Release 2.6.4
Part Number B15853-01
Contents
Previous
Next
| Oracle Workflow Developer's Guide Release 2.6.4 Part Number B15853-01 | Contents | Previous | Next |
Oracle Workflow provides some generic activities you can use to control your process. The activities are associated with the Standard item type but can be used within any process you define. The Standard item type is automatically installed on your Oracle Workflow server. You can also access the Standard item type from the file wfstd.wft located on your PC in the <ORACLE_HOME>\Wf\data\<language> directory.
Note: Predefined activities are also available for the predefined workflows shipped with Oracle Applications. For more information on Oracle Applications-specific workflow activities, consult the documentation or help for that specific Oracle Applications product.
Note: If you want to drag an activity into a process, where the activity is in a different data store than the process you are dragging it to, then you must first copy the item type that the activity belongs to into the same data store as the process. Suppose you are modifying a process that is stored in wfexample.wft and you want to add some standard activities into the process that are stored in wfstd.wft. First you need to open both files as data stores in Oracle Workflow Builder, then you need to copy the Standard item type in wfstd and paste it into the wfexample data store. Now you can drag any standard activity in the wfexample data store into your process.
Related Topics
Compare Execution Time Activity
Master/Detail Coordination Activities
Compare Event Property Activity
XML Compare Tag Value Activities
In cases where multiple parallel branches transition to a single node, you can decide whether that node should transition forward when any of those parallel branches complete or when all of the parallel branches complete. Use the And activity as the node for several converging branches to ensure that all branches complete before continuing. Use the Or activity as the node for several converging branches to allow the process to continue whenever any one of the branches completes.
And - Completes when the activities from all converging branches complete. Calls a PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.ANDJOIN.
Or - Completes when the activities from at least one converging branch complete. Calls a PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.ORJOIN.
The comparison activities provide a standard way to compare two numbers, dates, or text strings.
Compare Date - Use to compare the value of an item type attribute of type Date with a constant date.
Compare Number - Use to compare the value of an item type attribute of type Number with a constant number.
Compare Text - Use to compare the value of two item type attributes of type Text.
All the Comparison activities call a PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.COMPARE.
Each comparison activity has two activity attributes:
Test Value - a constant number, date, or text string which to compare to a reference value.
Reference Value - an item type attribute of type Number, Date, or Text.
The comparison activities use the Comparison lookup type for a result code. Possible values are "Greater Than," "Less Than," "Equal," or "Null," if the item type attribute is null. You can guide your workflow process based on how the value of an item type attribute compares to a given value that you set. See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
The Compare Execution Time activity provides a standard way to compare the elapsed execution time of a process with a constant test time.
The Compare Execution Time activity calls a PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.COMPAREEXECUTIONTIME.
The Compare Execution Time activity has two activity attributes:
Test Execution Time - the time, in seconds with which to compare the elapsed execution time.
Parent Type - takes as its value, the lookup codes, "Root" or "Parent". A value of "Root" compares the test time with the elapsed execution time of the current root process. A value of "Parent" compares the test time with the elapsed execution time of just the immediate parent process, which can be a subprocess.
The activity uses the Comparison lookup type for a result code. Possible values are "Greater Than," "Less Than," "Equal," or "Null," if the test time is null. See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
The Wait activity pauses the process for the time you specify. You can either wait until:
a specific date
a given day of the month
a given day of the week
a period of time after this activity is encountered
This activity calls the PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.WAIT.
Note: You must run a background engine for deferred activities to determine when the wait time has passed. The background engine then completes the Wait activity so that the process can continue. See: Setting Up Background Engines, Oracle Workflow Administrator's Guide.
The Wait activity has six activity attributes:
Wait Mode - use this attribute to specify how to calculate the wait. You can choose one of the following wait modes:
Absolute Date - to pause the activity until the date specified in the Absolute Date activity attribute is reached.
Relative Time - to pause the activity until the number of days specified in the Relative Time activity attribute passes.
Day of Month - to pause the activity until a specified day of the month, as indicated in the Day of Month activity attribute.
Day of Week - to pause the activity until a specified day of the week, as indicated in the Day of Week activity attribute.
Absolute Date - If Wait Mode is set to Absolute Date, enter an absolute date.
Relative Time - If Wait Mode is set to Relative Time, enter a relative time expressed in <days>.<fraction of days>. For example, enter 0.5 for a wait time of half a day (12 hours).
Day of Month - If Wait Mode is set to Day of Month, choose a day of the month from the list. If the day you choose has already passed in the current month, then the activity waits until that day in the following month.
Day of Week - If Wait Mode is set to Day of Week, choose a day of the week from the list. If the day you choose has already passed in the current week, then the activity waits until that day in the following week.
Time of Day - The Wait activity always pauses until midnight of the time specified, unless you use this Time of Day activity attribute to specify a time other than midnight that the Wait activity should pause until.
See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
The Block activity lets you pause a process until some external program or manual step completes and makes a call to the CompleteActivity Workflow Engine API. Use the Block activity to delay a process until some condition is met, such as the completion of a concurrent program. Make sure your program issues a CompleteActivity call when it completes to resume the process at the Block activity. See: CompleteActivity, Oracle Workflow API Reference.
This activity calls the PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.BLOCK.
The Defer Thread activity defers the subsequent process thread to the background queue without requiring you to change the cost of each activity in that thread to a value above the Workflow Engine threshold. This activity always interrupts the process thread by causing a disconnect to occur in the current database session, even if the thread is already deferred.
This activity calls the PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.DEFER.
The Launch Process activity lets you launch another workflow process from the current process. This activity calls the PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.LAUNCHPROCESS.
The Launch Process activity has six activity attributes:
Item Type - the item type of the process to launch. Specify the item type's internal name. This activity attribute requires a value.
Item Key - an item key for the process to launch. If you do not specify a value, the item key defaults to <current_item_type>:<current_item_key>-<n>, where <current_item_type> and <current_item_key> identify the current process instance, and <n> is the number of processes launched by the current process instance, starting at 1.
Note: The item key for a process instance can only contain single-byte characters. It cannot contain a multibyte value.
Process name - the internal name of the process to launch. If a process name is not specified, the activity will check the item type selector function of the process to launch for a process name.
User Key - a user defined key for the process to launch.
Owner - a role designated as the owner of the process to launch.
Defer immediate - choose between YES or NO to determine whether the process to launch should be immediately deferred to the background engine. The default is NO, so once the process is launched, it continues to execute until completion or until one of its activities is deferred.
See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
The Noop activity acts as a place holder activity that performs no action. You can use this activity anywhere you want to place a node without performing an action. You can change the display name of this activity to something meaningful when you include it in a process, so that it reminds you of what you want this activity to do in the future. This activity calls the PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.NOOP.
Use the Loop Counter activity to limit the number of times the Workflow Engine transitions through a particular path in a process. The Loop Counter activity can have a result of Loop or Exit.
This Loop Counter activity calls the PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.LOOPCOUNTER.
The Loop Counter activity has an activity attribute called Loop Limit. If the number of times that the Workflow Engine transitions to the Loop Counter activity is less than the value specified in Loop Limit, the Loop Counter activity will complete with a result of Loop and the engine will take the 'Loop' transition to the next activity. If the number of times that the Workflow Engine transitions to the Loop Counter activity exceeds the value of Loop Limit, the activity will complete with a result of Exit and the engine will take the 'Exit' transition to an alternative activity.
For example, suppose your workflow process contains a branch of activities that can be transitioned to from multiple source activities, and you want to ensure that that particular branch of activities gets executed just once in the process. Include a Loop Counter activity as the first activity in that branch and specify the Loop Limit activity attribute value as 1. Also draw an 'Exit' transition from the Loop Counter activity to an activity that you want the engine to execute if the Loop Counter activity is visited more than once, as shown in the diagram below.
Example Loop Counter Activity in a Branch
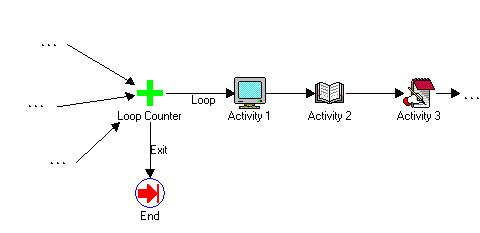
Additionally, for example, as shown in the diagram below, you can include a Loop Counter activity as the initial activity in a loop. The value you specify for the Loop Limit activity attribute will designate the number of times the engine is allowed to traverse through the loop. If the number of visits to the Loop Counter activity exceeds the value set in Loop Limit, then the process moves along the 'Exit' transition to the designated activity.
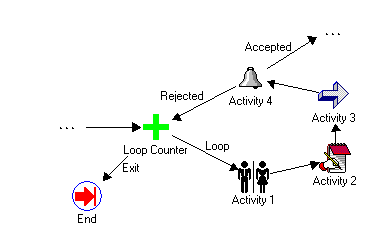
In this example, the engine moves from the Loop Counter activity through Activities 1, 2, 3, and 4 in the loop. If the result of Activity 4 is 'Accepted,' the process moves along the 'Accepted' transition. Otherwise, if the result is 'Rejected,' the process moves along the 'Rejected' transition to return to the Loop Counter activity. If the item is rejected multiple times, once the number of visits to the Loop Counter activity exceeds the Loop Limit value, the process moves along the 'Exit' transition and ends.
Example Loop Counter Activity in a Loop
See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
The Start activity marks the start of a process and does not perform any action. Although it is not necessary, you may include it in your process diagram to visually mark the start of a process as a separate node. This activity calls the PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.NOOP.
The End activity marks the end of a process and does not perform any action. You can use it to return a result for a completed process by specifying a Result Type for the activity. Although it is not necessary, you may include it in your process diagram to visually mark the end of your process as a separate node. This activity calls the PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.NOOP.
The Role Resolution activity lets you identify a single user from a role comprised of multiple users. In a process diagram, place the Role Resolution activity in front of a notification activity and specify the performer of that notification activity to be a role consisting of several users. The Role Resolution activity selects a single user from that role and assigns the notification activity to that user.
This activity calls the PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.ROLERESOLUTION.
Use the Method activity attribute in the Role Resolution activity to specify how you want to resolve the role. A value of "Load Balance" compares how many open notifications from that activity each qualified user has and selects the user with the fewest open notifications from that activity. A value of "Sequential" selects a user from the role sequentially by determining the user that experienced the longest interval of time since last receiving a notification from that activity. See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
The Notify function activity lets you send a notification, where the message being sent is determined dynamically at runtime by a prior function activity. To use the Notify activity, you must model a prerequisite function activity into the process that selects one of several predefined messages for the Notify activity to send.
Attention: Since the Notify activity is locked against modifications at access level 0, you cannot change the result type from its value of <None>. Therefore, the message that the function activity dynamically selects must not have a result type, that is, it can only be an informative message that does not solicit a response.
Attention: If you want the Notify activity to send a message that requires a response, then you must copy and create your own version of the Notify activity. Since any one of several messages (with response attributes) can be sent by your version of the Notify activity, you must model into your process all the possible notification results that can be returned.
Note: If you want to define an activity that always sends the same message, you should define a notification activity and not use this Notify function activity.
The Notify activity calls a PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.NOTIFY.
The Notify activity has three activity attributes:
Message Name - the name of the predefined message to send. The prerequisite function activity that determines which message to send should store the name of that message in an item attribute. The Message Name activity attribute should reference that item attribute to determine the name of the message to send.
Performer - the name of the role to which to send the notification message. If you load the roles from your database, you can select a constant role as the performer. Alternatively, you can set the performer to an item attribute that returns the name of a role at runtime.
Expand Roles - takes as its value, the lookup codes Yes or No. Set Expand Roles to Yes if you wish to send an individual copy of the notification message to every user in the role.
See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
The Vote Yes/No activity lets you send a notification to a group of users in a role and tally the Yes/No responses from those users. The results of the tally determine the activity that the process transitions to next.
The Vote Yes/No activity, classified as a notification activity, first sends a notification message to a group of users and then performs a PL/SQL post-notification function to tally the users' responses (votes).
The Vote Yes/No activity has three activity attributes:
Percent Yes - The percentage of Yes votes cast in order for the activity to complete with a result of Yes.
Percent No - The percentage of No votes cast in order for the activity to complete with a result of No
Note: The values for the Percent Yes and Percent No attributes are both defined as null in order to use a Popularity voting method, in which the result is the response with the highest number of votes. See: Example Voting Methods.
Voting Option - specify how the votes are tallied by selecting one of three values:
"Wait for All Votes" - the Workflow Engine waits until all votes are cast before tallying the results as a percentage of all the users notified. If a timeout condition occurs, the Workflow Engine calculates the resulting votes as a percentage of the total votes cast before the timeout occurred.
"Tally on Every Vote" - the Workflow Engine keeps a running tally of the cumulative responses as a percentage of all the users notified. If a timeout condition occurs, then the responses are tallied as a percentage of the total number of votes cast. Note that this option is meaningless if any of the custom response activity attributes have a blank value.
"Require All Votes" - the Workflow Engine evaluates the responses as a percentage of all users notified only after all votes are cast. If a timeout condition occurs, the Workflow Engine progresses along the standard timeout transition, or if none is available, raises an error, and does not tally any votes.
See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
Related Topics
The Master/Detail coordination activities let you coordinate the flow of master and detail processes. For example, a master process may spawn detail processes that need to be coordinated such that the master process continues only when every detail process has reached a certain point in its flow or vice versa.
When you spawn a detail process from a master process in Oracle Workflow, you are in effect creating a separate process with its own unique item type and item key. You define the master/detail relationship between the two processes by making a call to the Workflow Engine SetItemParent API after you call the CreateProcess API and before you call the StartProcess API when you create the detail process. See: SetItemParent, Oracle Workflow API Reference.
You can then use the two activities described below to coordinate the flow in the master and detail processes. One activity lets you pause a process and the other signals the halted process to continue. To use these activities, you place one activity in the master process and the other in each detail process.
Both activities contain two activity attributes that you use to identify the coordinating activity in the other process(es).
Place this activity in a master or detail process to pause the flow until the other corresponding detail or master process completes a specified activity. This activity calls a PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.WAITFORFLOW.
You can use multiple Wait for Flow activities in the same workflow process. For example, if a master process launches two different sets of detail processes at different stages, the master process should include a separate Wait for Flow activity node for each set of detail processes. In this case, when you call the WF_ENGINE.SetItemParent API to associate a detail process with the master process, you must specify the parent context as the activity label name for the Wait for Flow activity node that corresponds to this detail process.
If the parent process contains only one Wait for Flow activity, however, you can leave the parent context parameter null when calling WF_ENGINE.SetItemParent.
The Wait for Flow activity contains two activity attributes:
Continuation Flow - specify whether this activity is waiting for a corresponding "Master" or "Detail" process to complete.
Continuation Activity - specify the label of the activity node that must complete in the corresponding process before the current process continues. The default value is CONTINUEFLOW.
See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
Use this activity to mark the position in the corresponding detail or master process where, upon completion, you want the halted process to continue. This activity calls a PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.CONTINUEFLOW.
When a Continue Flow activity is executed, the WF_STANDARD.CONTINUEFLOW procedure checks whether the corresponding Wait for Flow activity is associated with any other processes that have not yet completed their Continue Flow activities. If so, the waiting process keeps waiting for those other processes. If the Wait for Flow activity is not waiting for any other processes, then the WF_STANDARD.CONTINUEFLOW procedure completes the Wait for Flow activity so that the process that was waiting now continues to the next activity.
The Continue Flow activity contains two activity attributes:
Waiting Flow - specify whether the halted process that is waiting for this activity to complete is a "Master" or "Detail" flow.
Waiting Activity - specify the label of the activity node in the halted process that is waiting for this activity to complete.
See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
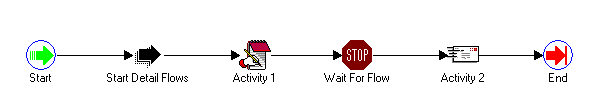
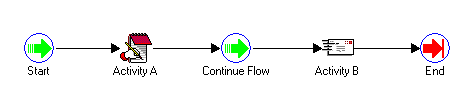
The following figures show an example of how these coordination activities can be used. In the master process example, after the process begins with the Start activity, the Start Detail Flows activity initiates several detail processes. The master process then completes Activity 1 before it pauses at the Wait For Flow activity. Wait For Flow is defined to wait for all its detail processes to complete a Continue Flow activity before allowing the master process to transition to Activity 2 and finally end. An example of one of the detail processes below shows that after the detail process begins with the Start activity, it completes Activity A. When it reaches the Continue Flow activity, it signals to the Workflow Engine that the master process can now continue from the Wait For Flow activity. The detail process itself then transitions to Activity B and finally ends.
Example Master Process
Example Detail Process
Note: You can include a Wait for Flow activity in a master process without including a Continue Flow activity in one or more of its corresponding detail processes. However, in this case you must ensure that all detail processes without a Continue Flow activity are entirely completed before the Workflow Engine attempts to continue the master process based on the coordination activities that you do include. That is, at least one of the following must occur after the detail processes without a Continue Flow activity are completed:
The master process reaches its Wait for Flow activity.
A detail process that contains a Continue Flow activity completes that Continue Flow activity.
Otherwise, the Workflow Engine cannot properly coordinate the continuation of the master process.
If it does not matter when any of the detail processes complete before a master process continues (or when a master process completes before all the detail processes continue), then you simply omit both of the coordination activities from your master/detail processes.
Attention: If you include a Continue Flow activity in a process, you must also include a Wait for Flow activity in its corresponding master or detail process as defined by the activity attributes in the Continue Flow activity.
The Assign activity lets you assign a value to an item attribute. This activity calls the PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.ASSIGN.
The Assign activity has an activity attribute called Item Attribute. Use Item Attribute to choose the item attribute that you want to assign a value to. Depending on the item attribute's format type, use the Date Value, Numeric Value, or Text Value activity attribute to specify the value that you want to assign to the item attribute.
The Get Monitor URL activity generates the URL for the Workflow Monitor diagram window and stores it in an item attribute that you specify. This activity calls the PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.GETURL.
The Get Monitor URL activity has two activity attributes:
Item Attribute - choose the name of the item attribute that you want to use to store the URL for the Workflow Monitor window.
Administration Mode - determine how the URL displays the Workflow Monitor window. If you set Administration Mode to "Yes", the URL displays the Workflow Monitor in 'ADMIN' mode, otherwise it displays the Workflow Monitor in 'USER' mode.
See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
The Get Event Property activity lets you retrieve a property of an event message from the Business Event System and store the property value in an item attribute. This activity calls the PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.GETEVENTPROPERTY.
The Get Event Property activity has four activity attributes:
Event - choose the item attribute of type event that contains the event message from which you want to retrieve a property.
Property - the event property whose value you want to retrieve. This attribute takes as its value a lookup code from the Event Property lookup type. Possible values are "Priority," "Send Date," "Receive Date," "Correlation ID," "Event Parameter," "Event Name," "Event Key," "From Agent," "From Agent Name," "From Agent System," "To Agent," "To Agent Name," and "To Agent System." See: Event Message Structure, Oracle Workflow API Reference.
Event Parameter - if you choose the Event Parameter property in the Property attribute, enter the name of the parameter whose value you want to retrieve. Oracle Workflow uses this name to identify the parameter within the event message's parameter list. If you choose any property other than Event Parameter, leave this attribute blank.
Item Attribute - the item attribute where you want to store the event property value.
See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
The Set Event Property activity lets you set the value of a property in an event message from the Business Event System. This activity calls the PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.SETEVENTPROPERTY.
The Set Event Property activity has six activity attributes:
Event - choose the item attribute of type event that contains the event message whose property you want to set.
Property - the event property whose value you want to set. This attribute takes as its value a lookup code from the Event Property lookup type. Possible values are "Priority," "Send Date," "Receive Date," "Correlation ID," "Event Parameter," "Event Name," "Event Key," "From Agent," "From Agent Name," "From Agent System," "To Agent," "To Agent Name," and "To Agent System." See: Event Message Structure, Oracle Workflow API Reference.
Event Parameter - if you choose the Event Parameter property in the Property attribute, enter the name of the parameter whose value you want to set. Oracle Workflow uses this name to identify the parameter within the event message's parameter list. If you choose any property other than Event Parameter, leave this attribute blank.
Date Value - the value of type date that you want to set for the event property, if you choose the Send Date or Receive Date property.
Numeric Value - the value of type number that you want to set for the event property, if you choose the Priority property.
Text Value - the value of type text that you want to set for the event property, if you choose the Correlation ID, Event Parameter, Event Name, Event Key, From Agent Name, From Agent System, To Agent Name, or To Agent System property.
Note: You must enter the value to set in the activity attribute that matches the data type of the event property you choose.
See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
The Compare Event Property activity lets you compare a property of an event message from the Business Event System with a test value that you specify. This activity calls the PL/SQL procedure named WF_STANDARD.COMPAREEVENTPROPERTY.
The Compare Event Property activity has six activity attributes:
Event - choose the item attribute of type event that contains the event message whose property you want to compare to a test value.
Property - the event property whose value you want to compare to a test value. This attribute takes as its value a lookup code from the Event Property lookup type. Possible values are "Priority," "Send Date," "Receive Date," "Correlation ID," "Event Parameter," "Event Name," "Event Key," "From Agent," "From Agent Name," "From Agent System," "To Agent," "To Agent Name," and "To Agent System." See: Event Message Structure, Oracle Workflow API Reference.
Event Parameter - if you choose the Event Parameter property in the Property attribute, enter the name of the parameter whose value you want to compare to a test value. Oracle Workflow uses this name to identify the parameter within the event message's parameter list. If you choose any property other than Event Parameter, leave this attribute blank.
Date Value - the test value of type date with which to compare the event property value, if you choose the Send Date or Receive Date property.
Numeric Value - the test value of type number with which to compare the event property value, if you choose the Priority property.
Text Value - the test value of type text with which to compare the event property value, if you choose the Correlation ID, Event Parameter, Event Name, Event Key, From Agent Name, From Agent System, To Agent Name, or To Agent System property.
The Compare Event Property activity uses the Comparison lookup type for a result code. Possible values are "Greater Than," "Less Than," "Equal," or "Null," if the test activity attribute value is null. You can guide your workflow process based on how the event property value compares to the test value. See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
Note: You must enter the test value in the activity attribute that matches the data type of the event property you choose. If you enter the test value in an inappropriate activity attribute, the Compare Event Property activity returns the "Null" result code.
Use the XML Get Tag Value activity to retrieve data from the contents of an event message from the Business Event System. This functionality is currently only available for the standalone version of Oracle Workflow. This activity retrieves the data contained within a particular XML tag set in the event message and stores the data in an item attribute that you specify. The XML Get Tag Value activity calls the external Java function named oracle.apps.fnd.wf.XMLGetTagValue.
Note: When the Workflow Engine encounters an external Java function activity, it places an entry on the 'Outbound' queue. To continue executing the activity, you must run the Java Function Activity Agent, which calls the appropriate Java function and places the result on the 'Inbound' queue. You must then run a background engine to process the 'Inbound' queue and complete the function activity. See: Setting Up the Java Function Activity Agent, Oracle Workflow Administrator's Guide and Setting Up Background Engines, Oracle Workflow Administrator's Guide.
The XML Get Tag Value activity has three activity attributes:
Event - choose the item attribute of type event that contains the event message from which you want to retrieve data.
Tag - the tag set within the event message from which you want to retrieve data. Specify the tag set in XPath notation. For example, for an XML document containing a purchase order, the XML path for the order number tag could be specified in the following format:
/order/header/ordernumber
The following example path locates the ITEMNO node on the third line of the purchase order document:
/order/orderlines/line[3]/itemno
The following example path locates the COST node on the second line of the purchase order document whose currency attribute is set to "AUD". The notation // indicates that the specified node is located among the descendants of the root node.
//line[2]/cost[@currency="AUD"]
For more information, see the W3C Recommendation XML Path Language (XPath).
Item Attribute - choose the item attribute of type date, number, or text where you want to store the data. The type of the item attribute must match the type of the data that you want to retrieve.
See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
Use the XML Compare Tag Value activities to compare data from an event message received through the Business Event System with a test value. This functionality is currently only available for the standalone version of Oracle Workflow. These activities compare the data contained within a particular XML tag set in the event message with the test value that you specify.
XML Compare Tag Value (Date) - Use this activity to compare date values.
XML Compare Tag Value (Number) - Use this activity to compare number values.
XML Compare Tag Value (Text) - Use this activity to compare text values.
All the XML Compare Tag Value activities call the external Java function named oracle.apps.fnd.wf.XMLCompareTag.
Note: When the Workflow Engine encounters an external Java function activity, it places an entry on the 'Outbound' queue. To continue executing the activity, you must run the Java Function Activity Agent, which calls the appropriate Java function and places the result on the 'Inbound' queue. You must then run a background engine to process the 'Inbound' queue and complete the function activity. See: Setting Up the Java Function Activity Agent, Oracle Workflow Administrator's Guide and Setting Up Background Engines, Oracle Workflow Administrator's Guide.
Each XML Compare Tag Value activity has three activity attributes:
Event - choose the item attribute of type event that contains the event message whose data you want to compare.
Tag - the tag set within the event message that contains the data you want to compare to a test value. Specify the tag set in XPath notation. For example, for an XML document containing an order, the XML path for the order number tag could be specified in the following format:
/order/header/ordernumber
The following example path locates the ITEMNO node on the third line of the purchase order document:
/order/orderlines/line[3]/itemno
The following example path locates the COST node on the second line of the purchase order document whose currency attribute is set to "AUD". The notation // indicates that the specified node is located among the descendants of the root node.
//line[2]/cost[@currency="AUD"]
For more information, see the W3C Recommendation XML Path Language (XPath).
Value - the test value of type date, number, or text with which to compare the event message data.
The XML Compare Tag Value activities use the Comparison lookup type for a result code. Possible values are "Greater Than," "Less Than," "Equal," or "Null," if the test activity attribute value is null. You can guide your workflow process based on how the event message data compares to the test value. See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
The XML Transform activity lets you apply an XML style sheet to the payload of an event message from the Business Event System. This functionality is currently only available for the standalone version of Oracle Workflow. The resulting document is stored in an item attribute of type event. This activity calls the external Java function named oracle.apps.fnd.wf.XSLTTransform.
Note: When the Workflow Engine encounters an external Java function activity, it places an entry on the 'Outbound' queue. To continue executing the activity, you must run the Java Function Activity Agent, which calls the appropriate Java function and places the result on the 'Inbound' queue. You must then run a background engine to process the 'Inbound' queue and complete the function activity. See: Setting Up the Java Function Activity Agent, Oracle Workflow Administrator's Guide and Setting Up Background Engines, Oracle Workflow Administrator's Guide.
The XML Transform activity has three activity attributes:
Event - choose the item attribute of type event that contains the event message you want to transform.
Stylesheet - a reference to the location of the style sheet that you want to apply. Specify this reference as a URL.
New Document - choose the item attribute of type event where you want to store the new document produced by applying the style sheet.
See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
Oracle Applications provides some generic activities you can use to control your process if you are using the version of Oracle Workflow embedded in Oracle Applications. These activities are associated with the Concurrent Manager Functions item type but can be used within any process you define:
The Concurrent Manager Functions item type is automatically installed on your Oracle Applications workflow server. You can also access this item type from the file fndwfaol.wft located in the $FND_TOP/admin/import directory.
The Execute Concurrent Program activity is available only in the version of Oracle Workflow embedded in Oracle Applications. It submits an Oracle Applications concurrent program from your workflow process and waits for it to complete, at which point it updates the status of the activity and returns execution of the workflow process to the background engine. The concurrent program can complete with any of the following results, as defined by the Concurrent Program Status lookup type: NORMAL, ERROR, WARNING, CANCELLED, or TERMINATED. You should make sure all of these results are modelled into your process diagram.
Attention: To use the Execute Concurrent Program activity, you must ensure that the background engine is set up to run.
Attention: Generally, the context for your process' item type is always set if your session is initiated from an Oracle Applications form. However, if an interrupt occurs in your session, for example, due to a notification or blocking activity, you must ensure that the context is set by calling FND_GLOBAL.APPS_INITIALIZE(user_id, resp_id, resp_appl_id) in SET_CTX mode in your Selector/Callback function. See: Standard API for an Item Type Selector or Callback Function and FNDSQF Routine APIs, Oracle Applications Developer's Guide.
The Execute Concurrent Program activity calls the standard Oracle Application Object Library API FND_WF_STANDARD.EXECUTECONCPROGRAM.
The Execute Concurrent Program activity has the following activity attributes:
Application Short Name - Short name of the application to which the concurrent program is registered.
Program Short Name - Short name of the concurrent program to run.
Number of Arguments - Number of arguments required for the concurrent program.
Item Attribute Name - Optional name of the item attribute to store the concurrent program request ID.
Argument1, Argument2, ... Argument100 - Value of each concurrent program argument, ordered to match the correct syntax of the concurrent program. Up to 100 arguments are allowed, but you should only specify as many argument values as you define in the Number of Arguments activity attribute.
See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
The Submit Concurrent Program activity is available only in the version of Oracle Workflow embedded in Oracle Applications. It submits an Oracle Applications concurrent program from your workflow process, but does not wait for it to execute or complete. Once this activity submits a concurrent request, the Workflow Engine continues with the next activity in the process.
Attention: Generally, the context for your process' item type is always set if your session is initiated from an Oracle Applications form. However, if an interrupt occurs in your session, for example, due to a notification or blocking activity, you must ensure that the context is set by calling FND_GLOBAL.APPS_INITIALIZE(user_id, resp_id, resp_appl_id) in SET_CTX mode in your Selector/Callback function. See: Standard API for an Item Type Selector or Callback Function.
The Submit Concurrent Program activity calls the standard Oracle Application Object Library API FND_WF_STANDARD.SUBMITCONCPROGRAM.
The Submit Concurrent Program activity has the following activity attributes:
Application Short Name - Short name of the application to which the concurrent program is registered.
Program Short Name - Short name of the concurrent program to run.
Number of Arguments - Number of arguments required for the concurrent program.
Item Attribute Name - Name of the item attribute to store the concurrent program request ID.
Argument1, Argument2, ... Argument100 - Value of each concurrent program argument, ordered to match the correct syntax of the concurrent program. Up to 100 arguments are allowed, but you should only specify as many argument values as you define in the Number of Arguments activity attribute.
See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.
The Wait for Concurrent Program activity is available only in the version of Oracle Workflow embedded in Oracle Applications. If you submit a concurrent program from your workflow process, you can use the Wait for Concurrent Program activity as a means of blocking the process from further execution until the concurrent program completes. When the concurrent program completes, this activity clears the block by updating the status of the activity and returning execution of the workflow process to the background engine. The concurrent program can complete with any of the following results, as defined by the Concurrent Program Status lookup type: NORMAL, ERROR, WARNING, CANCELLED, or TERMINATED. You should make sure all of these results are modelled into your process diagram.
Attention: To use the Wait for Concurrent Program activity, you must ensure that the background engine is set up to run.
The Wait for Concurrent Program activity calls the standard Oracle Application Object Library API FND_WF_STANDARD.WAITFORCONCPROGRAM.
The Wait for Concurrent Program activity has one activity attribute called Request ID, which should be set to the concurrent program request ID that you are waiting for to complete. See: To Define Activity Attribute Values.