About Online Redo Log Files
Every Oracle database has a set of two or more online redo log files. The set of online redo log files is collectively known as the redo log for the database. A redo log is made up of redo entries, which are also called redo records.
The online redo log stores a copy of the changes made to data. If a failure requires a data file to be restored from backup, then the recent data changes that are missing from the restored data file can be obtained from the online redo log files, so work is never lost. The online redo log files are used to recover a database after hardware, software, or media failure. To protect against a failure involving the online redo log file itself, Oracle Database can multiplex the online redo log file so that two or more identical copies of the online redo log file can be maintained on different disks.
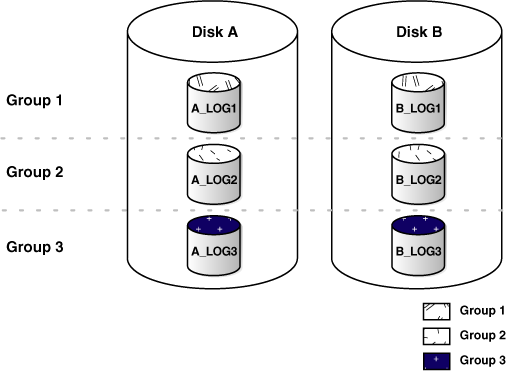
The online redo log for a database consists of groups of online redo log files. A group consists of an online redo log file and its multiplexed copies. Each identical copy is considered to be a member of that group. Each group is defined by a number, such as Group 1.
Figure 6-2 shows the configuration of a database that has three online redo log groups and two members in each group. For each group, the members are stored on separate disks for maximum availability. For example, the members of Group 1 are the redo log files A_LOG1 and B_LOG1.
Figure 6-2 Online Redo Log Groups and Their Members
Description of "Figure 6-2 Online Redo Log Groups and Their Members"
The database log writer process (LGWR) writes redo records from the memory buffer to a redo log group until the log files in that group reach their storage size limit, or until you request a log switch operation. The LGWR process then writes to the next log group. The LGWR process performs this action in a circular fashion so that the oldest group is overwritten by the most recent redo records.
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Concepts for an overview of online redo logs
-
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for detailed information about redo logs