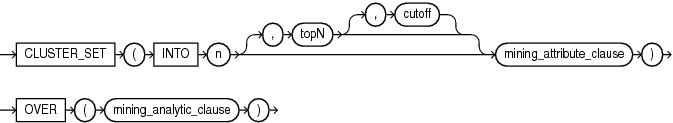
CLUSTER_SET

Description of the illustration cluster_set.gif
Description of the illustration cluster_set_analytic.gif
Description of the illustration mining_attribute_clause.gif
Description of the illustration mining_analytic_clause.gif
See Also:
"Analytic Functions" for information on the syntax, semantics, and restrictions ofmining_analytic_clauseCLUSTER_SET returns a set of cluster ID and probability pairs for each row in the selection. The return value is a varray of objects with field names CLUSTER_ID and PROBABILITY. The cluster identifier is an Oracle NUMBER; the probability is BINARY_DOUBLE.
You can specify topN and cutoff to limit the number of clusters returned by the function. By default, both topN and cutoff are null and all clusters are returned.
-
topNis theNmost probable clusters. If multiple clusters share theNth probability, then the function chooses one of them. -
cutoffis a probability threshold. Only clusters with probability greater than or equal tocutoffare returned. To filter bycutoffonly, specifyNULLfortopN.
To return up to the N most probable clusters that are greater than or equal to cutoff, specify both topN and cutoff.
CLUSTER_SET can score the data in one of two ways: It can apply a mining model object to the data, or it can dynamically mine the data by executing an analytic clause that builds and applies one or more transient mining models. Choose Syntax or Analytic Syntax:
-
Syntax — Use the first syntax to score the data with a pre-defined model. Supply the name of a clustering model.
-
Analytic Syntax — Use the analytic syntax to score the data without a pre-defined model. Include
INTOn, wherenis the number of clusters to compute, andmining_analytic_clause, which specifies if the data should be partitioned for multiple model builds. Themining_analytic_clausesupports aquery_partition_clauseand anorder_by_clause. (See "analytic_clause::=".)
mining_attribute_clause identifies the column attributes to use as predictors for scoring. When the function is invoked with the analytic syntax, these predictors are also used for building the transient models. The mining_attribute_clause behaves as described for the PREDICTION function. (See "mining_attribute_clause::=".)
See Also:
-
Oracle Data Mining User's Guide for information about scoring.
-
Oracle Data Mining Concepts for information about clustering.
About the Example:
The following example is excerpted from the Data Mining sample programs. For more information about the sample programs, see Appendix A in Oracle Data Mining User's Guide.This example lists the attributes that have the greatest impact (more that 20% probability) on cluster assignment for customer ID 100955. The query invokes the CLUSTER_DETAILS and CLUSTER_SET functions, which apply the clustering model em_sh_clus_sample.
SELECT S.cluster_id, probability prob,
CLUSTER_DETAILS(em_sh_clus_sample, S.cluster_id, 5 USING T.*) det
FROM
(SELECT v.*, CLUSTER_SET(em_sh_clus_sample, NULL, 0.2 USING *) pset
FROM mining_data_apply_v v
WHERE cust_id = 100955) T,
TABLE(T.pset) S
ORDER BY 2 DESC;
CLUSTER_ID PROB DET
---------- ----- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
14 .6761 <Details algorithm="Expectation Maximization" cluster="14">
<Attribute name="AGE" actualValue="51" weight=".676" rank="1"/>
<Attribute name="HOME_THEATER_PACKAGE" actualValue="1" weight=".557" rank="2"/>
<Attribute name="FLAT_PANEL_MONITOR" actualValue="0" weight=".412" rank="3"/>
<Attribute name="Y_BOX_GAMES" actualValue="0" weight=".171" rank="4"/>
<Attribute name="BOOKKEEPING_APPLICATION" actualValue="1" weight="-.003"rank="5"/>
</Details>
3 .3227 <Details algorithm="Expectation Maximization" cluster="3">
<Attribute name="YRS_RESIDENCE" actualValue="3" weight=".323" rank="1"/>
<Attribute name="BULK_PACK_DISKETTES" actualValue="1" weight=".265" rank="2"/>
<Attribute name="EDUCATION" actualValue="HS-grad" weight=".172" rank="3"/>
<Attribute name="AFFINITY_CARD" actualValue="0" weight=".125" rank="4"/>
<Attribute name="OCCUPATION" actualValue="Crafts" weight=".055" rank="5"/>
</Details>