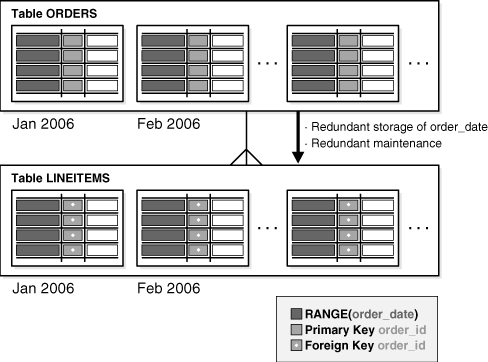
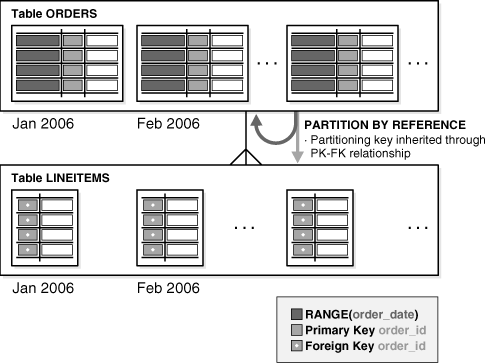
Reference Partitioning
Reference partitioning enables the partitioning of two tables that are related to one another by referential constraints. The partitioning key is resolved through an existing parent-child relationship, enforced by enabled and active primary key and foreign key constraints.
The benefit of this extension is that tables with a parent-child relationship can be logically equipartitioned by inheriting the partitioning key from the parent table without duplicating the key columns. The logical dependency also automatically cascades partition maintenance operations, thus making application development easier and less error-prone.
An example of reference partitioning is the Orders and LineItems tables related to each other by a referential constraint orderid_refconstraint. Namely, LineItems.order_id references Orders.order_id. The Orders table is range partitioned on order_date. Reference partitioning on orderid_refconstraint for LineItems leads to creation of the following partitioned table, which is equipartitioned on the Orders table, as shown in Figure 2-4 and Figure 2-5.
All basic partitioning strategies are available for reference partitioning. Interval partitioning can also be used with reference partitioning.