Overview of Oracle Flex ASM
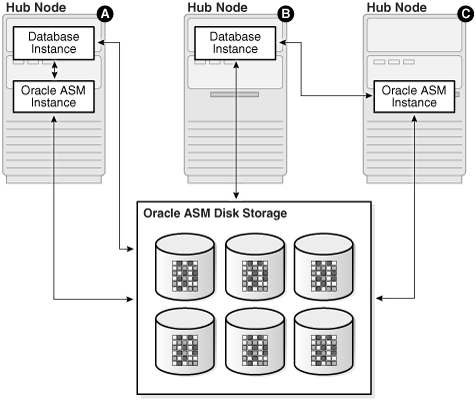
An Oracle ASM instance can operate in several configurations in Oracle Flex ASM, as shown in Figure 3-1. This illustration shows the distinct modes of operation which are available for Oracle Flex ASM in Oracle ASM 12c Release 1 (12.1).
Figure 3-1 Oracle Flex ASM Configurations
Description of "Figure 3-1 Oracle Flex ASM Configurations"
Oracle Flex ASM enables an Oracle ASM instance to run on a separate physical server from the database servers. With this deployment, larger clusters of Oracle ASM instances can support more database clients while reducing the Oracle ASM footprint for the overall system.
When using Oracle Flex ASM, Oracle ASM clients are configured with direct access to storage.
With Oracle Flex ASM, you can consolidate all the storage requirements into a single set of disk groups. All these disk groups are mounted by and managed by a small set of Oracle ASM instances running in a single cluster. You can specify the number of Oracle ASM instances with a cardinality setting. The default is three instances.
A cluster is a set of nodes that provide group membership services. Each cluster has a name that is globally unique. Every cluster has one or more Hub nodes. The Hub nodes have access to Oracle ASM disks. Every cluster has at least one private network and one public network. If the cluster is going to use Oracle ASM for storage, it has at least one Oracle ASM network. A single network can be used as both a private and an Oracle ASM network. For security reasons, an Oracle ASM network should never be public. There can be only one Oracle Flex ASM configuration running within a cluster.
The configurations of Oracle ASM in Oracle Flex ASM are:
-
Local Oracle ASM clients with direct access to Oracle ASM disks
With this mode (Standard Oracle ASM cluster), Oracle ASM continues to support existing standard architecture in which database clients are running with an Oracle ASM instance on the same host computer. The local client architecture is only supported on a Hub node. This mode is labeled A in Figure 3-1.
In this configuration, the database instances are on the same Hub node as the Oracle ASM instance and are referred to as local Oracle ASM client instances. Oracle ASM metadata moves between Oracle ASM and the database instances. This client has direct I/O access to Oracle ASM disks.
Local mode does not use Oracle Flex ASM, so clusters configured with local Oracle ASM do not require an Oracle ASM network, nor do they contain other Oracle Flex ASM services.
-
Oracle Flex ASM clients with direct access to Oracle ASM disks
With this mode, database clients that are running on Hub nodes of the Oracle ASM cluster access Oracle ASM remotely for metadata, but perform block I/O operations directly to Oracle ASM disks. The hosts running the Oracle ASM server and the remote database client must both be Hub nodes. A Hub node is a node in an Oracle ASM cluster that is tightly connected with other servers and has direct access to a shared disk. This mode is labeled B in Figure 3-1.
In this configuration, the database instances are on different host computers than the nearby Oracle ASM instance and are referred to as Oracle ASM client instances. This Oracle ASM instance is shown on the node labeled C in Figure 3-1. The databases are in the same Oracle ASM cluster as the Oracle ASM instance and the database instances are located on a Hub node. Oracle ASM metadata moves between Oracle ASM and the database instance. This client has direct I/O access to Oracle ASM disks.
Depending on the distribution of database instances and Oracle ASM instances, a database client may access Oracle ASM locally on the same node or remotely over the Oracle ASM network. This mode of operation is used by database clients on Hub nodes in the Oracle ASM cluster. Direct access mode is also the only Oracle Flex ASM configuration supported by Oracle ASM cluster file system.
-
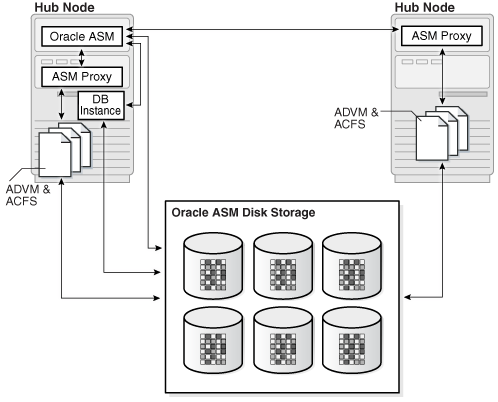
Oracle ACFS access through the Oracle ASM proxy instance
An Oracle ASM proxy instance is an Oracle instance running on a Hub node with a direct Oracle ASM client. Oracle Automatic Storage Management Cluster File System (Oracle ACFS) and Oracle ASM Dynamic Volume Manager (Oracle ADVM) are supported with an Oracle ASM proxy instance. This configuration is shown in Figure 3-2.
The
INSTANCE_TYPEinitialization parameter is set toASMPROXYfor Oracle ASM proxy instances.
Figure 3-2 shows the configuration of Oracle ACFS and Oracle ADVM in Oracle Flex ASM.
Figure 3-2 Oracle ACFS and Oracle ADVM in Oracle Flex ASM
Description of "Figure 3-2 Oracle ACFS and Oracle ADVM in Oracle Flex ASM"