RETURNING INTO Clause
The RETURNING INTO clause specifies the variables in which to store the values returned by the statement to which the clause belongs. The variables can be either individual variables or collections. If the statement affects no rows, then the values of the variables are undefined.
The static RETURNING INTO clause belongs to a DELETE, INSERT, or UPDATE statement. The dynamic RETURNING INTO clause belongs to the EXECUTE IMMEDIATE statement.
Note:
You cannot use theRETURNING INTO clause for remote or parallel deletes.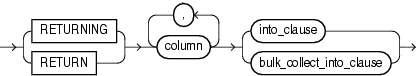
Description of the illustration static_returning_clause.gif
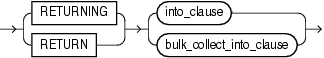
Description of the illustration dynamic_returning_clause.gif
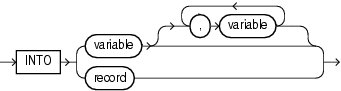
Description of the illustration into_clause.gif
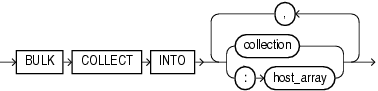
Description of the illustration bulk_collect_into_clause.gif
Expression whose value is the name of a column of a database table.
Specifies the variables or record in which to store the column values that the statement returns.
Restriction on into_clause Use into_clause in dynamic_returning_clause if and only if dynamic_sql_stmt (which appears in "EXECUTE IMMEDIATE Statement") returns a single row.
The name of a record variable in which to store the row that the statement returns. For each select_item in the statement, the record must have a corresponding, type-compatible field.
Either the name of a scalar variable in which to store a column that the statement returns or the name of a host cursor variable that is declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind variable. Each select_item in the statement must have a corresponding, type-compatible variable. The data type of a host cursor variable is compatible with the return type of any PL/SQL cursor variable.
Restriction on variable variable cannot have the data type BOOLEAN.
Specifies one or more existing collections or host arrays in which to store the rows that the statement returns. For each select_item in the statement, bulk_collect_into_clause must have a corresponding, type-compatible collection or host_array.
For the reason to use this clause, see "Bulk SQL and Bulk Binding".
Restrictions on bulk_collect_into_clause
-
Use the
bulk_collect_into_clauseclause indynamic_returning_clauseif and only ifdynamic_sql_stmt(which appears in "EXECUTE IMMEDIATE Statement") can return multiple rows. -
You cannot use
bulk_collect_into_clausein client programs. -
When the statement that includes
bulk_collect_into_clauserequires implicit data type conversions,bulk_collect_into_clausecan have only onecollectionorhost_array.
Name of a collection variable in which to store the rows that the statement returns.
-
collectioncannot be the name of an associative array that is indexed by a string. -
When the statement requires implicit data type conversions,
collectioncannot be the name of a collection of a composite type.
Name of an array declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind variable. Do not put space between the colon (:) and host_array.