Enabling Automatic Memory Management
If you did not enable automatic memory management when you installed and configured your database, then Oracle recommends that you do so after installation, unless you are an experienced DBA with specific reasons to manually tune memory sizes. With automatic memory management, the Oracle instance dynamically tunes all memory components to optimize performance as the workload changes.
To enable automatic memory management:
-
Start SQL*Plus and connect to the database as
SYSDBA. -
Calculate the minimum value for
MEMORY_TARGETas follows:-
Determine the current sizes of
SGA_TARGETandPGA_AGGREGATE_TARGETby entering the following SQL*Plus command:SHOW PARAMETER TARGET
SQL*Plus displays the values of all initialization parameters with the string TARGET in the parameter name.
NAME TYPE VALUE ------------------------------ ----------- ---------------- archive_lag_target integer 0 db_flashback_retention_target integer 1440 fast_start_io_target integer 0 fast_start_mttr_target integer 0 memory_max_target big integer 0 memory_target big integer 0 parallel_servers_target integer 32 pga_aggregate_target big integer 29M sga_target big integer 356M
Or, on the Initialization Parameters page in Oracle Enterprise Manager Database Express (EM Express), you can enter "TARGET" in the Search field to display the values of all the initialization parameters with the string TARGET in the parameter name, as described in "Viewing and Modifying Initialization Parameters."
-
Run the following query to determine the maximum instance Program Global Area (PGA) allocated since the database was started:
SQL> select value from v$pgastat where name='maximum PGA allocated'; VALUE ---------- 246844416246844416 bytes is approximately 235M.
-
Compute the maximum value between the query result from step 2.b and
PGA_AGGREGATE_TARGET. AddSGA_TARGETto this value.memory_target = sga_target + max(pga_aggregate_target, maximum PGA allocated)
For example, if
SGA_TARGETis 356M andPGA_AGGREGATE_TARGETis 29M as shown above, and if the maximum PGA allocated is determined to be 235M, thenMEMORY_TARGETshould be at least 591M (356M + 235M).
-
-
Choose the value for
MEMORY_TARGETthat you want to use.This can be the minimum value that you computed in step 2, or you can choose to use a larger value if you have enough physical memory available.
-
For the
MEMORY_MAX_TARGETinitialization parameter, decide on a maximum amount of memory that you would want to allocate to the database for the foreseeable future. That is, determine the maximum value for the sum of the System Global Area (SGA) and instance PGA sizes. This number can be larger than or the same as theMEMORY_TARGETvalue that you chose in the previous step. -
Do one of the following:
-
If you started your Oracle Database instance with a server parameter file, which is the default if you created the database with the Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA), enter the following SQL*Plus command:
ALTER SYSTEM SET MEMORY_MAX_TARGET = nM SCOPE = SPFILE;where n is the value that you computed in step 4.
The
SCOPE = SPFILEclause sets the value only in the server parameter file, and not for the running instance. You must include thisSCOPEclause becauseMEMORY_MAX_TARGETis not a dynamic initialization parameter.Or, you can also select the
MEMORY_MAX_TARGETinitialization parameter on the Initialization Parameters page in EM Express, click Set, specify a Scope of SPFile, and set a new value, as described in "Viewing and Modifying Initialization Parameters." -
If you started your instance with a text initialization parameter file, manually edit the file so that it contains the following statements:
memory_max_target = nM (650M for this example) memory_target = mM (591M for this example)
where n is the value that you determined in step 4, and m is the value that you determined in step 3.
Note:
In a text initialization parameter file, if you omit the line for
MEMORY_MAX_TARGETand include a value forMEMORY_TARGET, the database automatically setsMEMORY_MAX_TARGETto the value ofMEMORY_TARGET. If you omit the line forMEMORY_TARGETand include a value forMEMORY_MAX_TARGET, theMEMORY_TARGETparameter defaults to zero. After startup, you can then dynamically changeMEMORY_TARGETto a nonzero value, provided that it does not exceed the value ofMEMORY_MAX_TARGET.
-
-
Shut down and restart the database.
-
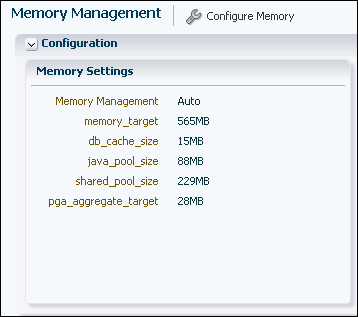
In EM Express, from the Configuration menu, select Memory.
The Memory Management page appears. In the Memory Settings section, the Memory Management value is Auto. This indicates that Automatic Memory Management is enabled for the database. The initialization parameter values shown on this page are the ones that have been specified in addition to
MEMORY_MAX_TARGET. -
If you started your Oracle Database instance with a server parameter file, make these changes to the following initialization parameter values:
MEMORY_TARGET = nM; (591M for this example) SGA_TARGET = 0; PGA_AGGREGATE_TARGET = 0;You can also set these initialization parameter values using the Initialization Parameters page in EM Express, specifying a scope of SPFile. See "Viewing and Modifying Initialization Parameters"for more information.
Note:
The preceding steps instruct you to set
SGA_TARGETandPGA_AGGREGATE_TARGETto zero so that the sizes of the SGA and instance PGA are tuned up and down as required, without restrictions. You can omit the statements that set these parameter values to zero and leave either or both of the values as positive numbers. In this case, the values act as minimum values for the sizes of the SGA or instance PGA.
See Also: