| Oracle® Enterprise Manager Concepts 10g Release 4 (10.2.0.4) Part Number B31949-07 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Enterprise Manager Concepts 10g Release 4 (10.2.0.4) Part Number B31949-07 |
|
|
View PDF |
Before you begin using Enterprise Manager, establish standard administrative settings in the Setup and Privileges pages, such as roles, notifications, passwords, templates, plug-ins, and more. These settings will help you manage user administration, communication, notification, standard actions and access, and security.
This chapter contains the following sections:
The Grid Control Setup area allows you to configure the following:
Figure 2-1 Grid Control's Overview of Setup Page
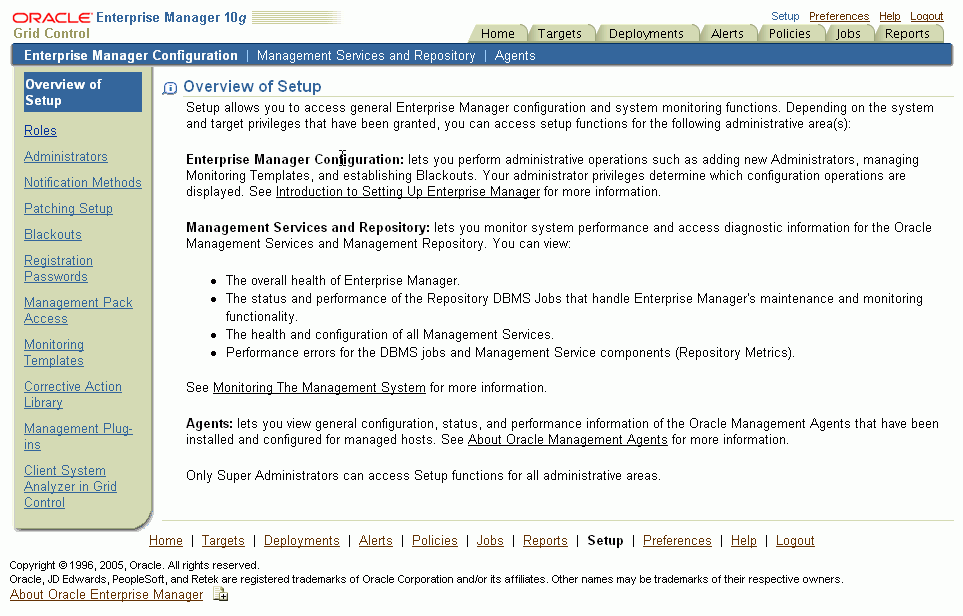
Roles allow you to group Enterprise Manager system and target privileges, and grant these to administrators or to other roles. Privileges give the administrator rights to perform management actions within Enterprise Manager. Using roles and privileges allows you to manage security across all functional areas of Enterprise Manager.
Creating roles is an easy way to grant a predefined set of privileges to a group of administrators. If you change a role, the changes are automatically propagated to all administrators who are assigned that role.
Roles can be based on:
Geographic location. For example, you can define a role for UK administrators to manage UK systems.
Line of business. For example, you can define a role for administrators of the human resource systems.
Any other IT model.
Administrators are database users defined in the Management Repository who can log in to Enterprise Manager to perform management tasks. The breadth of management tasks available in Enterprise Manager depends on the privileges and roles assigned to the administrators.
There are two types of accounts:
Enterprise Manager is installed with a default super administrator account named SYSMAN. During the installation, you are prompted provide a password for SYSMAN. You use the SYSMAN account for the initial login to Enterprise Manager. The super administrator account cannot be deleted or renamed.
The super administrator account can manage all other administrator accounts and set up all administrator credentials. The super administrator can:
Create Enterprise Manager privileges and roles
Perform the initial setup of Enterprise Manager, for example, defining e-mail configurations and defining global notifications rules
Add targets to Enterprise Manager
Perform any action on any target in the system
Oracle recommends that you create an administrator account for each individual user. The super administrator account should not be used to conduct daily administration tasks.
Administrator accounts provide users permission to perform administrative tasks and access administrative information. You can set up each administrator account to have its own:
E-mail address
Notification rules
Privileges
Role, or set of privileges
See Also:
"About Administrators and Roles" in the Enterprise Manager online helpNotification Methods allow you to define different mechanisms for sending notifications. These include e-mail, SNMP traps, or running custom scripts—or all three. Once defined, these methods can then be used with Notification Rules for sending notifications to administrators as a result of alert occurrences.
On the Patching Setup page, specify parameters that allow you to configure and use Grid Control's patching features. These features simplify the staging and application of Oracle patches and patch sets to any host on which the Oracle Management Agent is running. They also allow you to collect information about Oracle critical patch advisories that are relevant to your enterprise.
You can use this page to set your MetaLink credentials, set patch cache size, turn on patch set validation, configure proxy and connection details, as well as offline patching settings.
See Also:
"Patching" in Chapter 19, "Lifecycle Management"Blackouts allow Enterprise Manager administrators to suspend any data collection activity on one or more monitored targets, thus allowing Enterprise Manager administrators to perform scheduled maintenance on targets. For example, you can stop data collections during periods where a managed target is undergoing routine maintenance, such as a database backup or hardware upgrade. If you continue monitoring during these periods, the collected data will show trends and other monitoring information that are not the result of normal day-to-day operations. To get a more accurate, long-term picture of a target's performance, you can use blackouts to exclude these special-case situations from data analysis.
A blackout can be defined for individual target(s), a group of multiple targets that reside on different hosts, or for all targets on a host. The blackout can be scheduled to run immediately or in the future, and to run indefinitely or stop after a specific duration. Blackouts can be created on an as-needed basis, or scheduled to run at regular intervals. If, during the maintenance period, the administrator discovers that he needs more (or less) time to complete his maintenance tasks, he can easily extend (or stop) the blackout that is currently in effect.
Set registration passwords to secure Management Agents against any Management Service that uses the central Management Repository.
When defining registration passwords, you may specify an expire date after which the password will be invalid, or you may specify that the password can only be used one time, after which it is deleted automatically from the repository.
Oracle offers a number of management options, or "Management Packs," that bring together a set of technologies related to a specific area of Enterprise Manager.
Each pack has several premium features bundled as part of that pack. Having a pack licensed or unlicensed on a target has a very significant impact on the user experience because the corresponding links, which need the pack, are enabled or disabled accordingly.
See Also:
Chapter 3, "Licensable Management Features"Monitoring templates simplify the task of setting up monitoring for large numbers of targets by allowing administrators to specify the monitoring settings once, then apply them as often as needed. You can create, edit, and save a monitoring template that contains your enterprise's standards for monitoring—metrics, thresholds, corrective actions and/or policy rules. Once defined, you can propagate these standards by applying the template to managed targets.
Corrective Actions allow administrators to specify automated responses to alerts or policy violations. Corrective Actions ensure that routine responses to alerts or policy violations are automatically executed, thereby saving administrator time and ensuring problems are dealt with before they noticeably impact end users.
Corrective actions share many features in common with the Job System. By default, the corrective action will run on the target on which the alert or policy violation has triggered. Alternatively, a corrective action can be specified to contain multiple tasks, with each task running on a different target. Administrators can also receive notifications for the success or failure of corrective actions.
Use this page to display and manage corrective actions. The library allows administrators to re-use library corrective actions that have been created.
A Management Plug-in is a target type provided by the user or a third party to extend Enterprise Manager's set of predefined target types. This page is used to define new Management Plug-ins, import Management Plug-ins from, or export Management Plug-ins to a Management Plug-in Archive, or to deploy a Management Plug-in into your system.
The Tool Center is the central access point for all of the functionality available to you to operate on your Management Plug-ins. Any Management Plug-ins that have been imported into the Management Repository are listed on this page. Certain operations allow you to operate on multiple Management Plug-ins simultaneously (delete and export); some operations only allow you to operate on a single Management Plug-in at a time (deploy and undeploy); and import allows you to add Management Plug-ins to the table on this page. You also can search through the Management Plug-ins using the search criteria at the top of the page.
The Client System Analyzer (CSA) allows Web server administrators to collect and analyze end-user client data. End-users can directly access CSA or may be redirected to it from other applications.
An instance of the Client System Analyzer application is pre-installed with Grid Control. The application is run by the Oracle Management Services' web servers. It can be used to collect client information for any system that can reach the Oracle Management Services URLs. This option allows administrators to collect client data without setting up a separate web application.
See Also:
"Client Configurations" in Chapter 11, "Enterprise Configuration Management"The Grid Control Preferences area allows you to set options for the following:
You can specify one or more e-mail addresses and associated message formats for your Enterprise Manager account.
Specify the e-mail addresses and message formats you want associated with your Enterprise Manager account. All e-mail notifications you receive from Enterprise Manager will be sent to the e-mail addresses you specify.
Preferred credentials simplify access to managed targets by storing target login credentials in the Management Repository. With preferred credentials set, users can access an Enterprise Manager target that recognizes those credentials without being prompted to log into the target. Preferred credentials are set on a per user basis, thus ensuring the security of the managed enterprise environment.
The Preferred Credentials page provides a top-level view of all preferred credentials set for your Enterprise Manager environment. From this page, you can set preferred credentials for any managed target listed in the Preferred Credentials table. Each row of the table provides a credential summary for each target. Targets are organized according to target type.
From Preferences, you can set up notification rules and the schedule.
If you want to define a target or set of targets, the target availability states for which you would like to receive notifications, the metrics you want to monitor for thresholds, the policies you want to monitor for thresholds, the job status changes you want to monitor, and the notification action you want to take when a threshold is exceeded or a job's status changes, click the Create button.
Use the Notification Rules page to create, view, or edit notification rules. You can choose the targets and conditions for which you want to receive notifications from Enterprise Manager. The methods for sending notifications include e-mail, SNMP traps, running custom scripts, PL/SQL procedures, or all four.
Use the notification schedule page to select a user for which a notification schedule needs to be set. An e-mail address must be defined for the administrator prior to defining a notification schedule. For each administrator for which a notification schedule has been specified, all specifics pertaining to their schedule are displayed.