ALTER PROCEDURE Statement
The ALTER PROCEDURE statement explicitly recompiles a standalone procedure. Explicit recompilation eliminates the need for implicit runtime recompilation and prevents associated runtime compilation errors and performance overhead.
To recompile a procedure that is part of a package, recompile the entire package using the "ALTER PACKAGE Statement").
Note:
This statement does not change the declaration or definition of an existing procedure. To redeclare or redefine a standalone procedure, use the "CREATE PROCEDURE Statement" with theOR REPLACE clause.The ALTER PROCEDURE statement is very similar to the ALTER FUNCTION statement. See "ALTER FUNCTION Statement" for more information.
If the procedure is in the SYS schema, you must be connected as SYSDBA. Otherwise, the procedure must be in your schema or you must have ALTER ANY PROCEDURE system privilege.
Description of the illustration alter_procedure.gif

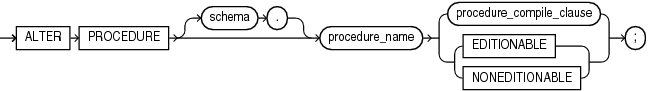
Description of the illustration procedure_compile_clause.gif
compiler_parameters_clause ::=
Description of the illustration compiler_parameters_clause.gif
Name of the schema containing the procedure. Default: your schema.
Name of the procedure to be recompiled.
Has the same behavior for a procedure as it does for a function. See "COMPILE".
See Also:
"Recompiling a Procedure: Example"Has the same behavior for a procedure as it does for a function. See "DEBUG".
See Also:
Oracle Database Development Guide for information about debugging proceduresHas the same behavior for a procedure as it does for a function. See "REUSE SETTINGS".
Has the same behavior for a procedure as it does for a function. See the ALTER FUNCTION "compiler_parameters_clause".
{ EDITIONABLE | NONEDITIONABLE }
Specifies whether the procedure becomes an editioned or noneditioned object if editioning is later enabled for the schema object type PROCEDURE in schema. Default: EDITIONABLE. For information about altering editioned and noneditioned objects, see Oracle Database Development Guide.
Recompiling a Procedure: Example To explicitly recompile the procedure remove_emp owned by the user hr, issue this statement:
ALTER PROCEDURE hr.remove_emp COMPILE;
If the database encounters no compilation errors while recompiling remove_emp, then remove_emp becomes valid. The database can subsequently run it without recompiling it at run time. If recompiling remove_emp results in compilation errors, then the database returns an error and remove_emp remains invalid.
the database also invalidates all dependent objects. These objects include any procedures, functions, and package bodies that invoke remove_emp. If you subsequently reference one of these objects without first explicitly recompiling it, then the database recompiles it implicitly at run time.