RECOVER
Use the RECOVER command to perform one of the following distinct tasks:
-
Perform complete recovery of the whole database or one or more restored data files
-
Perform point-in-time recovery of a database (DBPITR), pluggable database (PDB), tablespace (TSPITR), table, or table partition
-
Apply incremental backups to a data file image copy (not a restored data file) to roll it forward in time
-
Recover a corrupt data block or set of data blocks within a data file
See Also:
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide to learn how to recover data filesAll redo or incremental changes required for the recovery must exist on disk or in SBT. If RMAN needs to restore incremental backups or archived redo log files during recovery, then you must either have automatic channels configured or manually allocate channels of the same type that created these backups.
If you perform media recovery on an encrypted tablespace, then the Oracle keystore must be open when performing media recovery of this tablespace. See Oracle Database Administrator's Guide to learn about encrypted tablespaces.
Prerequisites Specific to RECOVER BLOCK
The following prerequisites apply to RECOVER BLOCK:
-
The target database must run in
ARCHIVELOGmode and be open or mounted with a current control file. -
RMAN can only recover blocks marked media corrupt. The
V$DATABASE_BLOCK_CORRUPTIONview indicates which blocks in a file were marked corrupt since the most recentBACKUPorBACKUP ... VALIDATEcommand was run against the file. -
The backups of the data files containing the corrupt blocks must be full backups and not proxy backups. If only proxy backups exist, then you can restore them to a nondefault location on disk, in which case RMAN considers them data file copies. You can then use the data file copies for block media recovery.
-
RMAN can use only archived redo log files for recovery. Block media recovery cannot survive a missing or inaccessible log, although it can sometimes survive missing or inaccessible records (see Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide).
-
For RMAN to be able to search the flashback logs for good copies of corrupt blocks, Flashback Database must be enabled on the target database.
-
For RMAN to be able to search a standby database for good copies of corrupt blocks, the target database must be associated with a physical standby database in a Data Guard environment. In addition, the physical standby database must be open read-only in managed recovery.
Note:
An active Data Guard license is required for this operation.By default, RMAN performs complete recovery. For point-in-time recovery, the best practice is to enter a SET UNTIL command before both the RESTORE and RECOVER commands in a RUN command so that the UNTIL time applies to both commands. If you run SET UNTIL after restoring the database, then you may not be able to recover the database to the target time because the restored files may have timestamps later than the target time.
Note:
You must open the database with theRESETLOGS option after incomplete recovery or recovery with a backup control file.Incremental Backups and Archived Redo Log Files
Except for RECOVER BLOCK, RMAN can use both incremental backups and archived redo log files for recovery. RMAN uses the following search order:
-
Incremental backup sets on disk or tape
-
Archived redo log files on disk
-
Archived redo log backups on disk
-
Archived redo log backup sets on tape
When RMAN chooses a destination to restore archived redo log files, it uses the following order of precedence:
-
SETARCHIVELOG DESTINATION -
The
LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_nparameter whose value is set toLOCATION=USE_DB_RECOVERY_FILE_DEST -
LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_1
RMAN can apply incremental backups to data files that were not restored from an incremental backup. If overlapping levels of incremental backup exist, then RMAN automatically chooses the level covering the longest period of time.
Recovery Using Storage Snapshots
Storage Snapshot Optimization enables you to use third-party technologies to take storage snapshots without putting the database or associated data files in BACKUP mode. When recovering the database using a storage snapshot, specify the SNAPSHOT TIME option.
See Also:
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for information about specifying the snapshot timeTo be usable in recovery operations, the snapshots must conform to the following requirements. Ask your vendor for a guarantee of compliance.
-
The database is crash consistent during the snapshot.
-
The snapshot preserves write order for each file.
-
The snapshot technology stores the time at which the snapshot is completed.
Caution:
Take care that the database snapshots are usable. Oracle Database does not use a snapshot for recovery if structural changes were made during the snapshot. Operations on data files and tablespaces likeOFFLINE, READONLY, ONLINE, DROP, RENAME, SHRINK, and ADD make database structural changes. Do not use these operations during a snapshot.You must RESTORE data files before you can recover them. RMAN can recover through RESETLOGS operations transparently if the data files to be recovered are from a parent incarnation. If required, the RECOVER command can also restore and apply archived redo log files and incremental backups from previous database incarnations, even if those logs were generated in previous releases of Oracle Database.
When recovering through an OPEN RESETLOGS, ensure that you have all logs needed for recovery. In a previous database incarnation, you must have the logs from the time of the backup until the SCN that is 1 less than the RESETLOGS SCN. The incarnation table must have a complete history of RESETLOGS operations from the creation time of the database backup. If the complete metadata is not found in V$DATABASE_INCARNATION, then you can re-create this metadata by using CATALOG for the archived redo log files from the missing incarnations.
See Also:
RESTORE command for explanation of the default location for restoring archived redo log files. RMAN automatically specifies the MAXSIZE option when staging logs in the fast recovery area.RMAN enables you to recover a whole multitenant container database (CDB), the root, one or more PDBs, and tablespaces in a root or PDB. You can perform complete recovery or point-in-time recovery for PDBs and CDBs. However, you cannot recover the root to a specified point in time.
The process of recovering CDBs and PDBs is similar to that of non-CDBs. The difference is in the process of connecting to the CDB or PDB and in the commands used. To recover the whole CDB, the root, or multiple PDBs, you connect to the root. To recover a particular PDB, connect to that PDB. To recover PDBs, you use the RECOVER PLUGGABE DATABASE command. To recover a whole CDB, use the RECOVER DATABASE command and to recover the root, use the RECOVER DATABASE ROOT command.
See Also:
"CONNECT" for information about connecting to CDBs and PDBsSee Also:
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for information about performing recovery of CDBs and PDBsIn a Data Guard environment, you may need to restore the entire CDB after the point-in-time recovery of a primary database, for the standby database to follow the primary database.
recover::=
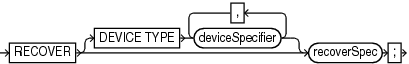
Description of the illustration recover.gif
(deviceSpecifier::=, recoverObject::=, recoverOptionList::=)
recoverSpec::=
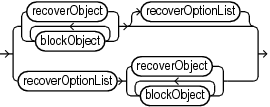
Description of the illustration recoverspec.gif
(recoverObject::=, blockObject::=, recoverOptionList::=)
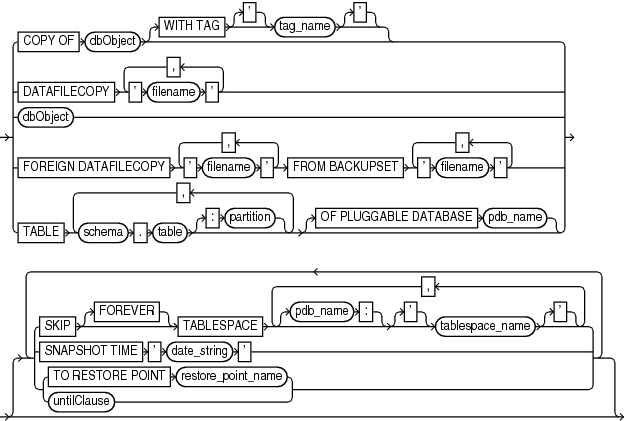
Description of the illustration recoverobject.gif
dbObject::=
Description of the illustration dbobject.gif
blockObject::=
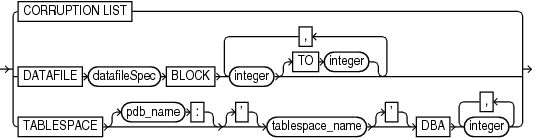
Description of the illustration blockobject.gif
Description of the illustration recoveroptionlist.gif
(remapTableList::=, sizeSpec::=)
Description of the illustration remaptablelist.gif
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
DEVICE TYPE deviceSpecifier |
Allocates automatic channels for the specified device type only. For example, if you configure automatic disk and tape channels, and if you issue RECOVER DEVICE TYPE DISK, then RMAN allocates only disk channels.
You configure a device type with the Note: You cannot manually allocate channels and then run See Also: |
recoverSpec |
Specifies the type of object being recovered. |
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
recoverObject |
Specifies the type of object being recovered. |
blockObject |
Specifies the blocks to be recovered with block media recovery. |
recoverOptionList |
Specifies recovery options. |
This subclause specifies which files to recover. Refer to recoverObject::= for the syntax diagram.
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
COPY OF dbObject |
Applies incremental backups to the specified image copy to roll it forward to any time equal to or before the most recent incremental backup of the file. The existing image copy is overwritten and remains in a fuzzy state during the recovery. RMAN makes an autobackup after recovering the image copy.
This command updates a data file copy and is not a media recovery of a current database file. This command is meant to be used with the The following requirements must be met:
RMAN selects one suitable copy if there are multiple possible copies to which the incremental backups can be applied to carry out the operation. Note: RMAN issues a warning (not an error) if it cannot recover to the specified time because no incremental backups are available. |
WITH TAG tag_name |
Specifies a tag name to identify the image copy to be rolled forward. |
DATAFILECOPY 'filename' |
Applies incremental backups to the specified data file image copy (see Example 3-4). Refer to description of RECOVER COPY OF. |
dbObject |
Specifies the data blocks that require recovery.
See Also: dbObject::= |
FOREIGN DATAFILECOPY'filename' |
Specifies the name of the foreign datafile copies that need to be made consistent by applying incremental backups. These foreign datafile copies were created during an inconsistent cross-platform backup by using either the CONVERT or BACKUP command with the ALLOW INCONSISTENT clause. |
FROM BACKUPSET 'filename' |
Specifies the name of the backup set containing the cross-platform incremental backup that must be applied to the foreign datafile copies specified using the FOREIGN DATAFILECOPY clause.
The following conditions must be satisfied for a cross-platform incremental backup to be applied:
If these conditions are not met, an error occurs and the cross-platform incremental backup is not applied to the foreign datafile copies. |
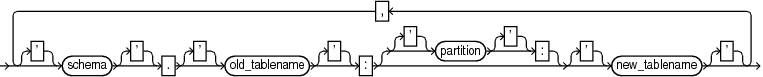
TABLE schema.table[:partition] |
Specifies the tables or table partitions that must be recovered. The target database must be in read-write mode.
You can assign new names for recovered tables or table partitions in the target database by using the When the recovered tables are imported into the target database, if a table with the same name exists in the target database, an error message is displayed indicating that the When you recover only certain partitions from a partitioned table, each partition is imported into the target database as separate table. If See Example 3-8, "Recovering Tables Partitions from a Backup" |
OF PLUGGABLE DATABASE pdb_name |
In a CDB, the name of a PDB in which the table or table partition that must be recovered resides. To recover tables or table partitions in a PDB, you must connect to the root as described in "Connecting to CDBs and PDBs". |
SKIP |
Takes the data files in the specified tablespaces offline before starting media recovery. These files are left offline after the media recovery is complete.
This option is useful for avoiding recovery of tablespaces containing only temporary data or for postponing recovery of some tablespaces. |
FOREVER |
Takes the data files offline with the DROP option (see Example 3-3). Use SKIP FOREVER TABLESPACE when you intend to drop the specified tablespaces after opening the database with the RESETLOGS option.
Note: If you perform incomplete recovery, then |
TABLESPACE tablespace_name |
Specifies the name of the tablespace to take offline. |
TABLESPACE pdb_name:tablespace_name |
The name of a tablespace in a PDB. |
SNAPSHOT TIME 'date_string' |
Specifies time-based recovery from a snapshot backup that was created using Storage Snapshot Optimization. date_string is the time at which the snapshot was completed and is specified in RMAN TIME format (defined by NLS_DATE_FORMAT environment variable).
You can combine See Also: "Recovery Using Storage Snapshots" for information about the requirements of the snapshot system and how to specify the snapshot time. |
TO RESTORE POINTrestore_point_name |
Specifies a restore point for termination of the RECOVER command, with the SCN at which the restore point was created as the upper, inclusive limit. Because the limit is inclusive, RMAN selects only files that it can use to recover up to and including the SCN corresponding to the restore point. |
untilClause |
Specifies a past time, SCN, or log sequence number for termination of the RECOVER command.
When used with one or more tablespaces, the clause indicates a tablespace point-in-time recovery (TSPITR) operation for the named tablespaces. Do not use this clause with See Also: |
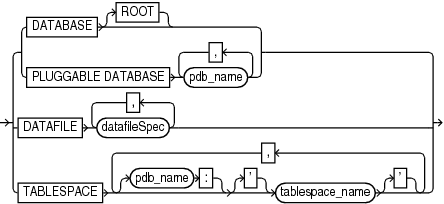
This subclause specifies whether to recover the database or a subset of the database. Refer to dbObject::= for the syntax diagram.
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
DATABASE |
Specifies the entire database (see Example 3-3). For CDBs, it specifies the entire CDB.
In a CDB, recovers the entire CDB. You connect to the root to backup the whole CDB as described in "Connecting to CDBs and PDBs". By default, the When recovering after the loss of control files, RMAN automatically updates the control file to point to the actual location of the data files on disk (see Example 3-5). If RMAN encounters redo for adding a data file, then RMAN automatically creates a new data file unless the tablespace containing the added data file is skipped during recovery. This situation can arise when a backup control file is restored before recovery and the backup control file does not contain a record of the recently-added data file. |
DATABASE ROOT |
Specifies only the root in a CDB. Connect to the root as described in "Connecting to CDBs and PDBs". |
PLUGGABLE DATABASE pdb_name |
Specifies one or more PDBs in a CDB. No other PDBs are affected; they can remain open and operational. Use a comma-delimited list to specify multiple PDBs. To use this clause, you must connect to the root.
Performing complete recovery does not require you to connect to the root. You connect to the root to perform any of the following operations for PDBs: point-in-time recovery, table recovery, TSPITR, or duplication. To connect to the root or a PDB, see "Connecting to CDBs and PDBs". |
DATAFILE datafileSpec |
Specifies a list of one or more data files by either file name or absolute data file number.
The target database must be mounted or open. If the database is open, then the data files to be recovered must be offline. If you are not using a recovery catalog, then the file name must be the name of the data file as recorded in the control file. If you are using a recovery catalog, then the file name of the data file must be the most recent name recorded in the catalog, even if the name in the control file has been updated more recently. For example, assume that a data file was renamed in the control file, but the instance fails before you resynchronize the catalog. Specify the old name of the data file in the Note: You cannot arbitrarily recover individual data files to different points in time, although you can recover the whole database to a single point in time or recover wholly contained tablespaces to a point in time different from the rest of the database (TSPITR). For more information on TSPITR, see the procedure described in Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide. See Also: |
TABLESPACE tablespace_name |
Specifies a list of one or more tablespaces. The target database must be mounted or open. If the database is open, then the tablespaces to be recovered must be offline.
When connected to the root in a CDB, specifies the tablespaces in the root. Specifies the names of tablespaces in a PDB when connected to a PDB. In a CDB, specifies the name of a tablespace in the root when connected to the root, and specifies the name of a tablespace in a PDB when connected to a PDB. Note: If the RMAN encounters redo for adding a data file, then RMAN automatically creates a new data file. This situation can arise when a backup control file is restored before recovery and the backup control file does not contain a record of the recently-added data file. |
TABLESPACE pdb-name:tablespace_name |
The name of the tablespace in a PDB. Multiple PDBs can have tablespaces with the same name. A qualifier before the name uniquely identifies the tablespace. This syntax is needed only when connected to the root. When connected directly to a PDB, use TABLESPACE tablespace_name. pdb-name is the name of a PDB.
See the previous description for |
This subclause specifies the data blocks that require recovery. Refer to blockObject::= for the syntax diagram. Refer to "Prerequisites Specific to RECOVER BLOCK" for prerequisites specific to block media recovery.
You can either use RECOVER CORRUPTION LIST to recover all blocks reported in the V$DATABASE_BLOCK_CORRUPTION view, or specify the data file number and block number or the tablespace and data block address (DBA). RMAN can only perform complete recovery of individual blocks.
By default, if Flashback Database is enabled, then RMAN searches the flashback logs for good copies of corrupt blocks. By default, if the target database exists in a Data Guard environment, then RECOVER BLOCK command can automatically retrieve blocks from a physical standby database to a primary database and vice-versa.
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
CORRUPTION LIST |
Recovers all physically corrupt blocks listed in the V$DATABASE_BLOCK_CORRUPTION view. Block media recovery may not be able to repair all listed logically corrupt blocks. In these cases, alternate recovery methods, such as tablespace point-in-time recovery, or dropping and recreating the affected objects, may repair the corruption.
The
The view does not record corruptions that can be detected by validating relationships between blocks and segments, but cannot be detected by a check of an individual block. Note: Any RMAN command that fixes or detects that a block is repaired updates |
DATAFILE datafileSpecBLOCK integer TO integer |
Recovers an individual data block or set of data blocks within a data file. It can copy blocks from either a standby or a primary database. The TO range is inclusive, so that BLOCK 10 TO BLOCK 20 includes both block 10 and block 20.
Block media recovery is useful when the data loss or corruption applies to a small number of blocks rather than to an entire data file. Typically, block corruption is reported in error messages in trace files or by the
If you do not specify an option from Blocks marked media corrupt are not accessible until recovery completes. Note: You can only perform complete recovery of individual blocks. In other words, you cannot stop recovery before all redo has been applied to the block. See Also: |
TABLESPACE tablespace_nameDBA integer |
Specifies the tablespace name or number containing the corrupt blocks and the data block address (DBA) of the corrupt block. You can only perform block media recovery on corrupt blocks.
Note: The data file header block (block 1) cannot be recovered. |
TABLESPACE pdb-name:tablespace_name DBA integer |
The name of the tablespace in a PDB. Multiple PDBs can have tablespaces with the same name. A qualifier before the name uniquely identifies the tablespace. pdb-name is the name of a PDB.
See the previous description of |
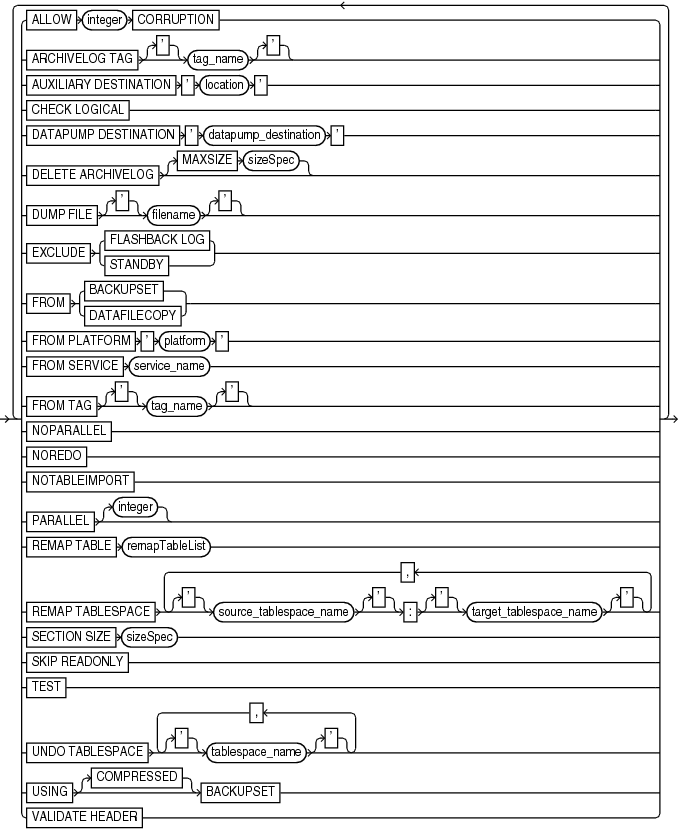
This subclause specifies various recovery options. Refer to recoverOptionList::= for the syntax diagram.
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
ALLOW integer CORRUPTION |
Specifies the number of corrupt blocks that can be tolerated while allowing recovery to proceed.You can set this parameter in case of redo log corruption. |
ARCHIVELOG TAG tag_name |
Specifies the tag for an archived log backup to be used during recovery. Tag names are not case sensitive and display in all uppercase. If the tagged backup does not contain all the necessary archived redo log files for recovery, then RMAN uses logs or incremental backups as needed from whatever is available. |
AUXILIARY DESTINATION'location' |
Specifies a location where auxiliary set data files, control files, and online redo logs are created during TSPITR if another location for an individual file is not explicitly specified.
If you do not specify While performing point-in-time recovery of PDBs, if no auxiliary destination is specified, then the fast recovery area is used as the auxiliary destination. When an auxiliary destination is not specified and a fast recovery area is not configured, the recovery of the PDB fails. See also: The chapter on TSPITR in Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for more details about the auxiliary destination |
CHECK LOGICAL |
Tests data and index blocks that pass physical corruption checks for logical corruption, for example, corruption of a row piece or index entry. If RMAN finds logical corruption, then it logs the block in the alert.log and server session trace file.
The If the total number of physical and logical corruptions detected for a file is less than its |
DATAPUMP DESTINATION 'datapump_destination' |
Specifies the location of the Data Pump export dump file that contains the tables or table partitions that are recovered from an RMAN backup.
If you do not specify a Data Pump destination, RMAN creates the export dump file in the destination indicated by |
DELETE ARCHIVELOG |
Deletes archived redo log files restored from backups or copies that are no longer needed. RMAN does not delete archived redo log files that were on disk before the RESTORE command started. If you do not specify MAXSIZE, then RMAN deletes restored archived redo log files as they are applied.
Note: If archived redo log files are restored to the fast recovery area, then the |
MAXSIZE sizeSpec |
Does not use more than sizeSpec amount of disk space for restored archived redo log files. If recovery requires the restore of a log larger than the MAXSIZE value, then RMAN reports an error indicating that you must increase the MAXSIZE value. If MAXSIZE is smaller than the backup set containing the logs, then RMAN must read the backup set more than once to extract the logs. In this situation, RMAN issues a warning to increase MAXSIZE. |
DUMP FILE 'filename' |
Specifies the name of the Data Pump export dump file that contains the recovered tables or table partitions. If you do not specify a name for the dump file, RMAN assigns a default name based on the operating system of the target database. The default name is tspitr_SID-of-clone_n.dmp where SID-of-clone is the Oracle SID of the auxiliary database used by RMAN for recovery and n is a randomly-generated number. The dump file is created in the location specified by DATAPUMP DESTINATION.
If See Also: DATAPUMP DESTINATION |
EXCLUDE FLASHBACK LOG |
Does not search the flashback logs for blocks to restore. By default, RMAN searches the flashback logs if Flashback Database is enabled. |
EXCLUDE STANDBY |
Does not search a physical standby database for blocks to restore. By default, in a Data Guard environment RMAN searches the blocks from a physical standby database. |
FROM BACKUPSET |
Specifies that only backup sets are restored.This clause is supported only while performing block media recovery. The RECOVER ... BLOCK command is used to perform block media recovery. |
FROM DATAFILECOPY |
Restores only data file image copies.
This clause is supported only while performing block media recovery. The |
FROM PLATFORM 'platform' |
Specifies the name of the source platform on which the cross-platform backup was created. The platform name specified must match the platform identifier stored in the cross-platform backup header.
This clause is required when conversion is performed on the destination database. If conversion is performed on the source database (by using the Note: Cross-platform data transportation using backup sets is supported starting with Oracle Database 12c Release 1 (12.1). See See Also: Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for more information about source and destination platform conversion. |
FROM SERVICE service_name |
Recovers data files using backup sets that are transferred, over the network, from a remote database. service_name specifies the service name of the remote database.
See "Restoring Data Files and Control Files Using Files from a Remote Host". |
FROM TAG 'tag_name' |
Specifies the tag for an incremental backup to be used during recovery. If the tagged backup does not contain all the necessary incrementals for recovery, then RMAN uses logs or incremental backups as needed from whatever is available. Tag names are not case sensitive and display in all uppercase.
See Also: |
NOPARALLEL |
Does not perform media recovery in parallel. Parallel execution is the default for RECOVER (see the description of the RECOVER ... PARALLEL option). |
NOREDO |
Suppresses the application of redo logs during recovery. Only incremental backups are applied.
One use of this option is to use incremental backups to update full backups of Note: Incremental backups of Another use is to update standby or duplicate databases. Incremental backups created with the |
NOTABLEIMPORT |
Specifies that RMAN must not import recovered tables or table partitions into the target database.
The recovered objects are stored in an Data Pump export dump file that is specified using When required, you need to explicitly import the tables or table partitions contained in the export dump file into the target database. Use the Data Pump import utility to import the recovered objects. Note: You cannot use |
PARALLEL |
Specifies parallel recovery (default).
By default, the database uses parallel media recovery to improve performance of the roll forward phase of media recovery. To override the default behavior of performing parallel recovery, use the In parallel media recovery, the database uses a "division of labor" approach to allocate different processes to different data blocks while rolling forward, thereby making the operation more efficient. The number of processes is derived from the Typically, recovery is I/O-bound on reads from and writes to data blocks. Parallelism at the block level may only help recovery performance if it increases total I/Os, for example, by bypassing operating system restrictions on asynchronous I/Os. Systems with efficient asynchronous I/O see little benefit from parallel media recovery. Note: The See Also: The description of the |
integer |
Specifies the integer degree of parallelism.
Each parallel thread may use one or two parallel execution servers. Optional. |
REMAP TABLE |
Renames recovered tables or table partitions in the target database. You cannot remap a table or partition that is not listed in the TABLE clause of the RECOVER command.
When a recover a partitioned table, if you remap only some partitions in the table, then all the table partitions are imported as separate tables. Named constraints and indexes are not imported when you use the REMAP option. |
REMAP TABLESPACE source_tablespace_name:target_tablespace_name |
Imports the recovered tables or table partitions into a tablespace that is different from the one to which they belonged in the source database.
Named constraints and indexes are not imported when you use the REMAP option. |
SECTION SIZE sizeSpec |
Parallelizes the validation by dividing each file into the specified section size. |
SKIP READONLY |
Omits read-only files from the recovery. |
TEST |
Initiates a trial recovery.
A trial recovery is useful if a normal recovery procedure has encountered a problem. It enables the database to look ahead into the redo stream to detect possible problems. The trial recovery applies redo in a way similar to normal recovery, but it does not write changes to disk and it rolls back its changes at the end of the trial recovery. Note: You can use this clause only if you have restored a backup taken since the last |
UNDO TABLESPACEtablespace_name |
Specifies a list of tablespaces with undo segments at the target time. Only for use with RECOVER TABLESPACE.
During TSPITR, RMAN needs information about which tablespaces had undo segments at the TSPITR target time. This information is usually available in the recovery catalog, if one is used. If there is no recovery catalog, or if the information is not found in the recovery catalog, then RMAN proceeds if the set of tablespaces with undo segments at the target time equals the set of tablespaces with undo segments now. If this assumption is not correct, then TSPITR fails with an error. In such a case, you can use |
USING [COMPRESSED] BACKUPSET |
Specifies that the files being recovered must be transferred from the remote database as compressed backup sets, if USING COMPRESSED BACKUPSET is used. By default, RMAN transfers files as backup sets. Therefore, even if you do not use the USING BACKUPSET clause, the files are transferred as backup sets.The compression algorithm from the RMAN configuration is used to perform compression. You can use a different compression algorithm by running the SET COMPRESSION ALGORITHM before your RECOVER command. |
VALIDATE HEADER |
Reports and validates—but does not restore—the backups that RMAN could use to restore files needed for the recovery.
When you run See Also: The description of the |
| Syntax Element | Description |
|---|---|
schema |
Name of the schema in the source database |
old_tablename |
Name of the table in the source database |
partition |
Name of the table partition in the source database |
new_tablename |
Name of the table in the target database, after the table has been recovered |
Example 3-1 Recovering a Tablespace in an Open Database
Assume that the disk containing the data files for tablespace users becomes unavailable because of a hardware error, but is repaired after a few minutes. This example takes tablespace users offline, uses automatic channels to restore the data files to their default location and recover them (deleting the logs that it restored from tape), then brings the tablespace back online.
ALTER TABLESPACE users OFFLINE IMMEDIATE; RESTORE TABLESPACE users; RECOVER TABLESPACE users DELETE ARCHIVELOG MAXSIZE 2M; ALTER TABLESPACE users ONLINE;
Example 3-2 Recovering Data Files Restored to New Locations
This example uses the preconfigured disk channel and manually allocates one media management channel to use data file copies on disk and backups on tape, and restores a data file in tablespace USERS to a different location.
RUN
{
ALLOCATE CHANNEL ch1 DEVICE TYPE sbt;
ALTER TABLESPACE users OFFLINE IMMEDIATE;
SET NEWNAME FOR DATAFILE '/disk1/oradata/prod/users01.dbf'
TO '/disk2/users01.dbf';
RESTORE TABLESPACE users;
SWITCH DATAFILE ALL;
RECOVER TABLESPACE users;
ALTER TABLESPACE users ONLINE;
}
Example 3-3 Performing DBPITR with a Backup Control File and Recovery Catalog
Assume that all data files, all control files, and archived redo log 58 were lost due to a disk failure. Also assume that you do not have incremental backups. You must recover the database with available archived redo log files. You do not need to restore tablespace TOOLS because it has been read-only since before the most recent backup. After connecting RMAN to the target database and recovery catalog, issue the following commands:
STARTUP FORCE NOMOUNT;
RUN
{
SET UNTIL SEQUENCE 40 THREAD 1; # Recover database until log sequence 40
RESTORE CONTROLFILE;
ALTER DATABASE MOUNT;
RESTORE DATABASE SKIP TABLESPACE tools;
RECOVER DATABASE SKIP TABLESPACE tools;
}
ALTER DATABASE OPEN RESETLOGS;
RMAN automatically skips the restore and recovery of data file 8, which is the data file in the read-only tablespace. The following portion of sample output indicates the skip:
using channel ORA_DISK_1 allocated channel: ORA_SBT_TAPE_1 channel ORA_SBT_TAPE_1: SID=104 device type=SBT_TAPE channel ORA_SBT_TAPE_1: Oracle Secure Backup skipping datafile 8; already restored to file /disk1/oradata/prod/tools01.dbf channel ORA_DISK_1: starting datafile backup set restore . . . Finished restore at 19-FEB-13 Starting recover at 19-FEB-13 using channel ORA_DISK_1 using channel ORA_SBT_TAPE_1 datafile 8 not processed because file is read-only
Example 3-4 Incrementally Updating Backups
By incrementally updating backups, you can avoid the overhead of making full image copy backups of data files, while also minimizing time required for media recovery of your database. This example enables you to recover to any SCN within the previous week, but enables you to avoid having to apply more than one day of redo.
Assume you run the following script daily. On first execution, the script creates an image copy backup of the database on disk with the specified tag. On the second through the seventh executions, the script creates a level 1 differential backup of the database. On the eighth and all subsequent executions, RMAN applies the level 1 incremental to the data file copy made 7 days ago and then makes a new level 1 backup with the changes from the previous day.
RUN
{
RECOVER COPY OF DATABASE
WITH TAG 'incr_update'
UNTIL TIME 'SYSDATE - 7';
BACKUP
INCREMENTAL LEVEL 1
FOR RECOVER OF COPY WITH TAG 'incr_update'
DATABASE;
}
Example 3-5 Recovery from Loss of a Control File on a Standby Database
Assume that the standby database dgprod3 control files are lost because of a media failure. The primary and standby database share SBT storage. A backup of the primary database control file exists on tape.
You start the RMAN client and connect to dgprod3 as TARGET and connect to the recovery catalog. The following RMAN commands restore a control file that is usable by the standby database, update the file names to existing files on disk, and recover the standby database:
RESTORE CONTROLFILE; ALTER DATABASE MOUNT; RECOVER DATABASE;
You can then start redo apply on the standby database.
Example 3-6 Recovering a NOARCHIVELOG Database
You can perform limited recovery of changes to a database running in NOARCHIVELOG mode by applying incremental backups. The incremental backups must be consistent, like all backups of a database run in NOARCHIVELOG mode, so you cannot back up the database when it is open.
Assume that you run database prod in NOARCHIVELOG mode with a recovery catalog. You shut down the database consistently and make a level 0 backup of database prod to tape on Sunday afternoon. You shut down the database consistently and make a level 1 differential incremental backup to tape at 3:00 a.m. on Wednesday and Friday.
On Saturday, a media failure destroys half of the data files and all the online redo logs. Because the online logs are lost, you must specify the NOREDO option in the RECOVER command. Otherwise, RMAN searches for the redo logs after applying the Friday incremental backup and issues an error message when it does not find them.
After connecting RMAN to prod and the catalog database, recover as follows:
STARTUP FORCE NOMOUNT; RESTORE CONTROLFILE; # restore control file from consistent backup ALTER DATABASE MOUNT; RESTORE DATABASE; # restore data files from consistent backup RECOVER DATABASE NOREDO; # specify NOREDO because online redo logs are lost ALTER DATABASE OPEN RESETLOGS;
The recovered database reflects only changes up through the time of the Friday incremental backup. Because there are no archived redo log files, there is no way to recover changes made after the incremental backup.
Example 3-7 Recovering All Block Corruption in the Database
This example runs a backup validation to populate the V$DATABASE_BLOCK_CORRUPTION view, then recovers any corrupt blocks recorded in the view. Sample output is included for both commands.
RMAN> VALIDATE DATABASE; Starting validate at 19-FEB-13 using channel ORA_DISK_1 channel ORA_DISK_1: starting validation of datafile channel ORA_DISK_1: specifying datafile(s) for validation . . . List of Datafiles ================= File Status Marked Corrupt Empty Blocks Blocks Examined High SCN ---- ------ -------------- ------------ --------------- ---------- 1 FAILED 0 4070 57600 555975 File Name: /disk1/oradata/prod/system01.dbf Block Type Blocks Failing Blocks Processed ---------- -------------- ---------------- Data 1 41550 Index 0 7677 Other 0 4303 . . . RMAN> RECOVER CORRUPTION LIST; Starting recover at 19-FEB-13 using channel ORA_DISK_1 allocated channel: ORA_SBT_TAPE_1 channel ORA_SBT_TAPE_1: SID=104 device type=SBT_TAPE channel ORA_SBT_TAPE_1: Oracle Secure Backup searching flashback logs for block images until SCN 547548 finished flashback log search, restored 1 blocks starting media recovery media recovery complete, elapsed time: 00:00:03 Finished recover at 19-FEB-13
Example 3-8 Recovering Tables Partitions from a Backup
This example recovers the partitions sales_2009 and sales_2010 from the table SALES to the time when the SCN of the target database was 34582. In the source database, the tables are owned by the schema SH. While importing these partitions into the target database, the partitions are created as tables named historic_sales_2009 and historic_sales_2010.
RECOVER TABLE SH.SALES:SALES_2009, SH.SALES:SALES_2010
UNTIL SCN 34582
AUXILIARY DESTINATION '/tmp/oracle/recover'
REMAP TABLE 'SH'.'SALES':'SALES_2009':'HISTORIC_SALES_2009', 'SH'.'SALES':'SALES_2010':'HISTORIC_SALES_2010';
Example 3-9 Recovering Tables to a Specified Log Sequence and Renaming the Tables
This example uses an auxiliary instance to recover the table EMP from the SCOTT schema to the time when the log sequence number of the database was 5466. After the EMP table is recovered, it is imported into the target database using the name MY_EMP.
RECOVER TABLE SCOTT.EMP
UNTIL SEQUENCE 5466
AUXILARY DESTINATION '/tmp/recover'
REMAP TABLE 'SCOTT'.'EMP':'MY_EMP';
Example 3-10 Recovering Tables to a Specified Time and Into a Different Tablespace
This example recovers tables EMP and DEPT to the point in time specified by the UNTIL TIME clause. The tables were originally part of the EXAMPLE tablespace. However, after the recovery operation, they are mapped to the tablespace MY_TBS in the target database.
RECOVER TABLE SCOTT.EMP, SCOTT.DEPT
UNTIL TIME "TO_CHAR('12/23/2012 12:00:00','mm/dd/yyyy hh24:mi:ss')"
AUXILIARY DESTINATION '/tmp/oracle/recover'
REMAP TABLESPACE 'EXAMPLE':'MY_TBS';