3 Viewing and Setting Object Properties in the DMU
This chapter provides a reference for elements of the user interface of the Database Migration Assistant for Unicode (DMU) and describes how to use them to view and set various object properties.
You can view various properties of a database object, such as database, schema, or table, by right-clicking the object's node in the Navigator pane, and selecting Properties from the context menu. A Properties tab tailored for the type of the object will be shown in the client pane of the DMU main window. Each Properties tab can have up to four subtabs: General, Scanning, Readiness, and Converting. To show a subtab, click its name in the left sidebar of the tab.
The subtabs show properties and information pertaining to particular steps in the migration process. The General subtab includes properties relevant to all phases of the migration. The Scanning subtab shows parameters controlling the scanning process and the scan results. The Readiness subtab shows if data contained in the object is ready for the actual conversion step. If the data is not ready, the subtab shows the reason for this. The Converting subtab includes parameters that control the conversion step. The following sections describe properties available on all object property tabs.
If you have changed any property on a Properties tab, click Apply to save the change.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Viewing and Setting Database Properties
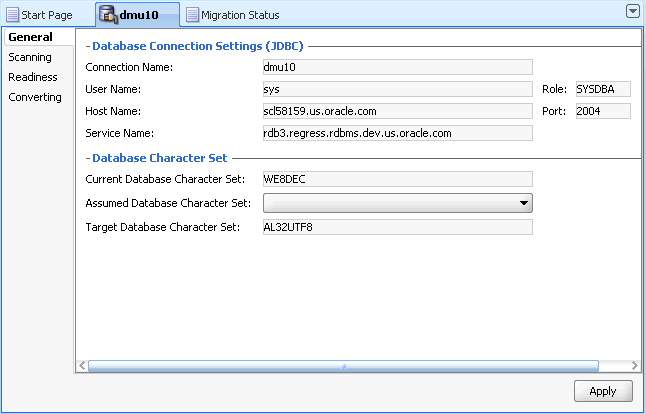
The Database Properties tab has four subtabs: General, Scanning, Readiness, and Converting, as shown in Figure 3-1.
Database Properties: General
On the General subtab of the Database Properties tab, you can see the following properties:
-
Connection details, such as user name and host name
The connection details are described in "Creating a Database Connection". The connection details can be changed only as described in that section.
-
Information about character sets of the database
The database character set information is composed of three properties:
-
Current Database Character Set
This is the current declared character set of the database that is used to interpret data stored in columns of the data types
VARCHAR2,CHAR,LONG, andCLOB. -
Assumed Database Character Set
The DMU uses the assumed database character set as the default source character set when scanning and converting character data during the migration. If the database has been used in a correct character set configuration, then the assumed character set should be the same as the database character set. However, in a pass-through configuration, as described in "Invalid Binary Storage Representation of Data", all or almost all character columns might store data in the character set of client workstations, which might be different from the declared database character set. In such a case, after you identify the real character set of the database contents, set it as the value of the Assumed Database Character Set property to let the DMU know how to correctly interpret the data.
-
Target Database Character Set
This is the target character set of the migration, either UTF8 or AL32UTF8. You can change this property only by uninstalling the migration repository and installing it again.
-
Click Apply to save any changes made on this subtab.
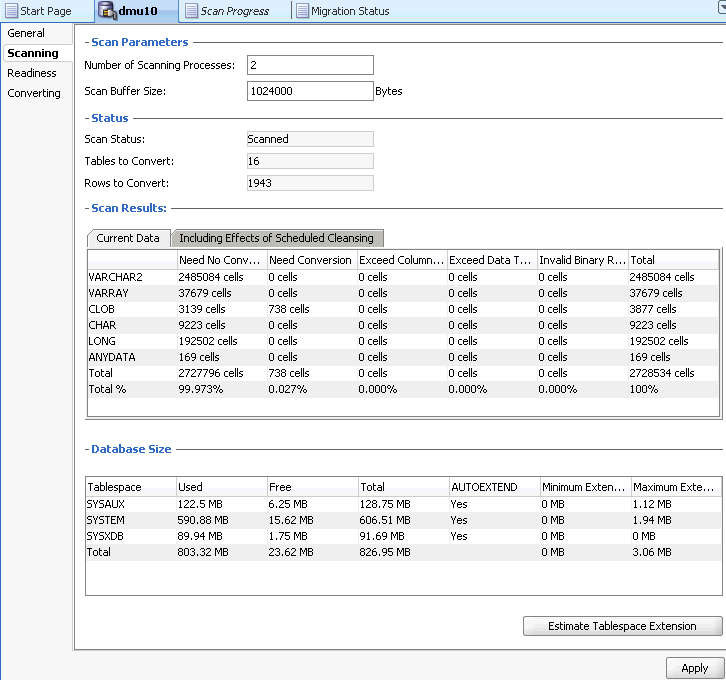
Database Properties: Scanning
On the Scanning subtab of the Database Properties tab, you can set general parameters controlling the process of scanning in this database, and view the aggregated scan results for the database. See Figure 3-2 for an illustration of the scanning subtabs.
The properties on the scanning subtab are:
-
Number of Scanning Processes
This specifies the number of concurrent processes used to scan the database. Each scanning process consists of a parallel thread in the DMU and a database session on the server created by this thread. The default value of the property is derived from the number of CPUs on the database server. You can tune this value by changing it and measuring the time required to complete one database scan. If you ask the DMU to scan only a small number of small tables, the number of processes used for this scan might be lower than the value of this property.
You can also change the Number of Scanning Processes in the Scan Wizard. See "Overview of the Database Scan Report" for more information.
-
Scan Buffer Size
This property controls the size in bytes of a buffer that the DMU allocates in each database server session to scan a table. The default value is 1000 kilobytes. The total buffer space used in a single scan is the number of scanning processes times the value of this property. Increasing the value of the property might speed up scanning but only as long as the allocated buffer memory fits into the available RAM on the database server.
You can also change the Scan Buffer Size in the Scan Wizard. See "Scanning the Database with the Scan Wizard" for more information.
-
Scan Status
This property shows the aggregated scan status of the database. The following values are possible:
-
Never scanned
No scan has been performed since the most recent installation of the migration repository.
-
In progress
A scan is currently in progress.
-
Scanned
All tables in the database have been scanned and have valid scan results.
-
Partially scanned
Some tables in the database have been scanned and have valid scan results, but the remaining tables either have never been scanned or their scan results have been invalidated by a cleansing action or by modification of their structure (metadata) outside of the DMU.
-
Issues found
One or more tables in the database contain data with convertibility issues. These may be length limit (expansion) issues, invalid binary representation issues, or convertible data in the data dictionary.
-
Failed
One or more tables in the database could not be scanned due to an unexpected error.
-
-
Tables to Convert
This is the number of tables in the database that are already identified as requiring conversion during the conversion step.
-
Rows to Convert
This is the sum of Rows to Convert property values for all tables requiring conversion in the database.
-
Scan Results
The scan results illustrate the classification of all scanned data cells in all tables in the database into categories of convertibility. A cell is a value of a given column in a given row. The categories are:
-
Invalid binary representation
The binary representation of the cell data is invalid under the current database character set (the converted value would contain replacement characters). This means that either the assumed character set of the column is incorrect, or the data is binary (for example, a JPEG image, an encryption result, or a text document in binary format is stored in the cell), or there are some corrupted character codes in the value.
-
Exceed data type limit
The cell data will be too long for its data type after conversion.
-
Exceed column limit
The cell data will not fit into a column after conversion.
-
Need conversion
The cell data must be converted, because its binary representation in the target character set is different than the representation in the current character set, but neither length limit issues nor invalid representation issues have been found.
-
Need no conversion
The data is fine, because the binary representation of the data does not change in the conversion.
The cells are assigned twice into the preceding categories. The first classification, displayed under the "Current data" heading, is based on the current column definitions in the database. The second classification, displayed under the "Including effects of scheduled cleansing" heading, is based on column definitions that will result from application of the scheduled cleansing actions. Because only the second classification corresponds to errors that the data would really cause in the conversion step, this classification is used to determine if the database contents are ready for conversion. You can use the first classification as a reference to tell the convertibility status of the database contents in case all scheduled cleansing actions are deleted.
-
-
Database Size
The scan result includes details about the different tablespaces:
-
Tablespace
The name of the tablespace that was scanned.
-
Used
The size of space in megabytes that is used.
-
Free
The size of space in megabytes that is free.
-
Total
The total size in megabytes of the tablespace.
-
AUTOEXTEND
Whether the tablespace is set to automatically extend itself by a specified amount when it reaches its size limit.
-
Minimum Extension
The minimum size in megabytes that the tablespace must be extended in order to accommodate the conversion space requirements, which assumes the best case scenario where the tables are converted sequentially one by one. It is calculated by taking into account the post-conversion data size expansion and the temporary space requirement of the largest table converted using the CTAS method.
An empty value indicates the tablespace is not affected by the database conversion. A value zero indicates that the tablespace has enough unused space to meet the minimum conversion space requirement. A value greater than zero indicates the tablespace must be extended by that amount to meet the minimum conversion space requirement. Note that if the tablespace is auto-extensible and the device has enough free space to accommodate the extension size, then it does not need to be extended before starting the database conversion.
-
Maximum Extension
The maximum size in megabytes that the tablespace must be extended in order to accommodate the conversion space requirements, which assumes the worst case scenario where the largest tables using the CTAS conversion method are converted at the same time. It is calculated by taking into account the post-conversion data size expansion and the temporary space requirements of the first N largest tables converted using the CTAS method (N is the number of conversion worker threads).
An empty value indicates the tablespace is not affected by the database conversion. A value zero indicates that the tablespace has enough unused space to meet the maximum conversion space requirement. A value greater than zero indicates the tablespace must be extended by that amount to meet the maximum conversion space requirement. Note that if the tablespace is auto-extensible and the device has enough free space to accommodate the extension size, then it does not need to be extended before starting the database conversion.
-
-
Estimate Tablespace Extension
Click this button to have the DMU calculate the minimum and maximum tablespace extensions for all tablespaces. Use the results as a guideline to size the tablespaces accordingly. If enough storage is available, extending the tablespaces close to the maximum extension sizes will reduce the chance of space allocation errors during the conversion phase.
Note that the DMU does not have information of inline
CLOBdata that remain inline when they are converted to Unicode. For the sake of simplicity, the DMU assumes that allCLOBdata are stored inLOBsegments upon estimating the size of post-conversion segments.
Click Apply to save any changes made on this subtab.
Database Properties: Readiness
This subtab shows the readiness of data for conversion. See Figure 3-3 for an illustration. The Data Readiness for Conversion property may have one of the following values:
-
Does not need conversion
All data in the database is classified as needing no conversion, and the database passed all conversion feasibility tests described in "Preparing the Conversion".
-
Ready for conversion
All data in the database is classified as either needing no conversion, or needing conversion, and the database passed all conversion feasibility tests.
-
Not ready for conversion
Some data in the database is classified as having invalid binary representation or exceeding length limits, or the database has not passed some conversion feasibility tests.
If the readiness status is "Not ready for conversion", additional information is displayed to explain the problem.
Figure 3-3 Database Properties: Readiness
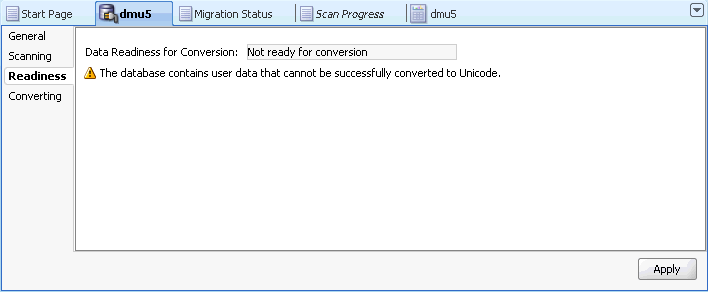
Description of "Figure 3-3 Database Properties: Readiness"
Database Properties: Converting
Properties on this subtab allow you to control certain aspects of the conversion processing. See Figure 3-4 for an illustration. The following properties can be set:
-
Degree of Parallelism
If the DMU converts a table using a
CREATETABLEASSELECT(CTAS) statement, this property sets the degree of parallelism that the parallel execution feature of the database should use for the operation. -
Number of Converting Processes
This specifies the number of concurrent processes used to convert the database. Each converting process consists of a parallel thread in the DMU and a database session on the server created by this thread. The default value of the property is derived from the number of CPUs on the database server.
-
Enable Row Movement for Partitioned Tables
Conversion of a partitioning key column value in a row of a range or hash partitioned table could cause the converted key to point to a partition other than the one currently containing the row. The database must move the row from the old partition to the new one, if the update of the key value succeeds. For reasons described for the Consider CTAS with Row Movement Disabled property, row movement is allowed only for tables for which it was enabled explicitly with the statement
ALTERTABLEENABLEROWMOVEMENT. You can set the property Enable Row Movement for Partitioned Tables to Yes to allow the DMU to temporarily enable row movement for partitioned tables that have partitioning key columns that require conversion. -
Consider CTAS with Row Movement Disabled
Because converting a table using a CTAS statement changes the physical addresses (rowids) of rows in the table, applications that store those addresses permanently could fail to locate the rows after the conversion. Therefore, by default, the DMU does not assign the CTAS conversion method to a table unless movement of rows in the table has been explicitly allowed with the statement
ALTERTABLEENABLEROWMOVEMENT. On the other hand, the row movement is disabled by default for a new table if it is not enabled explicitly in theCREATETABLEstatement. Therefore, most tables in most databases do not allow rows to be moved even though rowids are seldom stored by applications (primary keys are the recommended way to reference rows). If you know that applications connecting to the database do not store rowids, you can set the Consider CTAS with Row Movement Disabled property to Yes to allow the DMU to also assign the CTAS conversion method to tables that do not have the row movement enabled. -
Consider CTAS with User-named LOB Segments
By default, the DMU does not assign the CTAS conversion method for tables containing user-named LOB segments because the LOB segment names cannot be preserved with the CTAS conversion method. If there is no need to preserve the user-specified LOB segment names, you can set this property to Yes, which will allow the CTAS conversion method to be considered and the segments to be renamed after the conversion by appending a "$DMU" suffix.
-
Handling of Read-Only Materialized Views
This property determines how to handle read-only materialized views after their master tables have been converted. The choices are:
-
Refresh Automatically After Conversion
Refresh the read-only materialized views automatically in the post-conversion phase. This is the default option.
-
Generate SQL Script
Instead of refreshing the materialized views automatically, generate a SQL script containing the statements to refresh the read-only materialized views which can be executed subsequently outside of the DMU.
-
Do Nothing
Take no action on read-only materialized views.
-
-
Handling of Updatable Materialized Views
This property determines how to handle updatable materialized views after their master tables have been converted. The choices are:
-
Refresh Automatically After Conversion
Refresh the updatable materialized view automatically in the post-conversion phase.
-
Generate SQL Script
Instead of refreshing the materialized views automatically, generate a SQL script containing the statements to refresh the updatable materialized views which can be executed subsequently outside of the DMU.
-
Do Nothing
Take no action on updatable materialized views. This is the default.
-
-
Error Handling for Refreshing Materialized Views
This property determines how errors for refreshing materialized views are handled. The choices are:
-
Suspend Conversion and Ask
Suspend the failing SQL statement and let the user choose the appropriate action. This is the default option. You will be able to choose from retrying the failing statement, exporting the statement to an external script and continue, or skip the statement without exporting.
-
Skip Failing SQL and Continue
Automatically skip any failing SQL statements and continue with the conversion.
-
Export Failing SQL to Script and Continue
Automatically export any failing SQL statements to an external script that can be executed outside of the DMU and continue with the conversion.
-
-
Handling of Dropped Domain Indexes
This property determines how to handle dropped domain indexes. The choices are:
-
Recreate Automatically After Conversion
Recreate the dropped domain index automatically in the post-conversion phase. This is the default option.
-
Generate SQL Script
Instead of recreating the dropped domain index, generate a SQL script containing the statements to recreate the dropped domain index that can be executed subsequently outside of the DMU.
-
Do Nothing
Take no action on dropped domain indexes.
-
-
Error Handling for Recreating Domain Indexes
This property determines how errors for recreating domain indexes are handled. The choices are:
-
Suspend Conversion and Ask
Suspend the failing SQL statement and let the user choose the appropriate action. This is the default option. You will be able to choose from retrying the failing statement, exporting the statement to an external script and continue, or skip the statement without exporting.
-
Skip Failing SQL and Continue
Automatically skip any failing SQL statements and continue with the conversion.
-
Export Failing SQL to Script and Continue
Automatically export any failing SQL statements to an external script that can be executed outside of the DMU and continue with the conversion.
-
-
Error Handling for Rebuilding Other Indexes
This property determines how errors for rebuilding other indexes are handled. The choices are:
-
Suspend Conversion and Ask
Suspend the failing SQL statement and let the user choose the appropriate action. This is the default option. You will be able to choose from retrying the failing statement, exporting the statement to an external script and continue, or skip the statement without exporting.
-
Skip Failing SQL and Continue
Automatically skip any failing SQL statements and continue with the conversion.
-
Export Failing SQL to Script and Continue
Automatically export any failing SQL statements to an external script that can be executed outside of the DMU and continue with the conversion.
-
-
Directory for the SQL Scripts and its location (Browse button)
Displays the location and a Browse button to navigate where you want to put the output SQL script.
The default name for a read-only materialized view refresh script resembles:
-
RefreshMV_connectionName_timestamp.sql
The default name for an updatable materialized view refresh script resembles:
-
RefreshUpdMV_connectionName_timestamp.sql
The default name for a domain index recreation script resembles:
-
DomainIndexDDL_connectionName_timestamp.sql
The default name for a script with failed materialized view refresh SQL statements resembles:
-
FailedMVRefresh_connectionName_timestamp.sql
The default name for a script with failed domain index recreation SQL statements resembles:
-
FailedDomainIndex_connectionName_timestamp.sql
The default name for a script with failed other index rebuild SQL statements resembles:
-
FailedOtherIndex_connectionName_timestamp.sql
Note that changing the script directory location during the conversion will take effect for the next SQL script to be created.
-
Figure 3-4 Database Properties: Converting
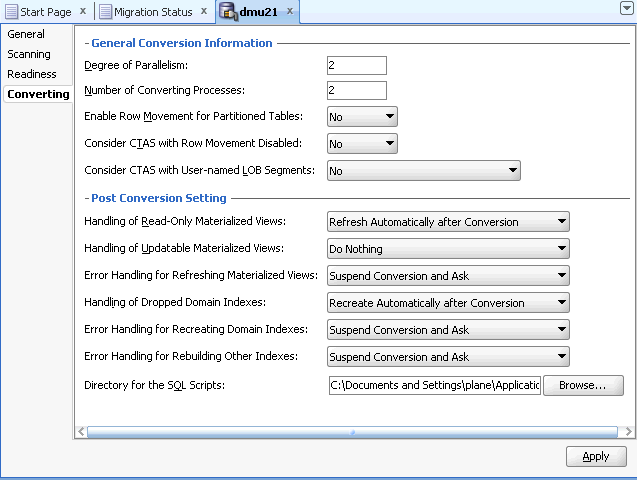
Description of "Figure 3-4 Database Properties: Converting"
Click Apply to save any changes made on this subtab.
Viewing and Setting Schema Properties
The Schema Properties tab has three subtabs: General, Scanning, and Readiness. There are no schema-level properties related to conversion.
Schema Properties: General
The General subtab of the Schema Properties tab shows the name of the schema and the default tablespace for storage objects, such as tables, created in this schema. These properties are read-only.
Schema Properties: Scanning
On the Scanning subtab of the Schema Properties tab, you can view the aggregated scan results for objects in this schema.
The properties on the Scanning subtab are:
-
Scan Status
This property shows the aggregated scan status of the schema. The following values are possible:
-
Never scanned
No table has been scanned in this schema since the most recent installation of the migration repository.
-
In progress
A table in the schema is currently being scanned.
-
Scanned
All tables in the schema have been scanned and have valid scan results.
-
Partially scanned
Some tables in the schema have been scanned and have valid scan results, but the remaining tables either have never been scanned or their scan results have been invalidated by a cleansing action or by modification of their structure (metadata) outside of the DMU.
-
Results invalidated
Scan results of all tables in the schema have been invalidated by a cleansing action or by modification of the table structure (metadata) outside of the DMU.
-
Issues found
One or more tables in the database contain data with convertibility issues. These could be length limit (expansion) issues, invalid binary representation issues, or, in the case of data dictionary schemas, presence of convertible data.
-
Failed
One or more tables in the schema could not be scanned due to an unexpected error.
-
-
Tables to Convert
This is the number of tables in the schema that are already identified as requiring conversion in the conversion step.
-
Rows to Convert
This is the sum of Rows to Convert property values for all tables requiring conversion in the schema.
-
Scan Results
The scan results illustrate the classification of all scanned data cells in tables of the schema into conversion categories. A cell is a value of a given column in a given row. The classification is the same as that for the database except that the results are summed up for all tables in the schema, not for all tables in the database – see "Scanning the Database".
All the preceding properties are read-only.
Schema Properties: Readiness
This subtab shows the readiness of data for conversion. The Data Readiness for Conversion property might have one of the following values:
-
Does not need conversion
All data in the schema is classified as needing no conversion.
-
Ready for conversion
All data in the schema is classified as either needing no conversion, or needing conversion. The data has no conversion issues.
-
Not ready for conversion
Some data in the schema is classified as having invalid binary representation or exceeding length limits, or some scan results are missing.
If the readiness status is "Not ready for conversion", additional information is displayed to explain the problem.
Viewing and Setting Table Properties
The Table Properties tab has four subtabs: General, Scanning, Readiness, and Converting. The Converting subtab may be hidden if the table is not ready for conversion or it requires no conversion.
Table Properties: General
The General subtab of the Table Properties tab shows the following properties of a table:
-
Table Name
This is the name of the table.
-
Schema Name
This is the name of the schema to which the table belongs.
-
Tablespace
This is the name of the tablespace that contains the table. For partitioned tables, the property shows the default tablespace for new partitions.
-
Table Size
This is the size of the table as determined by its highwater mark.
-
Columns That May Contain Text
This is the list of columns in the table that might contain character data in the database character set and therefore might require conversion. The list shows column names, column data types, length constraints, the presence of a
NOTNULLconstraint, and the information if a column belongs to the primary key of the table.
These properties are read-only.
Table Properties: Scanning
On the Scanning subtab of the Table Properties tab, you can control the scanning of the table, and view the aggregated scan results for columns of this table.
The properties on the Scanning subtab are:
-
Available Rowids
This property tells if the last scan of the table collected rowids to identify rows containing cell data of a specific type. The possible values are:
-
None
No rowids have been collected for this table.
-
All to convert
Rowids of all rows containing at least one column value that requires conversion have been collected. These rowids are required for the conversion method "Update only convertible rows".
-
With issues
Only rowids of rows with at least one column value with conversion issues have been collected. These rowids might improve effectiveness of working with the Cleansing Editor. See Chapter 6, "Using the DMU to Cleanse Data".
-
-
Rowids to Collect
You can set this property to tell the DMU which rowids to collect during the next scan of the table. The possible values of this property are the same as for the Available Rowids property.
You can override the value of this property in the Scan Wizard. See "Scanning the Database".
-
Split over Threshold
Set this property to Yes to let the DMU divide the table into multiple chunks and then scan the chunks in parallel by multiple scanning processes. The DMU will split the table only if it is larger than an internally calculated threshold.
-
Done split
The value of this property tells if the last scan of the table was performed on multiple chunks in parallel.
-
Scan Status
This property shows the aggregated scan status of the table. The following values are possible:
-
Never scanned
No column of this table has been scanned since the most recent installation of the migration repository.
-
In progress
The table is currently being scanned.
-
Scanned
All columns in the table have been scanned and have valid scan results.
-
Partially scanned
Some columns in the table have been scanned and have valid scan results, but the remaining columns either have never been scanned or their scan results have been invalidated by a cleansing action or by modifications of their structure (metadata) outside of the DMU.
-
Results invalidated
Scan results of all columns of the table have been invalidated by a cleansing action or by modification of the table structure (metadata) outside of the DMU.
-
Issues found
One or more columns in the table contain data with conversion issues. These could be length limit (expansion) issues, invalid binary representation issues, or, in the case of data dictionary tables, presence of convertible data.
-
Failed
The last scan of columns of this table failed due to an unexpected error.
-
-
Rows to Convert
This is the number of rows in the table containing at least one column value that requires conversion.
-
Scan Results
The scan results illustrate the classification of all scanned data cells in the table into conversion categories. A cell is a value of a given column in a given row. The classification is the same as that for the database except that the results are summed up for all columns of the table, not for all tables in the database. See "Scanning the Database".
The scan results of columns whose data type is nested table are not added to the results of the table containing the column. The DMU presents the storage tables of nested table columns as separate tables.
Click Apply to save any changes made on this subtab.
Table Properties: Readiness
This subtab shows the readiness of table data for conversion. The Data Readiness for Conversion property might have one of the following values:
-
Does not need conversion
All data in the table is classified as needing no conversion.
-
Ready for conversion
All data in the table is classified as either needing no conversion, or needing conversion. The data has no conversion issues.
-
Not ready for conversion
Some data in the table is classified as having invalid binary representation or exceeding length limits, or some scan results are missing.
If the readiness status is "Not ready for conversion", additional information is displayed to explain the problem.
Table Properties: Converting
Properties on this subtab allow you to control certain aspects of the conversion of the table. The following properties can be set:
-
Conversion Method
This property decides how the DMU will update data in the table to convert it to the target character set. The possible values are:
-
Exclude from conversion
The table will not be converted. Only the scheduled cleansing actions might be applied.
-
Copy data using
CREATETABLEASSELECTA copy of the table will be created by the CTAS statement and the original table will be dropped. Column values will be converted by the query contained in this statement.
-
Update all rows
An
UPDATEstatement without aWHEREclause will be used to update all rows of the table. -
Update only convertible rows
An
UPDATEstatement will update only those rows of the table whose rowids have been collected during the last scan of the table. -
Scan and update only rows changing in conversion
An
UPDATEstatement will update only those rows of the table that contain a convertible column value as determined by an internal scanning function included in theWHEREclause of the statement.
The DMU automatically assigns one of the preceding conversion methods to each scanned table. Various features of a given table and the convertibility of its data determine which of the preceding methods are valid for the table. If more than one method is valid and your tests show that one of the alternative methods will be more effective, you can change the automatic assignment by changing the value of this property.
-
-
User-preferred Conversion Method
This property can be used to override the DMU recommended conversion method if necessary. If it is explicitly set by the user to a specific conversion method, the setting will be honored unless the selected conversion method is not applicable to the current table. The default value is "No preference", which means the DMU recommended conversion method will be used.
-
Target Tablespace
If the conversion method for the table is "Copy data using
CREATETABLEASSELECT," you can select a tablespace from this drop-down list to specify the tablespace in which the converted copy of the table will be created. The default value of this property is the tablespace containing the table. -
Preserve Position of
LONGColumnDue to restrictions of the CTAS statement, if the conversion method for the table is "Copy data using
CREATETABLEASSELECT," anyLONGcolumn of the table must be converted and copied separately from the rest of the table. The default processing applied by the DMU in such a case could change the position of theLONGcolumn in the table. This might break applications that select columns from the table using the asterisk syntax (SELECT*FROM). If you know about such an application, you can set this property to Yes to let the DMU apply a method that is less effective, but that will preserve the position of theLONGcolumn.
Click Apply to save any changes made on this subtab.
Viewing and Setting Column Properties
The Column Properties tab has four subtabs: General, Scanning, Readiness, and Converting. The Converting subtab might be hidden if the column is not ready for conversion or it requires no conversion.
Column Properties: General
The General subtab of the Column Properties tab shows the following properties of a table:
-
Column Name
This is the name of the column.
-
Column Type
This is the data type of the column.
-
Column Length
This is the length constraint of the column. Only
VARCHAR2andCHARcolumns might have a length constraint. -
May Contain
NULLIf the value of this property is Yes, the column might contain
NULLvalues. Otherwise, there is aNOTNULLorPRIMARYKEYconstraint disallowingNULLvalues in the column. -
Belongs to Primary Key
If the value of this property is Yes, the column belongs to a
PRIMARYKEYconstraint.
These properties are read-only.
Column Properties: Scanning
On the Scanning subtab of the Column Properties tab, you can view the scan results for the column. The properties on the Scanning subtab are:
-
Assumed Column Character Set
The value of this property shows the assumed character set of the column set in the Cleansing Editor. See Chapter 6, "Using the DMU to Cleanse Data".
-
Scan Status
This property shows the scan status of the column. The following values are possible:
-
Never scanned
No column of this table has been scanned since the most recent installation of the migration repository.
-
In progress
The table is currently being scanned.
-
Scanned
All columns in the table have been scanned and have valid scan results.
-
Results invalidated
The scan results of the column have been invalidated by a cleansing action or by modification of the table structure (metadata) outside of the DMU.
-
Issues found
The column contains data with conversion issues. These could be length limit (expansion) issues, invalid binary representation issues, or, in the case of data dictionary tables, presence of convertible data.
-
Failed
The last scan of the column failed due to an unexpected error.
-
-
Maximum Pre-Conversion Length
This property shows the length in bytes of the longest current value in the column.
-
Maximum Post-Conversion Length
This property shows the length in bytes of the longest value in the column after it will be converted to the target character set.
-
Scan Results
The scan results illustrate the classification of all scanned data cells (row values) in the column into conversion categories. The classification is the same as that for the database except that the results provided are for a single column only, not for all columns in the database. See "Viewing and Setting Database Properties".
The properties on this subtab are read-only.
Column Properties: Readiness
The Readiness subtab of the Column Properties tab contains the following properties:
-
Scheduled Cleansing Action
This property shows the scheduled cleansing action defined for the column in the Cleansing Editor. See Chapter 6, "Using the DMU to Cleanse Data".
-
Data Readiness for Conversion
This property tells if data in the column is ready for conversion. It might have one of the following values:
-
Does not need conversion
All data in the column is classified as needing no conversion.
-
Ready for conversion
All data in the table is classified as either needing no conversion, or needing conversion. The data has no conversion issues.
-
Has exceptional data
Some data in the column is classified as having invalid binary representation or exceeding length limits.
If the readiness status is "Not ready for conversion," additional information is displayed to explain the problem.
-
Column Properties: Converting
Properties on this subtab allow you to control certain aspects of the conversion of the column. The following property can be set:
-
Exclude from Conversion
If you set this property to Yes, the DMU does not update the data in this column.
-
Allow Conversion of Data with Issues
If the scan results of the column show that some values have conversion issues, that is, the converted values will contain replacement characters or they will be truncated, you can still let the DMU convert the data by setting this property to Yes. This might be useful if you want to automatically truncate data that exceeds the column or data type limit or you are not concerned about a few corrupted values that happen to exist in the column but are of no real significance for applications that use this data. Be careful not to set the property to Yes just to avoid the process of cleansing the data.
Click Apply to save any changes made on this subtab.