About Oracle ASM Instances
An Oracle ASM instance is built on the same technology as an Oracle Database instance. An Oracle ASM instance has a System Global Area (SGA) and background processes that are similar to those of Oracle Database. However, because Oracle ASM performs fewer tasks than a database, an Oracle ASM SGA is much smaller than a database SGA. In addition, Oracle ASM has a minimal performance effect on a server. Oracle ASM instances mount disk groups to make Oracle ASM files available to database instances; Oracle ASM instances do not mount databases. For information about managing an Oracle ASM instance, see Administering Oracle ASM Instances.
Oracle ASM is installed in the Oracle Grid Infrastructure home before Oracle Database is installed in a separate Oracle home. Oracle ASM and database instances require shared access to the disks in a disk group. Oracle ASM instances manage the metadata of the disk group and provide file layout information to the database instances.
Oracle ASM metadata is the information that Oracle ASM uses to control a disk group and the metadata resides within the disk group. Oracle ASM metadata includes the following information:
-
The disks that belong to a disk group
-
The amount of space that is available in a disk group
-
The file names of the files in a disk group
-
The location of disk group data file extents
-
A redo log that records information about atomically changing metadata blocks
-
Oracle ADVM volume information
Oracle ASM instances can be clustered using Oracle Clusterware; there is one Oracle ASM instance for each cluster node. If there are several database instances for different databases on the same node, then the database instances share the same single Oracle ASM instance on that node.
If the Oracle ASM instance on a node in a Standard Oracle ASM cluster fails, then all of the database instances on that node also fail. However, in an Oracle Flex ASM configuration, Oracle 12c database instances would not fail as they would be able to access another Oracle ASM instance remotely on another node. For information about Oracle Flex ASM, refer to "Managing Oracle Flex ASM".
Unlike a file system driver failure, an Oracle ASM instance failure does not require restarting the operating system. In an Oracle RAC environment, the Oracle ASM and database instances on the surviving nodes automatically recover from an Oracle ASM instance failure on a node.
Figure 1-1 shows a single node configuration with one Oracle ASM instance and multiple database instances. The Oracle ASM instance manages the metadata and provides space allocation for the Oracle ASM files. When a database instance creates or opens an Oracle ASM file, it communicates those requests to the Oracle ASM instance. In response, the Oracle ASM instance provides file extent map information to the database instance.
In Figure 1-1, there are two disk groups: one disk group has four disks and the other has two disks. The database can access both disk groups. The configuration in Figure 1-1 shows multiple database instances, but only one Oracle ASM instance is needed to serve the multiple database instances.
Figure 1-1 Oracle ASM for Single-Instance Oracle Databases
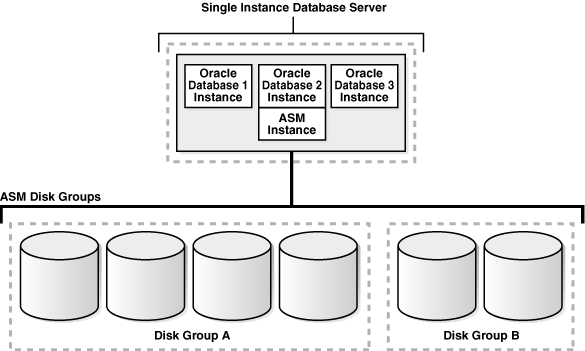
Description of "Figure 1-1 Oracle ASM for Single-Instance Oracle Databases "
Figure 1-2 shows an Oracle ASM cluster in an Oracle RAC environment where Oracle ASM provides a clustered pool of storage. There is one Oracle ASM instance for each node serving multiple Oracle RAC or single-instance databases in the cluster. All of the databases are consolidated and share the same two Oracle ASM disk groups.
Figure 1-2 Oracle ASM Cluster Configuration with Oracle RAC
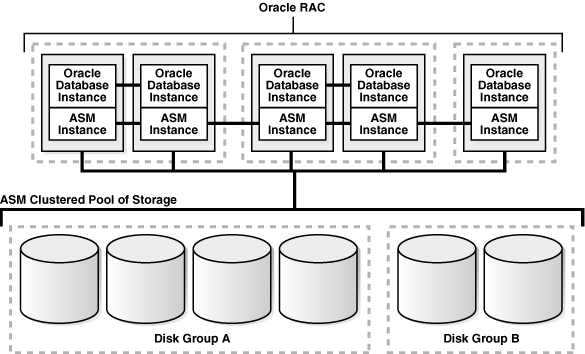
Description of "Figure 1-2 Oracle ASM Cluster Configuration with Oracle RAC"
A clustered storage pool can be shared by multiple single-instance Oracle Databases as shown in Figure 1-3. In this case, multiple databases share common disk groups. A shared Oracle ASM storage pool is achieved by using Oracle Clusterware. However, in such environments an Oracle RAC license is not required.
To share a disk group among multiple nodes, you must install Oracle Clusterware on all of the nodes, regardless of whether you install Oracle RAC on the nodes. Oracle ASM instances that are on separate nodes do not need to be part of an Oracle ASM cluster. However, if the Oracle ASM instances are not part of an Oracle ASM cluster, they cannot communicate with each other. Multiple nodes that are not part of an Oracle ASM cluster cannot share a disk group.
Figure 1-3 Oracle ASM Cluster with Single-Instance Oracle Databases
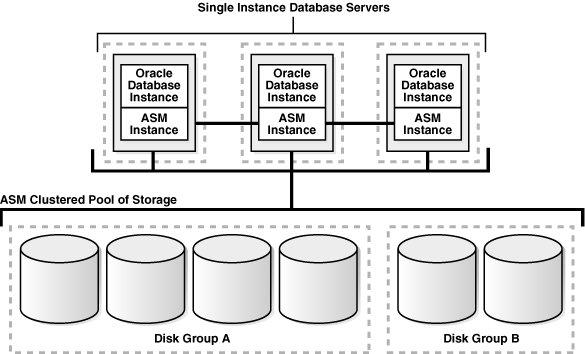
Description of "Figure 1-3 Oracle ASM Cluster with Single-Instance Oracle Databases"
For information about Oracle Flex ASM configurations, refer to "Managing Oracle Flex ASM".