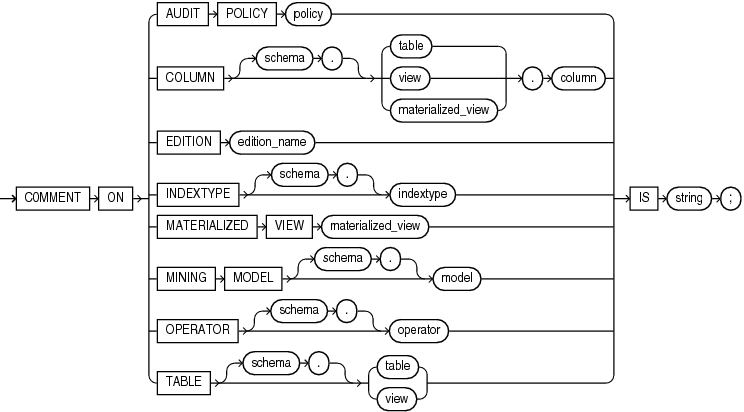
COMMENT
Use the COMMENT statement to add to the data dictionary a comment about a table or table column, unified audit policy, edition, indextype, materialized view, mining model, operator, or view.
To drop a comment from the database, set it to the empty string ' '.
See Also:
-
"Comments" for more information on associating comments with SQL statements and schema objects
-
Oracle Database Reference for information on the data dictionary views that display comments
The object about which you are adding a comment must be in your own schema or:
-
To add a comment to a table, view, or materialized view, you must have
COMMENTANYTABLEsystem privilege. -
To add a comment to a unified audit policy, you must have the
AUDITSYSTEMsystem privilege or theAUDIT_ADMINrole. -
To add a comment to an edition, you must have the
CREATEANYEDITIONsystem privilege, granted either directly or through a role. -
To add a comment to an indextype, you must have the
CREATEANYINDEXTYPEsystem privilege. -
To add a comment to a mining model, you must have the
COMMENTANYMININGMODELsystem privilege. -
To add a comment to an operator, you must have the
CREATEANYOPERATORsystem privilege.
Specify the name of the unified audit policy to be commented.
You can view the comments on a particular unified audit policy by querying the AUDIT_UNIFIED_POLICY_COMMENTS data dictionary view.
Specify the name of the column of a table, view, or materialized view to be commented. If you omit schema, then Oracle Database assumes the table, view, or materialized view is in your own schema.
You can view the comments on a particular table or column by querying the data dictionary views USER_TAB_COMMENTS, DBA_TAB_COMMENTS, or ALL_TAB_COMMENTS or USER_COL_COMMENTS, DBA_COL_COMMENTS, or ALL_COL_COMMENTS.
Specify the name of an existing edition to be commented.
You can query the data dictionary view ALL_EDITION_COMMENTS to view comments associated with editions that are accessible to the current user. You can query DBA_EDITION_COMMENTS to view comments associated with all editions in the database.
Specify the schema and name of the table or materialized view to be commented. If you omit schema, then Oracle Database assumes the table or materialized view is in your own schema.
Note:
In earlier releases, you could use this clause to create a comment on a materialized view. You should now use theCOMMENT ON MATERIALIZED VIEW clause for materialized views.Specify the name of the indextype to be commented. If you omit schema, then Oracle Database assumes the indextype is in your own schema.
You can view the comments on a particular indextype by querying the data dictionary views USER_INDEXTYPE_COMMENTS, DBA_INDEXTYPE_COMMENTS, or ALL_INDEXTYPE_COMMENTS.
Specify the name of the materialized view to be commented. If you omit schema, then Oracle Database assumes the materialized view is in your own schema.
You can view the comments on a particular materialized view by querying the data dictionary views USER_MVIEW_COMMENTS, DBA_MVIEW_COMMENTS, or ALL_MVIEW_COMMENTS.
Specify the name of the mining model to be commented.
You can view the comments on a particular mining model by querying the COMMENTS column of the data dictionary views USER_MINING_MODELS, DBA_MINING_MODELS, or ALL_MINING_MODELS.
Specify the name of the operator to be commented. If you omit schema, then Oracle Database assumes the operator is in your own schema.
You can view the comments on a particular operator by querying the data dictionary views USER_OPERATOR_COMMENTS, DBA_OPERATOR_COMMENTS, or ALL_OPERATOR_COMMENTS.
Specify the text of the comment. Refer to "Text Literals" for a syntax description of 'string'.
Creating Comments: Example To insert an explanatory remark on the job_id column of the employees table, you might issue the following statement:
COMMENT ON COLUMN employees.job_id IS 'abbreviated job title';
To drop this comment from the database, issue the following statement:
COMMENT ON COLUMN employees.job_id IS '';