9 Configuring Secure Application Roles for Oracle Database Vault
Secure application roles enable you to control how much access users have to an application.
Topics:
What Are Secure Application Roles in Oracle Database Vault?
In Oracle Database Vault, you can create a secure application role that you enable with an Oracle Database Vault rule set.
Regular Oracle Database secure application roles are enabled by custom PL/SQL procedures. You use secure application roles to prevent users from accessing data from outside an application. This forces users to work within the framework of the application privileges that have been granted to the role.
The advantage of basing database access for a role on a rule set is that you can store database security policies in one central place, as opposed to storing them in all your applications. Basing the role on a rule set provides a consistent and flexible method to enforce the security policies that the role provides. In this way, if you must update the security policy for the application role, you do it in one place, the rule set. Furthermore, no matter how the user connects to the database, the result is the same, because the rule set is bound to the role. All you need to do is to create the role and then associate it with a rule set. The associated rule set validates the user who is trying to enable the role.
See Also:
-
"Related Reports and Data Dictionary View" for information about how you can run reports secure application roles that you created in Oracle Database Vault
-
Chapter 17, "Oracle Database Vault Secure Application Role APIs" for information about using the PL/SQL interfaces and packages to create and manage Oracle Database Vault secure application roles
Creating Oracle Database Vault Secure Application Roles
You can create a Database Vault secure application role in Database Vault Administrator.
-
From Cloud Control, log into Oracle Database Vault Administrator as a user who has been granted the
DV_OWNERorDV_ADMINrole."Logging into Oracle Database Vault" explains how to log in.
-
Create a rule set that contains at least one rule to set the conditions for allowing or disallowing the user to enable the role.
When you create the underlying rule for the rule set, remember that the rule should validate the user who is trying to enable the role. See Chapter 6, "Configuring Rule Sets," for more information about rule sets.
-
In the Administration page, under Database Vault Components, click Secure Application Roles.
-
In the Secure Application Role page:
-
To create a new secure application role, click Create to display the Create Secure Application Role page.
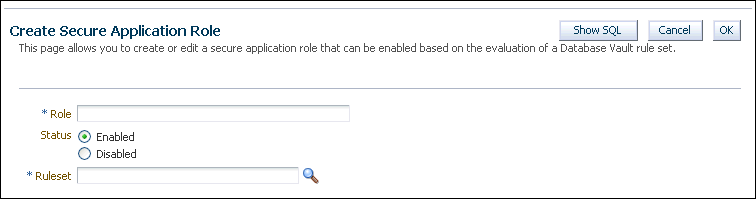
Description of the illustration create_secure_app_role.gif
-
-
In the Create Role page, enter the following settings under General:
-
Role: Enter the name using no more than 30 characters, with no spaces. Ensure that this name follows the standard Oracle naming conventions for role creation using the
CREATE ROLEstatement, described in Oracle Database SQL Language Reference. This attribute is mandatory. -
Status: Select either Enabled or Disabled to enable or disable the secure application role during run time. This attribute is mandatory.
-
Enabled: Enables the role to be available for use. That is, users are allowed to call the
DBMS_MACSEC_ROLES.SET_ROLEfunction to try to enable the role. Note that whether or not the role will be enabled depends on the evaluation result of the associated rule set.See "SET_ROLE Procedure" for more information about this function.
-
Disabled: Disables the role from being available for use. The
DBMS_MACSEC_ROLES.SET_ROLEfunction will not be able to enable the role.
-
-
-
In the Create Role page, under Rule Set, from the list, select the rule set that you want to associate with the secure application role. This attribute is mandatory.
When calling
DBMS_MACSEC_ROLES.SET_ROLE, if the rule set evaluates to true, then Oracle Database Vault enables the role for the database session. If the rule set evaluates to false, then the role is not enabled.See Chapter 6, "Configuring Rule Sets," for more information about rule sets.
-
Click OK.
Modifying a Secure Application Role
You can modify an existing secure application role only if it has been created in Oracle Database Vault.
You cannot modify secure application roles or database roles that have been created outside of Oracle Database Vault. If you want to modify an existing Oracle Database role so that it can work with Oracle Database Vault, create a new secure application role in Oracle Database Vault and then grant the existing role to the secure application role. For example, in SQL*Plus:
GRANT myExistingDBrole TO myDVrole;
After you create a new secure application role, you must modify your code to use this new role. You can use DBMS_MACSEC_ROLES.SET_ROLE in your application code to accomplish this.
Securing an Oracle Database Vault Secure Application Role
Users who have database administrative privileges may try to use the DROP ROLE SQL statement to delete secure application roles that were created using Oracle Database Vault.
Whenever an Oracle Database Vault secure application role has been created, Database Vault adds the secure application role to the Oracle Database Vault realm. This prevents database administrator from deleting the secure application role using the DROP ROLE statement.
Deleting an Oracle Database Vault Secure Application Role
You can delete Oracle Database Vault secure application roles in Oracle Database Vault Administrator.
-
If necessary, locate the various references to the secure application roles by querying the role-related Oracle Database Vault views.
See Chapter 22, "Oracle Database Vault Data Dictionary Views," for more information.
-
Check and modify any applications that may be using the secure application role that you want to delete.
-
From Cloud Control, log into Oracle Database Vault Administrator as a user who has been granted the
DV_OWNERorDV_ADMINrole."Logging into Oracle Database Vault" explains how to log in.
-
In the Administration page, under Database Vault Components, click Secure Application Roles.
-
In the Secure Application Roles page, select the role that you want to remove.
-
Click Delete.
-
In the Confirmation window, click Yes.
How Oracle Database Vault Secure Application Roles Work
The process flow for a secure application role that is managed by Oracle Database Vault begins after you create and set the secure application role.
-
Create or update the role either in Oracle Database Vault Administrator or by using the secure application role-specific functions in the
DBMS_MACADMpackage.See "DBMS_MACADM Secure Application Role Procedures" for more information.
-
Modify your application to call the role, by using the
DBMS_MACSEC_ROLES.SET_ROLEfunction.See "SET_ROLE Procedure" for more information.
-
Oracle Database Vault then evaluates the rule set associated with the secure application role.
If the rule set evaluates to true, then Oracle Database Vault enables the role for the current session. If the rule set evaluates to false, the role is not enabled. In either case, Oracle Database Vault processes the associated auditing and custom event handlers for the rule set associated with the secure application role.
Tutorial: Granting Access with Database Vault Secure Application Roles
This tutorial demonstrates how you can create a secure application role that uses a rule set to control a user's access to the OE.ORDERS table during work hours.
Topics:
About This Tutorial
In this tutorial, you restrict the SELECT SQL statement on the ORDERS table in the OE schema to a specific set of users.
Furthermore, these users can only perform these statements on the OE.ORDERS table from within the office, not from a remote connection. To accomplish this, you create an Oracle Database Vault secure application role that is enabled for the user only if the user passes the checks enforced by the rule set that you associate with the secure application role.
Step 1: Create Users for This Tutorial
First, you must create users for the tutorial.
-
Log in to SQL*Plus as a user who has been granted the
DV_ACCTMGRrole.For example:
sqlplus bea_dvacctmgr Enter password: password -
In a multitenant environment, connect to the appropriate pluggable database (PDB).
For example:
CONNECT bea_dvacctmgr@hrpdb Enter password: passwordTo find the available PDBs, query the
DBA_PDBSdata dictionary view. To check the current PDB, run theshow con_namecommand. -
Create the following user accounts:
GRANT CREATE SESSION TO eabel IDENTIFIED BY password; GRANT CREATE SESSION TO ahutton IDENTIFIED BY password; GRANT CREATE SESSION TO ldoran IDENTIFIED BY password;
Replace
passwordwith a password that is secure. See Oracle Database Security Guide for the minimum requirements for creating passwords.
Step 2: Enable the OE User Account
The OE schema will be used for this tutorial.
-
In SQL*Plus, connect as the
DV_ACCTMGRuser.For example:
CONNECT bea_dvacctmgr -- Or, CONNECT bea_dvacctmgr@hrpdb Enter password: password
-
Check the account status of the
OEaccount.SELECT USERNAME, ACCOUNT_STATUS FROM DBA_USERS WHERE USERNAME = 'OE';
-
If the
OEaccount is locked and expired, unlock it and assign it a new password.ALTER USER OE ACCOUNT UNLOCK IDENTIFIED BY password;
Step 3: Create the Rule Set and Its Rules
The rule set and rules will restrict who can modify orders in the OE.ORDERS table.
-
From Cloud Control, log in to Oracle Database Vault Administrator as a user who has been granted the
DV_OWNERorDV_ADMINrole and theSELECT ANY DICTIONARYsystem privilege."Logging into Oracle Database Vault" explains how to log in.
-
In the Administration page, select Rule Sets.
The Rule Sets page appears.
-
Click Create.
The Create Rule Set page appears.
-
Enter the following information:
-
Name: Enter
Can Modify Orders. -
Description: Enter
Rule set to control who can modify orders in the OE.ORDERS table. -
Status: Select Enabled.
-
Evaluation Options: Select All True.
-
-
Leave the remaining settings and their defaults, and then click Next to go to the Rules Associated with Rule Sets page.
-
Click Create Rule and in the Create Rule dialog box, enter the following settings:
-
Name:
Check IP Address -
Expression:
DVF.F$CLIENT_IP = 'your_IP_address'
For the Check IP Address rule, replace
your_IP_addresswith the IP address for your computer. In a real-world scenario, you would create an expression that includes all the IP addresses for the users who should be allowed access.This rule uses the default factor Client_IP. If this factor has been removed, then you can use the following rule expression instead:
UPPER(SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','IP_ADDRESS')) = 'your_IP_address' -
-
Click OK.
-
Click Create Rule again and in the Create Rule dialog box, enter the following settings:
-
Name:
Check Session User -
Expression:
DVF.F$SESSION_USER IN ('EABEL','AHUTTON')
This rule uses the default factor Session_User. If this factor have been removed or modified, you can use the following rule expression instead:
UPPER(SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','SESSION_USER')) IN ('EABEL','AHUTTON') -
-
Click OK.
-
Click Done, then click Finish.
Step 4: Create the Database Vault Secure Application Role
The Database Vault secure application role will be set when the rule set conditions are satisfied.
-
In Oracle Database Vault, return to the Administration page.
-
Under Administration, select Secure Application Roles.
The Secure Application Roles page appears.
-
Click Create.
The Create Role page appears.
-
In the Role box, enter
ORDERS_MGMTto name the role. -
Under Rule Set, select Can Modify Orders.
-
Click OK.
At this stage, the Database Vault secure application role and its associated rule set are created, though the role does not yet have any privileges.
Step 5: Grant the SELECT Privilege to the Secure Application Role
The secure application role must be granted the SELECT privilege.
-
In SQL*Plus, connect as user
OE.CONNECT OE -- Or, CONNECT OE@hrpdb Enter password: password
-
Grant the
SELECTprivilege to theORDERS_MGMTDatabase Vault Secure application role.GRANT SELECT ON ORDERS TO ORDERS_MGMT;
Step 6: Test the Database Vault Secure Application Role
With all the components in place, you are ready to test the Database Vault secure application role.
-
In SQL*Plus, connect directly to the database as user
eabel.connect eabel@orcl Enter password: passwordReplace
orclwith the name of your database instance. -
Set the
ORDERS_MGMTrole.EXEC DBMS_MACSEC_ROLES.SET_ROLE('ORDERS_MGMT');Typically, you would embed this call in the application that the user logs in to.
-
Select from the
OE.ORDERStable.SELECT COUNT(*) FROM OE.ORDERS;
The following output should appear:
COUNT(*) ---------- 105Because user
eabelis logging directly into the database from the correct IP address and is listed as a valid session user, she can select from theOE.ORDERStable. If userahuttonlogs in to SQL*Plus in the same manner, she also can select from theOE.ORDERStable. -
Reconnect as user
eabelwithout specifying the database instance, and then try to select from theOE.ORDERStable again.CONNECT eabel Enter password: password EXEC DBMS_MACSEC_ROLES.SET_ROLE('ORDERS_MGMT');The following output should appear:
Error at line 1: ORA-47305: Rule Set Violation on SET ROLE (Can Modfiy Orders) ...
Next:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM OE.ORDERS;
The following output should appear:
ERROR at line 1: ORA-00942: table or view does not exist
Even though user
eabelis a valid user, she has violated the Check IP Address rule in the rule set, so she cannot enable theORDERS_MGMTrole. The only way for the IP address to be recognized is to connect by specifying the database instance, as usereabeldid in Step 1. (For an explanation about how this works, see Step 9 in "Step 3: Map the Domain Factor Identities to the Client_IP Factor", in Chapter 8.) -
Connect as user
ldoran.CONNECT ldoran -- Or, CONNECT ldoran@hrpdb Enter password: password
-
Enter the following statements:
EXEC DBMS_MACSEC_ROLES.SET_ROLE('ORDERS_MGMT'); SELECT COUNT(*) FROM OE.ORDERS;Because user
ldoranis not a valid user, she cannot enable theORDERS_MGMTrole. Therefore, she cannot select from theOE.ORDERStable.
Step 7: Remove the Components for This Tutorial
You can remove the components that you created for this tutorial if you no longer need them.
-
From Cloud Control, log in to Oracle Database Vault Administrator as a user who has been granted the
DV_OWNERorDV_ADMINrole."Logging into Oracle Database Vault" explains how to log in.
-
Delete the
ORDERS_MGMTsecure application role: From the Secure Application Roles page, select theORDERS_MGMTsecure application role, and then click Delete, and then Yes in the Confirmation dialog box. -
Select the Rule Sets page, select the Can Modify Orders rule set, and then click Delete.
-
In the Confirmation dialog box, select Yes to remove the rule set.
-
Select the Rules page, select the Check IP Address and Check Session User rules, and then select Delete. Select Yes in the Confirmation box.
Hold the Control key down to select multiple rules.
-
In SQL*Plus, connect as the Database Vault Account Manager and drop the users.
For example:
CONNECT bea_dvacctmgr -- Or, CONNECT bea_dvacctmgr@hrpdb Enter password: password DROP USER eabel; DROP USER ahutton; DROP USER ldoran;
-
If unnecessary, lock and expire the
OEuser account.ALTER USER OE ACCOUNT LOCK PASSWORD EXPIRE;
How Secure Application Roles Affect Performance
You can check system performance by running tools such as Oracle Enterprise Manager (including Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control, which is installed by default with Oracle Database), Automatic Workload Repository (AWR), and TKPROF.
For more information about Oracle Enterprise Manager, see the Oracle Enterprise Manager documentation set. For information about Cloud Control, refer to its online Help. See Oracle Database Performance Tuning Guide to learn how to monitor database performance, and Oracle Database SQL Tuning Guide to monitor the performance of individual SQL and PL/SQL statements.
Related Reports and Data Dictionary View
Table 9-1 lists Oracle Database Vault reports that are useful for analyzing Oracle Database Vault secure application roles. See Chapter 24, "Oracle Database Vault Reports," for information about how to run these reports.
Table 9-1 Reports Related to Secure Application Roles
You can use the DBA_DV_ROLE data dictionary view to find the Oracle Database Vault secure application roles used in privilege management. See "DVSYS.DBA_DV_ROLE View" for more information.