not load XSU in the database when installing Oracle, you can install XSU manually as follows:
-
Ensure that Oracle XML DB is installed (it is installed by default as part of Oracle Database).
-
Load the
xsu12.jarfile into the database. This JAR file, which has a dependency onxdb.jarforXMLTypeaccess, is described in Table 3-1. -
Run the
$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/dbmsxsu.sqlscript. This SQL script builds the XSU PL/SQL API.
As explained in "Using XSU: Basic Process," you do not have to load XSU into the database to use it. XSU can reside in any tier that supports Java.
These sections describe your installation options:
Installing XSU in the Database
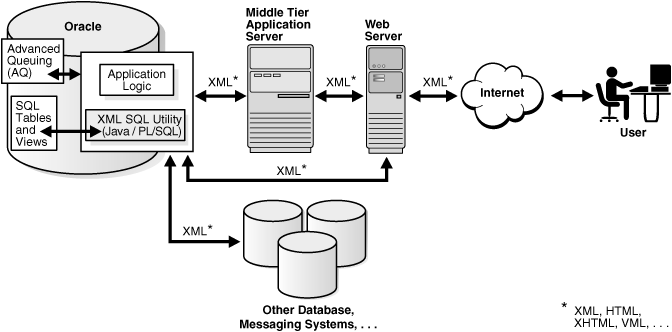
Figure 13-3 shows the typical architecture for applications that use the XSU libraries installed in the database. XML generated from XSU running in the database can be placed in advanced queues in the database to be queued to other systems or clients. You deliver the XML internally through stored procedures in the database or externally through web servers or application servers.
In Figure 13-3 all lines are bidirectional. Because XSU can generate and save data, resources can deliver XML to XSU running inside the database, which can then insert it in the appropriate database tables.
Installing XSU in an Application Server
Your application architecture may require an application server in the middle tier. The application tier can be a database or an application server that supports Java programs.
You can generate XML in the middle tier from SQL queries or ResultSets for various reasons, for example, to integrate different JDBC data sources in the middle tier. In this case, you can install the XSU in your middle tier, thereby enabling your Java programs to make use of XSU through its Java API.
Figure 13-4 shows a typical architecture for running XSU in a middle tier. In the middle tier, data from JDBC sources is converted by XSU into XML and then sent to web servers or other systems. Again, the process is bidirectional, which means that the data can be put back into the JDBC sources (database tables or views) with XSU. If a database is used as the application server, then you can use the PL/SQL front end instead of Java.
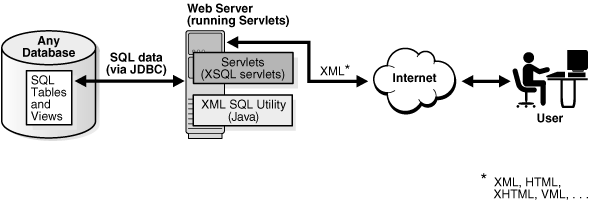
Figure 13-4 Running XSU in the Middle Tier
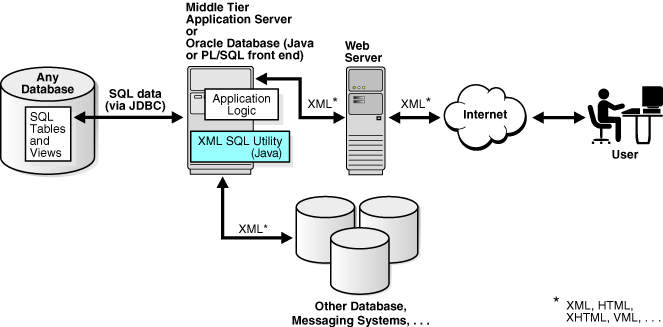
Description of "Figure 13-4 Running XSU in the Middle Tier"
Installing XSU in a Web Server
Figure 13-5 shows that XSU can live in the web server because the web server supports Java servlets. In this way you can write Java servlets that use XSU. XSQL Servlet is a standard servlet provided by Oracle. It is built on top of XSU and provides a template-like interface to XSU functionality. To perform XML processing in the web server and avoid intricate servlet programming, you can use the XSQL Servlet.
See Also:
-
Oracle XML DB Developer's Guide, especially the chapter on generating XML, for examples on using XSU with
XMLType -
Oracle Database XML Java API Reference to learn about the classes
OracleXMLQueryandOracleXMLSave -
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference to learn about the package
DBMS_XMLQuery -
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference to learn about the package
DBMS_XMLSave -
Chapter 16, "Using the XSQL Pages Publishing Framework" to learn about XSQL Servlet
Running the XSU Demo Programs
Demo programs for XSU are included in $ORACLE_HOME/xdk/demo/java/xsu. Table 13-1 describes the XML files and programs that you can use to test XSU.
| File | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
An PL/SQL script that binds values for |
|
|
A PL/SQL program that gets the first 20 rows of the |
|
|
A SQL script that sets up an object-relational schema and populates it. See "XML Mapping Against an Object-Relational Schema." |
|
|
A SQL script that sets up an object-relational schema and populates it. See "Altering the Database Schema or SQL Query." |
|
|
A SQL script that creates a relational table and then creates a customer view that contains a customer object on top of it. See "Altering the Database Schema or SQL Query." |
|
|
An XML document that describes a customer. See "Altering the Database Schema or SQL Query." |
|
|
A PL/SQL program that deletes an employee by primary key. See "Deleting by Key with DBMS_XMLSave: Example." |
|
|
A PL/SQL program that deletes an employee by row. See "Deleting by Row with DBMS_XMLSave: Example." |
|
|
A program that generates a DOM tree and then traverses it in document order, printing the nodes one by one. See "Generating a DOM Tree with OracleXMLQuery." |
|
|
A README that describes the programs in the demo directory. |
|
|
A PL/SQL program that inserts an XML document into a table. See "Inserting Values into All Columns with DBMS_XMLSave." |
|
|
A SQL script that creates a table called |
|
|
A SQL script that inserts an XML document into the |
|
|
A SQL script that inserts an XML document into the |
|
|
A SQL script that inserts an XML document into the |
|
|
A PL/SQL script that invokes the |
|
|
A PL/SQL script that invokes the |
|
|
A SQL script that queries the |
|
|
An XML document that describes a new employee. See "Running the testInsert Program." |
|
|
An XML document that describes a new employee. See "Running the testInsertSubset Program." |
|
|
A program that throws an exception when there are no more rows. See "Raising a No Rows Exception." |
|
|
A program that uses the JDBC |
|
|
A program that generates an XML page that paginates results. See "Paginating Results with OracleXMLQuery: Example." |
|
|
A PL/SQL script that paginates results. It skips the first 3 rows of the |
|
|
A PL/SQL script that prints a CLOB to the output buffer. See "Generating XML from Simple Queries with DBMS_XMLQuery." |
|
|
A PL/SQL script that invokes the |
|
|
A program that generates XML from the results of the SQL query defined in the |
|
|
A program that queries the |
|
|
A program that inserts |
|
|
A program that queries the |
|
|
A sample XML data document that |
|
|
A SQL script that creates the |
|
|
A PL/SQL script that selects 20 rows from the |
|
|
A PL/SQL script that uses the same context and settings to perform DML depending on user input. See "Reusing the Context Handle with DBMS_XMLSave." |
|
|
A program that limits the number of elements used to identify a row, which improves performance by caching the |
|
|
A PL/SQL script that deletes a row from the |
|
|
A program that accepts an XML document file name as input and deletes the rows corresponding to the elements in the document. See "Deleting by Row with OracleXMLSave." |
|
|
A SQL script that deletes a row from the |
|
|
A sample program shown that throws a runtime exception and then gets the parent exception by invoking |
|
|
A Java program that inserts XML values into all columns of the |
|
|
A PL/SQL script that inserts XML data into a subset of columns. See "Inserting into a Subset of Columns with DBMS_XMLSave." |
|
|
A program shown that inserts XML data into a subset of columns. See "Inserting XML into a Subset of Columns with OracleXMLSave." |
|
|
A PL/SQL script that creates a function that defines a REF cursor and returns it. Every time the |
|
|
A sample program that updates the |
|
|
A PL/SQL that creates a PL/SQL procedure called |
|
|
Suppose you want to update only the salary and job title for each employee and ignore the other information. If you know that all the elements to be updated are the same for all |
|
|
A SQL script that creates the procedure |
|
|
A sample program that uses XSU to generate XML as a |
|
|
An XML document that contains updated salary and other information for a series of employees. See "Running the testUpdate Program." |
|
|
An XML document that contains updated salary and other information for a series of employees. See "Running the testUpdate Program." |
|
|
An XML document that contains new data for two employees. See "Running the testUpdateList Program." |
|
|
A PL/SQL script that passes an XML document to the |
The steps for running the demos are:
-
Change into the
$ORACLE_HOME/xdk/demo/java/xsudirectory (UNIX) or%ORACLE_HOME%\xdk\demo\java\xsudirectory (Windows). -
Ensure that your environment variables are set as described in "Setting Up the XDK for Java Environment." In particular, ensure that the Java classpath includes
xsu12.jarfor XSU andojdbc6.jar(Java 1.6) for JDBC. If you use a multibyte character set other than UTF-8, ISO8859-1, or JA16SJIS, then placeorai18n.jarin your classpath so that JDBC can convert the character set of the input file to the database character set. -
Compile the Java programs as shown in this example:
javac samp1.java samp2.java samp10.java
-
Connect to a database as user
hrand run SQL scriptcreateRelSchema:CONNECT hr @$ORACLE_HOME/xdk/demo/java/xsu/createRelSchema
These sections describe the XSU demos in detail.
Using the XSU Command-Line Utility
XDK includes a command-line Java interface for XSU. XSU command-line options are provided through the Java class OracleXML. To use this API ensure that your Java classpath is set as described in "Setting Up the XDK for Java Environment."
To print usage information for XSU to standard output, run this command:
java OracleXML
To use XSU, invoke it with either the getXML or putXML parameter:
java OracleXML getXML options java OracleXML putXML options
Table 13-2 describes the getXML options.
| getXML Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Specifies the user name and password to connect to the database. The connect string is also specified. You can specify the user name and password as part of the connect string. |
|
|
Specifies the JDBC database connect string. By default the connect string is: " |
|
|
Instructs the XSU to generate the DTD along with the XML document. |
|
|
Instructs the XSU to generate the schema along with the XML document. |
|
|
Specifies the rowset tag, which is tag that encloses all the XML elements corresponding to the records returned by the query. The default rowset tag is |
|
|
Specifies the row tag that encloses the data corresponding to a database row. The default row tag is |
|
|
Names the attribute of the |
|
- |
Specifies that the value of a scalar column from the query is to be used as the value of the |
|
|
Names the attribute of an XML list element that keeps track of the cardinality of the elements of the list. The generated XML lists correspond to either a cursor query, or collection. If you specify an empty string ("") as the |
|
|
Specifies the use type name for the column-element tag. By default XSU uses the |
|
|
Specifies the attribute |
|
|
Specifies the style sheet in the XML processing instruction. |
|
|
Specifies the style sheet type in the XML processing instruction. |
|
|
Specifies the XSLT style sheet to apply to the XML document. |
|
|
Sets the XSLT external entity reference. |
|
|
Generates lowercase or uppercase tag names. The default is to match the case of the SQL object names from which the tags are generated. |
|
|
Specifies the treatment of characters that are legal in SQL object names but illegal in XML tags. If such a character is encountered, then it is escaped so that it does not throw an exception. |
|
|
Specifies the tag to enclose error messages that are formatted as XML. |
|
|
Specifies that XSU must throw a Java exception. By default XSU catches any error and produces the XML error. |
|
|
Raises an exception if no rows are returned. |
|
|
Performs strict checking on input data. |
|
|
Specifies the maximum number of rows to be retrieved and converted to XML. |
|
|
Specifies the number of rows to be skipped. |
|
|
Specifies the character set encoding of the generated XML. |
|
|
Specifies the date format for the date values in the XML document. |
|
|
Specifies the file name that contains the query or the query itself. |
Table 13-3 describes the putXML options.
| putXML Options | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Specifies the user name and password to connect to the database. The connect string is also specified. You can specify the user name and password as part of the connect string. |
|
|
Specifies the JDBC database connect string. By default the connect string is: " |
|
|
Specifies the batch size that controls the number of rows that are batched together and inserted in a single trip to the database to improve performance. |
|
|
Specifies the number of inserted records after which a commit is to be executed. If the autocommit is |
|
|
Specifies the |
|
|
Specifies the date format for the date values in the XML document. |
|
|
Turns on reverse mapping if SQL to XML name escaping was used when generating the doc. |
|
|
Makes the matching of the column names with tag names case insensitive. For example, |
|
|
Preserves the white space in the inserted XML document. |
|
|
Specifies the XSLT to apply to the XML document before inserting. |
|
|
Sets the XSLT external entity reference. |
|
|
Specifies the XML document to insert: a local file, a URL, or an XML document as a string on the command line. |
|
|
Specifies the name of the table to put the values into. |
Generating XML with the XSU Command-Line Utility
To generate XML from the database schema use the getXML parameter. For example, to generate an XML document by querying the employees table in the hr schema, you can use this syntax:
java OracleXML getXML -user "hr/password" "SELECT * FROM employees"
The preceding command performs these tasks:
-
Connects to the current default database
-
Executes the specified
SELECTquery -
Converts the SQL result set to XML
-
Prints the XML to standard output
The getXML parameter supports a wide range of options, which are explained in Table 13-2.
Generating XMLType Data with the XSU Command-Line Utility
You can use XSU to generate XML from tables with XMLType columns. Suppose that you run the demo script setup_xmltype.sql to create and populate the parts table. You can generate XML from this table with XSU:
java OracleXML getXML -user "hr/password" -rowTag "Part" "SELECT * FROM parts"
The output of the command is shown below:
<?xml version = '1.0'?>
<ROWSET>
<Part num="1">
<PARTNO>1735</PARTNO>
<PARTNAME>Gizmo</PARTNAME>
<PARTDESC>
<Description>
<Title>Description of the Gizmo</Title>
<Author>John Smith</Author>
<Body>
The <b>Gizmo</b> is <i>grand</i>.
</Body>
</Description>
</PARTDESC>
</Part>
</ROWSET>
Performing DML with the XSU Command-Line Utility
To insert an XML document called new_employees.xml into the hr.employees table, use this syntax:
java OracleXML putXML -user "hr/password" -fileName "new_employees.xml" employees
The preceding command performs these tasks:
-
Connects to the current database as
hr -
Reads the XML document named
new_emp.xml -
Parses the XML document, matching the tags with column names
-
Inserts the values appropriately into the
employeestable
The getXML parameter supports a wide range of options, which are explained in Table 13-2.
Programming with the XSU Java API
Generating a String with OracleXMLQuery
The testXMLSQL.java demo program uses XSU to generate XML as a String object. This program queries the hr.employees table and prints the result set to standard output.
The testXMLSQL.java program follows these steps:
-
Register the JDBC driver and create a database connection. This code fragment uses the OCI JDBC driver and connects with the user name
hr:import oracle.jdbc.*;...Connection conn = getConnection("hr","password"); ... private static Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException { // register the JDBC driver DriverManager.registerDriver(new oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver()); // create the connection using the OCI driver Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:oci:@",username,password); return conn; } -
Create an XML query object and initialize it with a SQL query. This code fragment initializes the object with a
SELECTstatement onhr.employees:OracleXMLQuery qry = new OracleXMLQuery(conn, "SELECT * FROM employees");
-
Get the query result set as a
Stringobject. ThegetXMLString()method transforms the object-relational data specified in the constructor into an XML document. This example shows this technique:String str = qry.getXMLString();
-
Close the query object to release any resources, as shown in this code:
qry.close();
Running the testXMLSQL Program
To run the testXMLSQL.java program perform these steps:
-
Compile
testXMLSQL.javawithjavac. -
Execute
java testXMLSQLon the command line.
You must have the CLASSPATH pointing to this directory for the Java executable to find the class. Alternatively, use visual Java tools such as Oracle JDeveloper to compile and run this program. When run, this program prints out the XML file to the screen. This code shows sample output with some rows edited out:
<?xml version = '1.0'?>
<ROWSET>
<ROW num="1">
<EMPLOYEE_ID>100</EMPLOYEE_ID>
<FIRST_NAME>Steven</FIRST_NAME>
<LAST_NAME>King</LAST_NAME>
<EMAIL>SKING</EMAIL>
<PHONE_NUMBER>515.123.4567</PHONE_NUMBER>
<HIRE_DATE>6/17/1987 0:0:0</HIRE_DATE>
<JOB_ID>AD_PRES</JOB_ID>
<SALARY>24000</SALARY>
<DEPARTMENT_ID>90</DEPARTMENT_ID>
</ROW>
<!-- ROW num="2" through num="107" ... -->
</ROWSET>
Generating a DOM Tree with OracleXMLQuery
To generate a DOM tree from the XML generated by XSU, you can directly request a DOM document from XSU. This technique saves the overhead of creating a string representation of the XML document and then parsing it to generate the DOM tree.
XSU invokes the Oracle XML parser to construct the DOM tree from the data values. The domTest.java demo program generates a DOM tree and then traverses it in document order, printing the nodes one by one.
The first two steps in the domTest.java program are the same as in the testXMLSQL.java program described in "Generating a String with OracleXMLQuery." The program proceeds as follows:
-
Get the DOM by invoking
getXMLDOM()method. The following example shows this technique:XMLDocument domDoc = (XMLDocument)qry.getXMLDOM();
-
Print the DOM tree. The following code prints to standard output:
domDoc.print(System.out);
You can also create a
StringWriterand wrap it in aPrintWriter:StringWriter s = new StringWriter(10000); domDoc.print(new PrintWriter(s)); System.out.println(" The string version ---> \n"+s.toString());
After compiling the program, run it from the command line:
java domTest
Paginating Results with OracleXMLQuery
Limiting the Number of Rows in the Result Set
In testXMLSQL.java and domTest.java, XSU generated XML from all rows returned by the query. Suppose that you query a table that contains 1000 rows, but you want only 100 rows at a time. One approach is to execute one query to get the first 100 rows, another to get the next 100 rows, and so on. With this technique you cannot skip the first five rows of the query and then generate the result. To avoid these problems, use these Java methods:
-
OracleXMLSave.setSkipRows()forces XSU to skip the desired number of rows before starting to generate the result. The command-line equivalent to this method is the-skipRowsparameter. -
OracleXMLSave.setMaxRows()limits the number of rows converted to XML. The command-line equivalent to this method is the-maxRowsparameter.
Example 13-1 sets skipRows to a value of 5 and maxRows to a value of 1, which causes XSU to skip the first 5 rows and then generate XML for the next row when querying the hr.employees table.
Example 13-1 Specifying skipRows and maxRows on the Command Line
java OracleXML getXML -user "hr/password" -skipRows 5 -maxRows 1 \
"SELECT * FROM employees"
The following shows sample output (only row 6 of the query result set is returned):
<?xml version = '1.0'?>
<ROWSET>
<ROW num="6">
<EMPLOYEE_ID>105</EMPLOYEE_ID>
<FIRST_NAME>David</FIRST_NAME>
<LAST_NAME>Austin</LAST_NAME>
<EMAIL>DAUSTIN</EMAIL>
<PHONE_NUMBER>590.423.4569</PHONE_NUMBER>
<HIRE_DATE>6/25/1997 0:0:0</HIRE_DATE>
<JOB_ID>IT_PROG</JOB_ID>
<SALARY>4800</SALARY>
<MANAGER_ID>103</MANAGER_ID>
<DEPARTMENT_ID>60</DEPARTMENT_ID>
</ROW>
</ROWSET>
Keeping the Object Open for the Duration of the User's Session
In some situations, you might want to keep the query object open for the duration of the user session. You can handle such cases with the maxRows() method and the keepObjectOpen() method.
Consider a web search engine that paginates search results. The first page lists 10 results, the next page lists 10 more, and so on. To perform this task with XSU, request 10 rows at a time and keep the ResultSet open so that the next time you ask XSU for more results, it starts generating from where the last generation finished. If OracleXMLQuery creates a result set from the SQL query string, then it typically closes the ResultSet internally because it assumes no more results are required. Thus, you must invoke keepObjectOpen() to keep the cursor active.
A different case requiring an open query object is when the number of rows or number of columns in a row is very large. In this case, you can generate multiple small documents rather than one large document.
Paginating Results with OracleXMLQuery: Example
The paginateResults.java program shows how you can generate an XML page that paginates results. The output XML displays only 20 rows of the hr table.
The first step of the paginateResults.java program, which creates the connection, is the same as in testXMLSQL.java. The program continues as follows:
-
Create a SQL statement object and initialize it with a SQL query. The following code fragment sets two options in
java.sql.ResultSet:Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE, ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY); -
Create the query as a string and execute it by invoking
Statement.executeQuery(). The return object is of typeResultSet. The following example shows this technique:String sCmd = "SELECT first_name, last_name FROM hr.employees"; ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sCmd);
-
Create the query object, as shown in this code:
OracleXMLQuery xmlQry = new OracleXMLQuery(conn, rs);
-
Configure the query object. The following code specifies that the query object is open for the duration of the session. It also limits the number of rows returned to 20:
xmlQry.keepObjectOpen(true); xmlQry.setRowsetTag("ROWSET"); xmlQry.setRowTag("ROW"); xmlQry.setMaxRows(20); -
Retrieve the result as a
Stringand print:String sXML = xmlQry.getXMLString(); System.out.println(sXML);
After compiling the program, run it from the command line:
java paginateResults
Generating Scrollable Result Sets
In some situations, you might want to perform a query and then retrieve a previous page of results from within the result set. To enable scrolling, instantiate the Oracle.jdbc.ResultSet class. You can use the ResultSet object to move back and forth within the result set and use XSU to generate XML each time.
The pageTest.java program shows how to use the JDBC ResultSet to generate XML a page at a time. Using ResultSet may be necessary in cases that are not handled directly by XSU, for example, when setting the batch size and binding values.
The pageTest.java program creates a pageTest object and initializes it with a SQL query. The constructor for the pageTest object performs these steps:
-
Create a JDBC connection by invoking the same
getConnection()method defined inpaginateResults.java:Connection conn; ... conn = getConnection("hr","password"); -
Create a statement:
Statement stmt; ... stmt = conn.createStatement();
-
Execute the query passed to the constructor to get the scrollable result set. The following code shows this technique:
ResultSet rset = stmt.executeQuery(sqlQuery);
-
Create a query object by passing references to the connection and result set objects to the constructor. The following code fragment shows this technique:
OracleXMLQuery qry; ... qry = new OracleXMLQuery(conn,rset);
-
Configure the query object. The following code fragment specifies that the query object be kept open, and that it raise an exception when there are no more rows:
qry.keepObjectOpen(true); qry.setRaiseNoRowsException(true); qry.setRaiseException(true);
-
After creating the query object by passing it the string
"SELECT * FROM employees", the program loops through the result set. ThegetResult()method receives integer values specifying the start row and end row of the set. It sets the maximum number of rows to retrieve by calculating the difference of these values and then retrieves the result as a string. The followingwhileloop retrieves and prints ten rows at a time:int i = 0; while ((str = test.getResult(i,i+10))!= null) { System.out.println(str); i+= 10; }
After compiling the program, run it from the command line:
java pageTest
Generating XML from Cursor Objects
The OracleXMLQuery class provides XML conversion only for query strings or ResultSet objects. If your program uses PL/SQL procedures that return REF cursors, then how do you perform the conversion? You can use the ResultSet conversion mechanism described in "Generating Scrollable Result Sets."
REF cursors are references to cursor objects in PL/SQL. These cursor objects are SQL statements over which a program can iterate to get a set of values. The cursor objects are converted into OracleResultSet objects in the Java world. In your Java program you can initialize a CallableStatement object, execute a PL/SQL function that returns a cursor variable, get the OracleResultSet object, and then send it to the OracleXMLQuery object to get the desired XML.
Consider the testRef PL/SQL package defined in the testRef.sql script. It creates a function that defines a REF cursor and returns it. Every time the testRefCur PL/SQL function is called, it opens a cursor object for the SELECT query and returns that cursor instance. To convert the object to XML, do this:
-
Run the
testRef.sqlscript to create thetestRefpackage in thehrschema. -
Compile and run the
refCurTest.javaprogram to generate XML from the results of the SQL query defined in thetestRefCurfunction.
To apply the style sheet, you can use the applyStylesheet command, which forces the style sheet to be applied before generating the output.
Inserting Rows with OracleXMLSave
To insert a document into a table or view, supply the table or view name and then the document. XSU parses the document (if a string is given) and then creates an INSERT statement into which it binds all the values. By default XSU inserts values into all columns of the table or view. An absent element is treated as a NULL value. The following example shows how you can store the XML document generated from the hr.employees table in the table.
Inserting XML into All Columns with OracleXMLSave
The testInsert.java demo program inserts XML values into all columns of the hr.employees table.
The program follows these steps:
-
Create a JDBC OCI connection. The program invokes the same
getConnection()method used by the previous examples in this chapter:Connection conn = getConnection("hr","password"); -
Create an XML save object. You initialize the object by passing it the
Connectionreference and the name of the table on which you want to perform DML. The following example shows this technique:OracleXMLSave sav = new OracleXMLSave(conn, "employees");
-
Insert the data in an input XML document into the
hr.employeestable. The following code fragment creates a URL from the document file name specified on the command line:sav.insertXML(sav.getURL(argv[0]));
-
Close the XML save object:
sav.close();
Running the testInsert Program
Assume that you write the new_emp.xml document to describe new employee Janet Smith, who has employee ID 7369. You pass the file name new_emp.xml as an argument to the testInsert program:
java testInsert "new_emp.xml"
The program inserts a new row in the employees table that contains the values for the columns specified. Any absent element inside the row element is treated as NULL.
Running the program generates an INSERT statement of this form:
INSERT INTO hr.employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?);
XSU matches the element tags in the input XML document that match the column names and binds their values.
Inserting XML into a Subset of Columns with OracleXMLSave
In some situations, you might not want to insert values into all columns. For example, the group of values that you get might not be the complete set, requiring you to use triggers or default values for the remaining columns. The testInsertSubset.java demo program shows how to handle this case.
The program follows these steps:
-
Create a JDBC OCI connection. The program invokes the same
getConnection()method used by the previous examples in this chapter:Connection conn = getConnection("hr","password"); -
Create an XML save object. Initialize the object by passing it the
Connectionreference and the name of the table on which you want to perform DML. The following example shows this technique:OracleXMLSave sav = new OracleXMLSave(conn, "employees");
-
Create an array of strings. Each element of the array must contain the name of a column in which values are inserted. The following code fragment specifies the names of five columns:
String [] colNames = new String[5]; colNames[0] = "EMPLOYEE_ID"; colNames[1] = "LAST_NAME"; colNames[2] = "EMAIL"; colNames[3] = "JOB_ID"; colNames[4] = "HIRE_DATE";
-
Configure the XML save object to update the specified columns. The following statement passes a reference to the array to the
OracleXMLSave.setUpdateColumnList()method:sav.setUpdateColumnList(colNames);
-
Insert the data in an input XML document into the
hr.employeestable. The following code fragment creates a URL from the document file name specified on the command line:sav.insertXML(sav.getURL(argv[0]));
-
Close the XML save object:
sav.close();
Running the testInsertSubset Program
Assume that you use the new_emp2.xml document to store data for new employee Adams, who has employee ID 7400. You pass new_emp2.xml as an argument to the testInsert program:
java testInsert new_emp2.xml
The program ignores values for the columns that were not specified in the input file. It performs an INSERT for each ROW element in the input and batches the INSERT statements by default.
The program generates this INSERT statement:
INSERT INTO hr.employees (employee_id, last_name, email, job_id, hire_date) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?);
Updating Rows with OracleXMLSave
To update the fields in a table or view, supply the table or view name and then the XML document. XSU parses the document (if a string is given) and then creates one or more UPDATE statements into which it binds all the values. The following examples show how you can use an XML document to update the hr.employees table.
Updating Key Columns with OracleXMLSave
The testUpdate.java demo program updates the hr.employees table by invoking the OracleXMLSave.setKeyColumnList() method.
The testUpdate.java program follows these steps:
-
Create a JDBC OCI connection. The program invokes the same
getConnection()method used by the previous examples in this chapter:Connection conn = getConnection("hr","password"); -
Create an XML save object. You initialize the object by passing it the
Connectionreference and the name of the table on which you want to perform DML. The following example shows this technique:OracleXMLSave sav = new OracleXMLSave(conn, "employees");
-
Create a single-element
Stringarray to hold the name of the primary key column in the table to be updated. The following code fragment specifies the name of theemployee_idcolumn:String [] keyColNames = new String[1]; colNames[0] = "EMPLOYEE_ID";
-
Set the XML save object to the primary key specified in the array. The following statement passes a reference to the
keyColNamesarray to theOracleXMLSave.setKeyColumnList()method:sav.setKeyColumnList(keyColNames);
-
Update the rows specified in the input XML document. The following statement creates a URL from the file name specified on the command line:
sav.updateXML(sav.getURL(argv[0]));
-
Close the XML save object:
sav.close();
Running the testUpdate Program
You can use XSU to update specified fields in a table. Example 13-2 shows upd_emp.xml, which contains updated salary and other information for the two employees that you just added, 7369 and 7400.
<?xml version='1.0'?>
<ROWSET>
<ROW num="1">
<EMPLOYEE_ID>7400</EMPLOYEE_ID>
<SALARY>3250</SALARY>
</ROW>
<ROW num="2">
<EMPLOYEE_ID>7369</EMPLOYEE_ID>
<JOB_ID>SA_REP</JOB_ID>
<MANAGER_ID>145</MANAGER_ID>
</ROW>
<!-- additional rows ... -->
</ROWSET>
For updates, supply XSU with the list of key column names in the WHERE clause of the UPDATE statement. In the hr.employees table the employee_id column is the key.
Pass the file name upd_emp.xml as an argument to the preceding program:
java testUpdate upd_emp.xml
The program generates two UPDATE statements. For the first ROW element, the program generates an UPDATE statement to update the SALARY field:
UPDATE hr.employees SET salary = 3250 WHERE employee_id = 7400;
For the second ROW element the program generates this statement:
UPDATE hr.employees SET job_id = 'SA_REP' AND MANAGER_ID = 145 WHERE employee_id = 7369;
Updating a Column List with OracleXMLSave
You may want to update a table by using only a subset of the elements in an XML document. You can achieve this goal by specifying a list of columns. This technique speeds processing because XSU uses the same UPDATE statement with bind variables for all the ROW elements. You can also ignore other tags in the XML document.
Note:
When you specify a list of columns to update, if an element corresponding to an update column is absent, XSU treats it asNULL.Suppose you want to update the salary and job title for each employee and ignore the other data. If you know that all the elements to be updated are the same for all ROW elements in the XML document, then you can use the OracleXMLSave.setUpdateColumnNames() method to specify the columns. The testUpdateList.java program shows this technique.
The testUpdateList.java program follows these steps:
-
Create a JDBC OCI connection. The program invokes the same
getConnection()method used by the previous examples in this chapter:Connection conn = getConnection("hr","password"); -
Create an XML save object. You initialize the object by passing it the
Connectionreference and the name of the table on which you want to perform DML. The following example shows this technique:OracleXMLSave sav = new OracleXMLSave(conn, "employees");
-
Create an array of type
Stringto hold the name of the primary key column in the table to be updated. The array contains only one element, which is the name of the primary key column in the table to be updated. The following code fragment specifies the name of theemployee_idcolumn:String [] colNames = new String[1]; colNames[0] = "EMPLOYEE_ID";
-
Set the XML save object to the primary key specified in the array. The following statement passes a reference to the
colNamesarray to theOracleXMLSave.setKeyColumnList()method:sav.setKeyColumnList(keyColNames);
-
Create an array of type
Stringto hold the name of the columns to be updated. The following code fragment specifies the name of theemployee_idcolumn:String[] updateColNames = new String[2]; updateColNames[0] = "SALARY"; updateColNames[1] = "JOB_ID";
-
Set the XML save object to the list of columns to be updated. The following statement performs this task:
sav.setUpdateColumnList(updateColNames);
-
Update the rows specified in the input XML document. The following code fragment creates a URL from the file name specified on the command line:
sav.updateXML(sav.getURL(argv[0]));
-
Close the XML save object:
sav.close();
Running the testUpdateList Program
Suppose that you use the sample XML document upd_emp2.xml to store new data for employees Steven King, who has an employee ID of 100, and William Gietz, who has an employee identifier (ID) of 206. You pass upd_emp2.xml as an argument to the testUpdateList program:
java testUpdateList upd_emp2.xml
In this example, the program generates two UPDATE statements. For the first ROW element, the program generates this statement:
UPDATE hr.employees SET salary = 8350 AND job_id = 'AC_ACCOUNT' WHERE employee_id = 100;
For the second ROW element the program generates this statement:
UPDATE hr.employees SET salary = 25000 AND job_id = 'AD_PRES' WHERE employee_id = 206;
Deleting Rows with OracleXMLSave
When deleting from XML documents, you can specify a list of key columns. XSU uses these columns in the WHERE clause of the DELETE statement. If you do not supply the key column names, then XSU creates a new DELETE statement for each ROW element of the XML document. The list of columns in the WHERE clause of the DELETE statement matches those in the ROW element.
Deleting by Row with OracleXMLSave
The testDeleteRow.java demo program accepts an XML document file name as input and deletes the rows corresponding to the elements in the document.
The testDeleteRow.java program follows these steps:
-
Create a JDBC OCI connection. The program invokes the same
getConnection()method used by the previous examples in this chapter:Connection conn = getConnection("hr","password"); -
Create an XML save object. You initialize the object by passing it the
Connectionreference and the name of the table on which you want to perform DML. The following example shows this technique:OracleXMLSave sav = new OracleXMLSave(conn, "employees");
-
Delete the rows specified in the input XML document. The following code fragment creates a URL from the file name specified on the command line:
sav.deleteXML(sav.getURL(argv[0]));
-
Close the XML save object:
sav.close();
Running the testDelete Program
This section shows how to delete the employees 7400 and 7369 that you added in "Inserting Rows with OracleXMLSave."
To make this example work correctly, connect to the database and disable a constraint on the hr.job_history table:
CONNECT hr ALTER TABLE job_history DISABLE CONSTRAINT JHIST_EMP_FK; EXIT
Now pass upd_emp.xml to the testDeleteRow program:
java testDeleteRow upd_emp.xml
The program forms the DELETE statements based on the tag names present in each ROW element in the XML document. It executes these statements:
DELETE FROM hr.employees WHERE salary = 3250 AND employee_id = 7400; DELETE FROM hr.employees WHERE job_id = 'SA_REP' AND MANAGER_ID = 145 AND employee_id = 7369;
Deleting by Key with OracleXMLSave
To use only the key values as predicates on the DELETE statement, invoke the OracleXMLSave.setKeyColumnList() method. This approach limits the number of elements used to identify a row, which has the benefit of improving performance by caching the DELETE statement and batching transactions. The testDeleteKey.java program shows this technique.
The testDeleteKey.java program follows these steps:
-
Create a JDBC OCI connection. The program invokes the same
getConnection()method used by the previous examples in this chapter:Connection conn = getConnection("hr","password"); -
Create an XML save object. You initialize the object by passing it the
Connectionreference and the name of the table on which you want to perform DML. The following example shows this technique:OracleXMLSave sav = new OracleXMLSave(conn, "employees");
-
Create an array of type
Stringto hold the name of the primary key column in the table. The array contains only one element. The following code fragment specifies the name of theemployee_idcolumn:String [] colNames = new String[1]; colNames[0] = "EMPLOYEE_ID";
-
Set the XML save object to the primary key specified in the array. The following statement passes a reference to the
colNamesarray to theOracleXMLSave.setKeyColumnList()method:sav.setKeyColumnList(keyColNames);
-
Delete the rows specified in the input XML document. The following code fragment creates a URL from the file name specified on the command line:
sav.deleteXML(sav.getURL(argv[0]));
-
Close the XML save object:
sav.close();
Running the testDeleteKey Program
This section shows how to delete employees 7400 and 7369 that you added in "Updating Key Columns with OracleXMLSave." If you deleted these employees in the previous example, you can add them back to the employees table:
java testInsert new_emp.xml java testInsert new_emp2.xml
Delete employees 7400 and 7369 by passing the same upd_emp.xml document to the testDeleteRow program:
java testDeleteKey upd_emp.xml
The program forms this single generated DELETE statement:
DELETE FROM hr.employees WHERE employee_id=?;
The program executes these DELETE statements, one for each employee:
DELETE FROM hr.employees WHERE employee_id = 7400; DELETE FROM hr.employees WHERE employee_id = 7369;
Handling XSU Java Exceptions
XSU catches all exceptions that occur during processing and throws oracle.xml.sql.OracleXMLSQLException, which is a generic runtime exception. The invoking program does not have to catch this exception if it can still perform the appropriate action. The exception class provides methods to get error messages and also get any existing parent exception.
Getting the Parent Exception
The testException.java demo program throws a runtime exception and then gets the parent exception by invoking Exception.getParentException().
Running the preceding program generates this error message:
Caught SQL Exception:ORA-00904: "SD": invalid identifier
Raising a No Rows Exception
When there are no rows to process, XSU returns a null string. You can throw an exception every time there are no more rows, however, so that the program can process this exception through exception handlers. When a program invokes OracleXMLQuery.setRaiseNoRowsException(), XSU raises an oracle.xml.sql.OracleXMLSQLNoRowsException whenever there are no rows to generate for the output. This is a runtime exception and need not be caught.
The noRowsTest.java demo program instantiates the pageTest class defined in pageTest.java. The condition to check the termination changed from checking whether the result is null to an exception handler.
The noRowsTest.java program creates a pageTest object and initializes it with a SQL query. The program proceeds as follows:
-
Configure the query object or raise a no rows exception. The following code fragment shows this technique:
pageTest test = new pageTest("SELECT * from employees"); ... test.qry.setRaiseNoRowsException(true); -
Loop through the result set infinitely, retrieving ten rows at a time. When no rows are available, the program throws an exception. The following code fragment invokes
pageTest.nextPage(), which scrolls through the result set ten rows at a time:try { while(true) System.out.println(test.nextPage()); } -
Catch the no rows exception and print "END OF OUTPUT". The following code shows this technique:
catch(oracle.xml.sql.OracleXMLSQLNoRowsException e) { System.out.println(" END OF OUTPUT "); try { test.close(); } catch ( Exception ae ) { ae.printStackTrace(System.out); } }
After compiling the program, run it from the command line:
java noRowsTest
Programming with the XSU PL/SQL API
Note:
For increased performance, consider usingDBMS_XMLGen and DBMS_XMLStore as alternatives to DBMS_XMLQuery and DBMS_XMLSave. The two former packages are written in C and are built in to the database kernel. You can also use SQL and XML functions such as XMLElement for XML access in the database.Generating XML from Simple Queries with DBMS_XMLQuery
This section shows how you can use the DBMS_XMLQuery package to generate XML from a SQL query. To make the example work, connect to the database as hr and run the printClobOut.sql script. The script creates printClobOut, which is a simple procedure that prints a CLOB to the output buffer. If you run the printClobOut procedure in SQL*Plus, it prints the input CLOB to the screen. Set server output to ON to see the results. You might have to increase your display buffer to see all the output.
Run the simpleQuery.sql script to select 20 rows from the hr.employees table and get an XML document as a CLOB. The program first gets the context handle by passing in a query and then invokes the getXML function to get the CLOB value. The document is in the same encoding as the database character set. This sample application assumes that you created the printClobOut procedure by running printClobOut.sql.
Specifying Element Names with DBMS_XMLQuery
With the XSU PL/SQL API you can change the default ROW and the ROWSET element names, which are the default names placed around each row of the result and around the whole output XML document. Use the PL/SQL procedures setRowTagName and setRowSetTagName to accomplish this task.
Connect as hr and run the changeElementName.sql script in SQL*Plus to get the first 20 rows of the employees table as an XML document. The anonymous PL/SQL block changes the ROW and ROWSET element names to EMP and EMPSET. The block invokes the printClobOut procedure that you created by running printClobOut.sql.
The generated XML document has an <EMPSET> document element. Each row is separated with the <EMP> tag.
Paginating Results with DBMS_XMLQuery
You can paginate query results by invoking these PL/SQL functions:
-
setMaxRowssets the maximum number of rows to be converted to XML. This maximum is relative to the current row position from which the previous result was generated. -
setSkipRowsspecifies the number of rows to skip before converting the row values to XML.
Run the paginateResult.sql script to execute an anonymous block that paginates results. It skips the first 3 rows of the employees table and prints the rest of the rows 10 at a time by setting skipRows to 3 for the first batch of 10 rows and then to 0 for the rest of the batches. For multiple fetches, you must determine when there are no more rows to fetch, which you can do by invoking setRaiseNoRowsException. This procedure raises an exception if no rows are written to the CLOB. This exception can be caught and used as the termination condition.
Setting Style Sheets in XSU
The XSU PL/SQL API provides the ability to set style sheets on the generated XML documents as follows:
-
Set the style sheet header in the result with the
setStylesheetHeaderprocedure. This procedure adds the XML processing instruction that includes the style sheet. -
Apply a style sheet to the resulting XML document before generation. This method increases performance dramatically because otherwise the XML document must be generated as a CLOB, sent to the parser again, and have the style sheet applied. XSU generates a DOM document, invokes the parser, applies the style sheet and then generates the result. To apply the style sheet to the resulting XML document, use the
setXSLTprocedure, which uses the style sheet to generate the result.
Binding Values in XSU
The XSU PL/SQL API provides the ability to bind values to a SQL statement. The SQL statement can contain named bind variables, which must be prefixed with a colon (:). The bindSQLVariables.sql script runs an anonymous PL/SQL block that binds values for EMPLOYEE_ID and FIRST_NAME to columns in the employees table.
Inserting XML with DBMS_XMLSave
To insert a document into a table or view, supply the table or the view name and then the XML document. XSU parses the XML document (if a string is given) and then creates an INSERT statement into which it binds all the values. By default, XSU inserts values into all the columns of the table or view and treats absent elements as NULL.
Inserting Values into All Columns with DBMS_XMLSave
Run the insProc.sql demo script to create a PL/SQL stored procedure, insProc, which accepts these parameters:
-
An XML document as a
CLOB -
The name of the table in which to insert the document
You can invoke the insProc procedure to insert an XML document into the table.
Run the insertClob.sql script to create a table called xmldocument and store an XML document in the table as a CLOB. The XML document describes employee 7370, Liz Gardner, whom you want to insert into the hr.employees table.
CREATE TABLE hr.xmldocument
(docid NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
xml_text CLOB);
-- insert an XML document into the CLOB column
INSERT INTO hr.xmldocument (docid,xml_text)
VALUES (1,
'<?xml version="1.0"?>
<ROWSET>
<ROW num="1">
<EMPLOYEE_ID>7370</EMPLOYEE_ID>
<FIRST_NAME>Liz</FIRST_NAME>
<LAST_NAME>Gardner</LAST_NAME>
<EMAIL>liz.gardner@business.com</EMAIL>
<PHONE_NUMBER>650-555-6127</PHONE_NUMBER>
<HIRE_DATE>12/18/2004 0:0:0</HIRE_DATE>
<SALARY>3000</SALARY>
<COMMISSION_PCT>0</COMMISSION_PCT>
<JOB_ID>SH_CLERK</JOB_ID>
<MANAGER_ID>103</MANAGER_ID>
<DEPARTMENT_ID>20</DEPARTMENT_ID>
</ROW>
</ROWSET>');
Run the insertEmployee.sql script shown in Example 13-4 to call the insProc stored procedure and insert Liz Gardner into the employees table.
Example 13-4 insertEmployee.sql
DECLARE
v_xml_text CLOB;
BEGIN
SELECT xml_text
INTO v_xml_text
FROM hr.xmldocument
WHERE docid = 1;
insProc(v_xml_text, 'employees');
END;
/
As in "Inserting Rows with OracleXMLSave," running the callinsProc procedure generates an INSERT statement of the form shown in Example 13-5.
Example 13-5 Form of the INSERT Statement
INSERT INTO hr.employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, hire_date, salary, commission_pct, manager_id, department_id) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?);
XSU matches the element tags in the input XML document that match the column names and binds their values.
Inserting into a Subset of Columns with DBMS_XMLSave
As explained in "Inserting XML into a Subset of Columns with OracleXMLSave," you may not want to insert values into all columns. You can create a list of column names for insert processing and pass it to the DBMS_XMLSave procedure. You can set these values by invoking the setUpdateColumnName procedure repeatedly and passing in a column name to update every time. Clear the column name settings by invoking clearUpdateColumnList.
Run the testInsert.sql demo script to create a PL/SQL stored procedure called testInsert. You can use this procedure to insert XML data of type CLOB into the hr.employees table.
Run the insertClob2.sql script shown in Example 13-6 to insert an XML document describing new employee Jordan into a CLOB column of the xmldocument table. The document does not contain an element corresponding to every column in the employees table.
-- insert an XML document into the CLOB column of the xmldocument table with only
-- some of the possible elements
INSERT INTO hr.xmldocument (docid, xml_text)
VALUES (2,
'<?xml version="1.0"?>
<ROWSET>
<ROW num="1">
<EMPLOYEE_ID>7401</EMPLOYEE_ID>
<LAST_NAME>Jordan</LAST_NAME>
<EMAIL>jim.jordan@business.com</EMAIL>
<JOB_ID>SH_CLERK</JOB_ID>
<HIRE_DATE>12/17/2004 0:0:0</HIRE_DATE>
</ROW>
</ROWSET>');
Running the insertEmployee2.sql script shown in Example 13-7 inserts the data for employee Jim Jordan into a subset of the columns in the hr.employees table.
Example 13-7 insertEmployee2.sql
DECLARE
v_xml_text CLOB;
BEGIN
SELECT xml_text
INTO v_xml_text
FROM hr.xmldocument
WHERE docid = 2;
testInsert(v_xml_text);
END;
/
As in "Inserting XML into a Subset of Columns with OracleXMLSave," invoking testInsert generates this INSERT statement:
INSERT INTO hr.employees (employee_id, last_name, email, job_id, hire_date) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?);
Updating with DBMS_XMLSave
As described in "Updating Rows with OracleXMLSave," you can use an XML document to update specified fields in a table. You can either specify a column to use as a key or pass a list of columns for updating.
Updating Key Columns with DBMS_XMLSave
Run the testUpdateKey.sql script to create a PL/SQL procedure called testUpdateKey. This procedure uses the employee_id column of the hr.employees table as a primary key.
Run the insertClob3.sql script shown in shown in Example 13-8 to insert an XML document into the CLOB column of the xmldocument table. The document specifies a new salary for employee 7400 and a new job ID and manager ID for employee 7369.
INSERT INTO hr.xmldocument (docid, xml_text)
VALUES (3,
'<?xml version="1.0"?>
<ROWSET>
<ROW num="1">
<EMPLOYEE_ID>7400</EMPLOYEE_ID>
<SALARY>3250</SALARY>
</ROW>
<ROW num="2">
<EMPLOYEE_ID>7369</EMPLOYEE_ID>
<JOB_ID>SA_REP</JOB_ID>
<MANAGER_ID>145</MANAGER_ID>
</ROW>
</ROWSET>');
Run the updateEmployee.sql script shown in Example 13-9 to pass the XML document to the testUpdateKey procedure and generate two UPDATE statements.
Example 13-9 updateEmployee.sql
DECLARE
v_xml_text CLOB;
BEGIN
SELECT xml_text
INTO v_xml_text
FROM hr.xmldocument
WHERE docid = 3;
testUpdateKey(v_xml_text);
END;
/
For the first ROW element, the program generates an UPDATE statement:
UPDATE hr.employees SET salary = 3250 WHERE employee_id = 7400;
For the second ROW element the program generates this statement:
UPDATE hr.employees SET job_id = 'SA_REP' AND MANAGER_ID = 145 WHERE employee_id = 7369;
Specifying a List of Columns with DBMS_XMLSave: Example
As described in "Updating a Column List with OracleXMLSave," you can specify a list of columns to update.
Run the testUpdateSubset.sql script creates the PL/SQL procedure testUpdateSubset. The procedure uses the employee_id column as key and updates only the salary and job_id columns of the hr.employees table.
Run the insertClob4.sql script to insert an XML document into the xmldocument table. The <ROW> elements in the document describe employees 100 and 206. Each <ROW> element has ten subelements that contain descriptive text.
Run the updateEmployee2.sql script shown in Example 13-10 to pass the XML CLOB to the testUpdateSubset procedure and generate two UPDATE statements.
Example 13-10 updateEmployee2.sql
DECLARE
v_xml_text CLOB;
BEGIN
SELECT xml_text
INTO v_xml_text
FROM hr.xmldocument
WHERE docid = 4;
testUpdateSubset(v_xml_text);
END;
/
The procedure updates only those columns specified in the setUpdateColumn procedure, salary and email, for employees 100 and 206.
Deleting with DBMS_XMLSave
As described in "Deleting Rows with OracleXMLSave," you can supply a list of key columns that XSU uses to determine which rows to delete. XSU specifies these columns in the WHERE clause of the DELETE statement.
Deleting by Row with DBMS_XMLSave: Example
Create the testDeleteRow PL/SQL procedure by running the testDeleteRow.sql script. The procedure deletes a row from the hr.employees table for every <ROW> element in an input XML document.
Suppose you want to delete the employee Jim Jordan that you added in Example 13-7. Run the deleteEmployeeByRow.sql script shown in Example 13-11 to pass the XML document as a CLOB to the testDeleteRow stored procedure.
DECLARE
v_xml_text CLOB;
BEGIN
SELECT xml_text
INTO v_xml_text
FROM hr.xmldocument
WHERE docid = 2;
testDeleteRow(v_xml_text);
END;
/
The preceding invocation of testDeleteRow generates this DELETE statement:
DELETE FROM hr.employees WHERE employee_id = 7401 AND last_name = 'JORDAN' AND email = 'jim.jordan@business.com' AND job_id = 'SH_CLERK' AND hire_date = '12/17/2004 0:0:0';
The program forms the DELETE statements based on the tag names present in each <ROW> element in the XML document.
Deleting by Key with DBMS_XMLSave: Example
As explained in "Deleting by Key with OracleXMLSave," you can specify a column to use as a primary key for the deletions. Use the DBMS_XMLSave.setKeyColumn function to specify the key.
The testDeleteKey procedure created by running testDeleteKey.sql deletes a row from the employees table for every <ROW> element in an input XML document.
Suppose you want to delete the employee Liz Gardner that you added in Example 13-4. Run the deleteEmployeeByKey.sql script shown in Example 13-12 to pass the XML document as a CLOB to the testDeleteKey stored procedure.
DECLARE
v_xml_text CLOB;
BEGIN
SELECT xml_text
INTO v_xml_text
FROM hr.xmldocument
WHERE docid = 1;
testDeleteKey(v_xml_text);
END;
/
In the preceding procedure call, XSU generates a single DELETE statement of this form:
DELETE FROM hr.employees WHERE employee_id=?
XSU uses this statement for all ROW elements in the input XML document.
Handling Exceptions in the XSU PL/SQL API
Good PL/SQL coding practice accounts for possible exceptions. The anonymous PL/SQL block in raiseException.sql demonstrates how to invoke the DBMS_XMLQuery.getExceptionContent procedure. Run the script in SQL*Plus to print this error message:
Exception caught 904 ORA-00904: "Z": invalid identifier
Reusing the Context Handle with DBMS_XMLSave
In the DML examples described in the preceding sections, you can use the same context handle to perform more than one operation. That is, you can perform more than one INSERT with the same context if all of the insertions access the same table specified when creating the save context. You can also use the same context to mix DML statements.
The testDML.sql script shows how to use the same context and settings to perform DML depending on user input. The example uses a PL/SQL supplied package static variable to store the context so that the same context can be used for all function invocations.
In the testDML package created by the script, you create a context once for the whole package (and thus the session) and reuse the context for multiple DML operations.
Note:
The key columnemployee_id is used both for updates and deletes as a way of identifying the row.You can call any of the three procedures created by the script to update the employees table:
testDML.insertXML(xmlclob); testDML.deleteXML(xmlclob); testDML.updateXML(xmlclob);
Each procedure call uses the same context, which improves the performance of these operations, particularly if these operations are performed frequently.
Tips and Techniques for Programming with XSU
This section provides additional tips and techniques for writing programs with XSU.
How XSU Maps Between SQL and XML
The fundamental component of a table is a column, whereas the fundamental components of an XML document are elements and attributes. How do tables map to XML documents? For example, if the hr.employees table has a column called last_name, how is this structure represented in XML: as an <EMPLOYEES> element with a last_name attribute or as a <LAST_NAME> element within a different root element? This section answers such questions by describing how SQL maps to XML and the reverse.
Default SQL-to-XML Mapping
To display data from some column of the hr.employees table as an XML document, run XSU at the command line:
java OracleXML getXML -user "hr/password" -withschema \
"SELECT employee_id, last_name, hire_date FROM employees"
XSU outputs an XML document based on the input query. The root element of the document is <DOCUMENT>. The following shows sample output, with extraneous lines replaced by comments:
<?xml version = '1.0'?>
<DOCUMENT xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<!-- children of schema element ... -->
</xsd:schema>
<ROWSET xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="#/DOCUMENT/xsd:schema[not(@targetNamespace)]">
<ROW num="1">
<EMPLOYEE_ID>100</EMPLOYEE_ID>
<LAST_NAME>King</LAST_NAME>
<HIRE_DATE>6/17/1987 0:0:0</HIRE_DATE>
</ROW>
<!-- additional rows ... -->
</ROWSET>
</DOCUMENT>
In the generated XML, the rows returned by the SQL query are children of the <ROWSET> element. The XML document has these features:
-
The
<ROWSET>element has zero or more<ROW>child elements corresponding to the number of rows returned. If the query generates no rows, then no<ROW>elements are included; if the query generates one row, then one<ROW>element is included, and so forth. -
Each
<ROW>element contains data from one table row. Specifically, each<ROW>element has one or more child elements whose names and content are identical to the database columns specified in theSELECTstatement.
XML Mapping Against an Object-Relational Schema
Assume a case in which you generate an XML document from an object-relational schema. Run the createObjRelSchema.sql script in SQL*Plus to set up and populate an object-relational schema. The schema contains a dept1 table with two columns that employ user-defined types.
You can query the dept1 table by invoking XSU from the command line:
% java OracleXML getXML -user "hr/password" -withschema "SELECT * FROM dept1"
XSU returns the XML document shown in Example 13-13, which is altered so that extraneous lines are replaced by comments.
Example 13-13 XSU-Generated Sample Document
<?xml version='1.0'?>
<DOCUMENT xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<schema targetNamespace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/SYSTEM"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:SYSTEM="http://xmlns.oracle.com/xdb/SYSTEM">
<!-- children of schema element ... -->
</xsd:schema>
<ROWSET xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="#/DOCUMENT/xsd:schema[not(@targetNamespace)]">
<ROW num="1">
<DEPTNO>120</DEPTNO>
<DEPTNAME>Treasury</DEPTNAME>
<DEPTADDR>
<STREET>2004 Charade Rd</STREET>
<CITY>Seattle</CITY>
<STATE>WA</STATE>
<ZIP>98199</ZIP>
</DEPTADDR>
<EMPLIST>
<EMPLIST_ITEM>
<EMPLOYEE_ID>1</EMPLOYEE_ID>
<LAST_NAME>Mehta</LAST_NAME>
<SALARY>6000</SALARY>
<EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS>
<STREET>500 Main Road</STREET>
<CITY>Seattle</CITY>
<STATE>WA</STATE>
<ZIP>98199</ZIP>
</EMPLOYEE_ADDRESS>
</EMPLIST_ITEM>
</EMPLIST>
</ROW>
</ROWSET>
</DOCUMENT>
As in the previous example, the mapping is canonical, that is, <ROWSET> contains <ROW> child elements, which in turn contain child elements corresponding to the columns in dept1. For example, the <DEPTNAME> element corresponds to the dept1.deptname column. The elements corresponding to scalar type columns contain the data from the columns.
Default Mapping of Complex Type Columns to XML
The situation is more complex with elements corresponding to a complex type column. In Example 13-13, <DEPTADDR> corresponds to the dept1.deptAddr column, which is of object type AddressType. Consequently, <DEPTADDR> contains child elements corresponding to the attributes specified in the type AddressType. The AddressType attribute street corresponds to the child XML element <STREET> and so forth. These subelements can contain data or subelements of their own, depending on whether the attribute they correspond to is of a simple or complex type.
Default Mapping of Collections to XML
When dealing with elements corresponding to database collections, the situation is also different. In Example 13-13, the <EMPLIST> element corresponds to the emplist column of type EmployeeListType. Consequently, the <EMPLIST> element contains a list of <EMPLIST_ITEM> elements, each corresponding to an element of the collection. Note:
-
The
<ROW>elements contain a cardinality attributenum. -
If a particular column or attribute value is
NULL, then for that row, the corresponding XML element is omitted. -
If a top-level scalar column name starts with the at sign (@) character, then the column is mapped to an XML attribute instead of an XML element.
Default XML-to-SQL Mapping
XML to SQL mapping is the reverse of SQL to XML mapping. Consider these differences when using XSU to map XML to SQL:
-
When transforming XML to SQL, XSU ignores XML attributes. Thus, there is really no mapping of XML attributes to SQL.
-
When transforming SQL to XML, XSU performs the mapping on a single
ResultSetcreated by a SQL query. The query can span multiple database tables or views. When transforming XML into SQL, note:-
To insert one XML document into multiple tables or views, you must create an object-relational view over the target schema.
-
If the view is not updatable, then you can use
INSTEAD OF INSERTtriggers.
-
If the XML document does not perfectly map to the target database schema, then you can perform these actions:
-
Modify the target. Create an object-relational view over the target schema and make the view the new target.
-
Modify the XML document by using XSLT to transform the XML document. You can register the XSLT style sheet with XSU so that the incoming XML is automatically transformed before it attempts any mapping.
-
Modify XSU's XML-to-SQL mapping. You can instruct XSU to perform case-insensitive matching of XML elements to database columns or attributes. For example, you can instruct XSU to do this:
-
Use the name of the element corresponding to a database row instead of
ROW. -
Specify the date format to use when parsing dates in the XML document.
-
Customizing Generated XML
In some situations, you might have to generate XML with a specific structure. Because the desired structure may differ from the default structure of the generated XML document, you want to have some flexibility in this process. You can customize the structure of a generated XML document by using one of these methods:
Altering the Database Schema or SQL Query
You can perform source customizations by altering the SQL query or the database schema. The simplest and most powerful source customizations include:
-
In the database schema, create an object-relational view that maps to the desired XML document structure.
-
In your query, do this:
-
Use cursor subqueries or cast-multiset constructs to create nesting in the XML document that comes from a flat schema.
-
Alias column and attribute names to get the desired XML element names.
-
Alias top-level scalar type columns with identifiers that begin with the at sign (@) to make them map to an XML attribute instead of an XML element. For example, executing these statement generates an XML document in which the
<ROW>element has the attributeempno:SELECT employee_name AS "@empno",... FROM employees;
-
Consider the customer.xml document shown in Example 13-14.
<?xml version = "1.0"?>
<ROWSET>
<ROW num="1">
<CUSTOMER>
<CUSTOMERID>1044</CUSTOMERID>
<FIRSTNAME>Paul</FIRSTNAME>
<LASTNAME>Astoria</LASTNAME>
<HOMEADDRESS>
<STREET>123 Cherry Lane</STREET>
<CITY>SF</CITY>
<STATE>CA</STATE>
<ZIP>94132</ZIP>
</HOMEADDRESS>
</CUSTOMER>
</ROW>
</ROWSET>
Suppose you must design a set of database tables to store this data. Because the XML is nested more than one level, you can use an object-relational database schema that maps canonically to the preceding XML document. Run the createObjRelSchema2.sql script in SQL*Plus to create such a database schema.
You can load the data in the customer.xml document into the customer_tab table created by the script. Invoke XSU for Java from the command line:
java OracleXML putXML -user "hr/password" -fileName customer.xml customer_tab
To load customer.xml into a database schema that is not object-relational, you can create objects in views on top of a standard relational schema. For example, you can create a relational table that contains the necessary columns, then create a customer view that contains a customer object on top of it, as shown in the createRelSchema.sql script in Example 13-15.
Example 13-15 createRelSchema.sql
CREATE TABLE hr.cust_tab
( customerid NUMBER(10),
firstname VARCHAR2(20),
lastname VARCHAR2(20),
street VARCHAR2(40),
city VARCHAR2(20),
state VARCHAR2(20),
zip VARCHAR2(20)
);
CREATE VIEW customer_view
AS
SELECT customer_type(customerid, firstname, lastname,
address_type(street,city,state,zip)) customer
FROM cust_tab;
You can load data into customer_view:
java OracleXML putXML -user "hr/password" -fileName customer.xml customer_view
Alternatively, you can flatten your XML with XSLT and then insert it directly into a relational schema. However, this is the least recommended option.
To map a particular column or a group of columns to an XML attribute instead of an XML element, you can create an alias for the column name and prepend the at sign (@) before the name of this alias. For example, you can use the mapColumnToAtt.sql script to query the hr.employees table, rendering employee_id as an XML attribute.
You can run the mapColumnToAtt.sql script from the command line:
java OracleXML getXML -user "hr/password" -fileName "mapColumnToAtt.sql"
Note:
All attributes must appear before any nonattribute.Modifying XSU
XSU enables you to modify the rules that it uses to transform SQL data into XML. You can make any of these changes when mapping SQL to XML:
-
Change or omit the
<ROWSET>or<ROW>tag. -
Change or omit the attribute
num, which is the cardinality attribute of the<ROW>element. -
Specify the case for the generated XML element names.
-
Specify that XML elements corresponding to elements of a collection must have a cardinality attribute.
-
Specify the format for dates in the XML document.
-
Specify that null values in the XML document must be indicated with a nullness attribute rather than by omitting the element.
How XSU Processes SQL Statements
This section describes how XSU interacts with the database:
How XSU Queries the Database
XSU executes SQL queries and retrieves the ResultSet from the database. XSU then acquires and analyzes metadata about the ResultSet. Using the mapping described in "Default SQL-to-XML Mapping," XSU processes the SQL result set and converts it into an XML document.
XSU cannot handle certain types of queries, especially those that mix columns of type LONG or LONG RAW with CURSOR() expressions in the SELECT clause. LONG and LONG RAW are two examples of data types that JDBC accesses as streams and whose use is deprecated. If you migrate these columns to CLOBs, then the queries succeed.
How XSU Inserts Rows
When inserting the contents of an XML document into a table or view, XSU performs these steps:
-
Retrieves metadata about the target table or view.
-
Generates a SQL
INSERTstatement based on the metadata. For example, assume that the target table isdept1and the XML document is generated fromdept1. XSU generates thisINSERTstatement:INSERT INTO dept1 (deptno, deptname, deptaddr, emplist) VALUES (?,?,?,?)
-
Parses the XML document, and for each record, it binds the appropriate values to the appropriate columns or attributes. For example, it binds the values for
INSERTstatement:deptno <- 100 deptname <- SPORTS deptaddr <- AddressType('100 Redwood Shores Pkwy','Redwood Shores', 'CA','94065') emplist <- EmployeeListType(EmployeeType(7369,'John',100000, AddressType('300 Embarcadero','Palo Alto','CA','94056'),...) -
Executes the statement. You can optimize
INSERTprocessing to insert in batches and commit in batches.
See Also:
-
"Inserting Rows with OracleXMLSave" for more detail on batching
How XSU Updates Rows
Updates and delete statements differ from inserts in that they can affect more than one row in the database table. For inserts, each <ROW> element of the XML document can affect at most one row in the table if no triggers or constraints are on the table. With updates and deletes, the XML element can match more than one row if the matching columns are not key columns in the table.
For update statements, you must provide a list of key columns that XSU must identify the row to update. For example, assume that you have an XML document that contains this fragment:
<ROWSET>
<ROW num="1">
<DEPTNO>100</DEPTNO>
<DEPTNAME>SportsDept</DEPTNAME>
</ROW>
</ROWSET>
You want to change the DEPTNAME value from Sports to SportsDept. If you supply the DEPTNO as the key column, then XSU generates this UPDATE statement:
UPDATE dept1 SET deptname = ? WHERE deptno = ?
XSU binds the values in this way:
deptno <- 100 deptname <- SportsDept
For updates, you can also choose to update only a set of columns and not all the elements present in the XML document.
See Also:
"Updating Rows with OracleXMLSave"How XSU Deletes Rows
For deletes, you can choose to provide a set of key columns so that XSU can identify the rows to be deleted. If you do not provide the set of key columns, then the DELETE statement tries to match all the columns in the document. Assume that you pass this document to XSU:
<ROWSET>
<ROW num="1">
<DEPTNO>100</DEPTNO>
<DEPTNAME>Sports</DEPTNAME>
<DEPTADDR>
<STREET>100 Redwood Shores Pkwy</STREET>
<CITY>Redwood Shores</CITY>
<STATE>CA</STATE>
<ZIP>94065</ZIP>
</DEPTADDR>
</ROW>
<!-- additional rows ... -->
</ROWSET>
XSU builds a DELETE statement for each ROW element:
DELETE FROM dept1 WHERE deptno = ? AND deptname = ? AND deptaddr = ?
The binding is:
deptno <- 100
deptname <- sports
deptaddr <- addresstype('100 redwood shores pkwy','redwood city','ca',
'94065')
See Also:
"Deleting Rows with OracleXMLSave"How XSU Commits After DML
By default XSU performs no explicit commits. If AUTOCOMMIT is on, which is the default for a JDBC connection, then after each batch of statement executions XSU executes a COMMIT. You can override this behavior by turning AUTOCOMMIT off and then using setCommitBatch to specify the number of statement executions before XSU commits. If an error occurs, then XSU rolls back to either the state the target table was in before the call to XSU, or the state after the last commit made during the current call to XSU.